In the MBA program at a prestigious university in the Pacific Northwest, students bid for electives in the second year of their program. Each student has 100 points to bid (total) and must take two electives. There are four electives available: Management Science, Finance, Operations Management, and Marketing. Each class is limited to 3 students. The bids submitted for each of the 5 students are shown in the table below. Student George Fred Ann Eric Susan Management Science 60 20 45 50 30 Finance 10 20 45 20 30 Operations Management 10 40 5 5 30 Marketing 20 20 5 25 10 This is a variant of an assignment problem where the assignees are the students and the tasks are the classes. However, each student is to be assigned to two classes rather than just one and each class is to be assigned three students. Furthermore, the objective here involves maximization rather than minimization of costs as assumed by the assignment problem. To convert to an equivalent problem involving minimization, we can multiply each bid by -1. To avoid negative costs, we then can add the largest bid (60) to each of these negative bids. (A number larger than 60 also could have been added to each of these negative bids.) Before splitting each student and each class into multiple assignees and multiple tasks. Formulate this as an assignment problem by constructing the appropriate cost table. Do not need to solve it.
In the MBA program at a prestigious university in the Pacific Northwest, students bid for electives in the second year of their program. Each student has 100 points to bid (total) and must take two electives. There are four electives available: Management Science, Finance, Operations Management, and Marketing. Each class is limited to 3 students. The bids submitted for each of the 5 students are shown in the table below. Student George Fred Ann Eric Susan Management Science 60 20 45 50 30 Finance 10 20 45 20 30 Operations Management 10 40 5 5 30 Marketing 20 20 5 25 10 This is a variant of an assignment problem where the assignees are the students and the tasks are the classes. However, each student is to be assigned to two classes rather than just one and each class is to be assigned three students. Furthermore, the objective here involves maximization rather than minimization of costs as assumed by the assignment problem. To convert to an equivalent problem involving minimization, we can multiply each bid by -1. To avoid negative costs, we then can add the largest bid (60) to each of these negative bids. (A number larger than 60 also could have been added to each of these negative bids.) Before splitting each student and each class into multiple assignees and multiple tasks. Formulate this as an assignment problem by constructing the appropriate cost table. Do not need to solve it.
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter6: Optimization Models With Integer Variables
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 79P
Related questions
Question
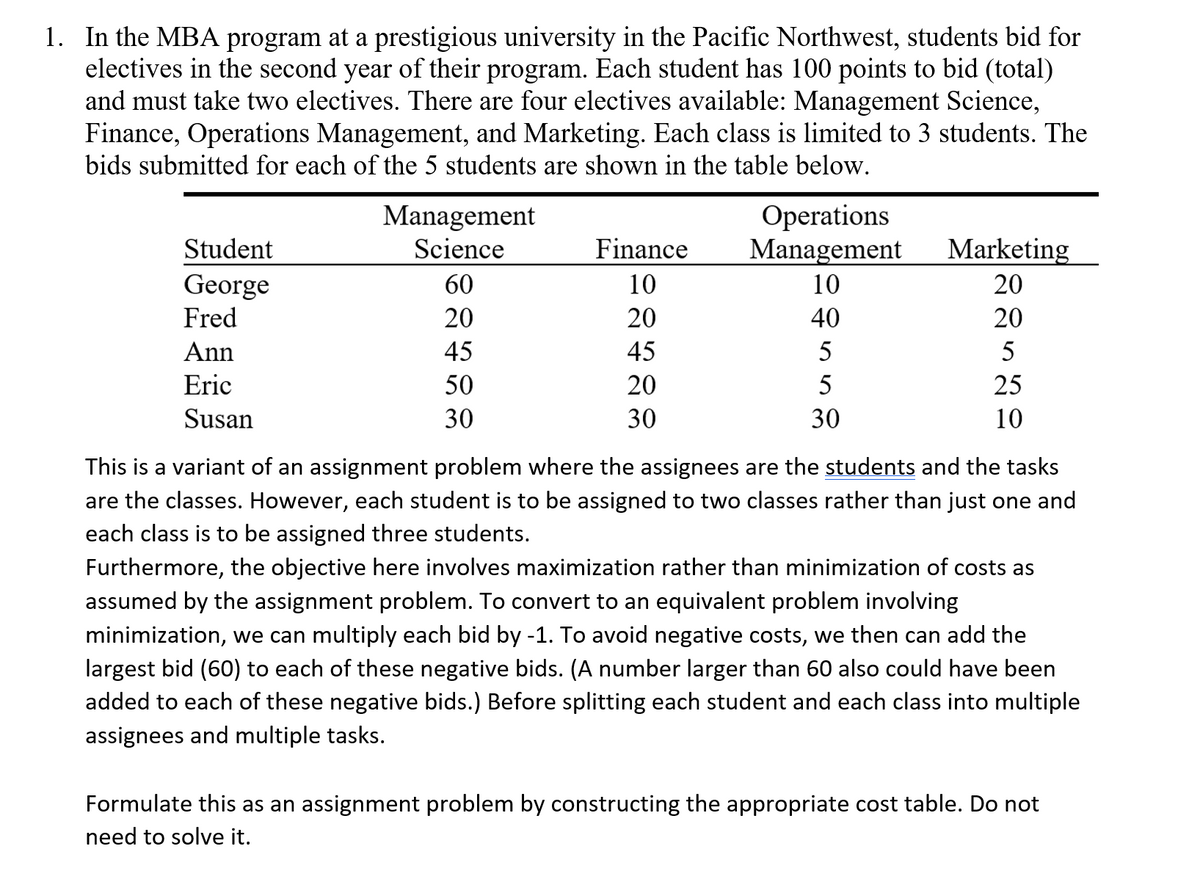
Transcribed Image Text:1. In the MBA program at a prestigious university in the Pacific Northwest, students bid for
electives in the second year of their program. Each student has 100 points to bid (total)
and must take two electives. There are four electives available: Management Science,
Finance, Operations Management, and Marketing. Each class is limited to 3 students. The
bids submitted for each of the 5 students are shown in the table below.
Student
George
Fred
Ann
Eric
Susan
Management
Science
60
20
45
50
30
Finance
12429
10
20
45
20
30
Operations
Management
10
40
5
5
30
Marketing
20
20
5
25
10
This is a variant of an assignment problem where the assignees are the students and the tasks
are the classes. However, each student is to be assigned to two classes rather than just one and
each class is to be assigned three students.
Furthermore, the objective here involves maximization rather than minimization of costs as
assumed by the assignment problem. To convert to an equivalent problem involving
minimization, we can multiply each bid by -1. To avoid negative costs, we then can add the
largest bid (60) to each of these negative bids. (A number larger than 60 also could have been
added to each of these negative bids.) Before splitting each student and each class into multiple
assignees and multiple tasks.
Formulate this as an assignment problem by constructing the appropriate cost table. Do not
need to solve it.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,