In this problem, we use your critical values table to explore the significance of r based on different sample sizes. Critical Values for Correlation Coefficient na- 0.05 3 1.00 « - 0.01 a- 0.05 a- 0.01 a- 0.05 a- 0.01 1.00 13 0.53 0.68 23 0.41 0.53 4 0.95 0.99 14 0.53 0.66 24 0.40 0.52 0.88 0.96 15 0.51 0.64 25 0.40 0.51 6. 0.81 0.92 16 0.50 0.61 26 0.39 0.50 7 0.75 0.87 17 0.48 0.61 27 0.38 0.49 0.71 0.83 18 0.47 0.59 28 0.37 0.48 0.67 0.80 19 0.46 0.58 29 0.37 0.47 10 0.63 0.76 20 0.44 0.56 30 0.36 0.46 0.60 0.73 21 043 0.55 12 0.58 0.71 22 0.42 0.54 (a) Is a sample correlation coefficient p = 0.86 significant at the a = 0.01 level based on a sample size of n = 3 data pairs? What about n = 12 data pairs? (Select all that apply.) O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01. O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01. O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01. O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01. O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01. O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01. O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01. O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01. (b) Is a sample correlation coefficient p = 0.40 significant at the a = 0.05 level based on a sample size of n = 18 data pairs? What about n = 30 data pairs? (Select all that apply.) O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 30 and a = 0.05.
In this problem, we use your critical values table to explore the significance of r based on different sample sizes. Critical Values for Correlation Coefficient na- 0.05 3 1.00 « - 0.01 a- 0.05 a- 0.01 a- 0.05 a- 0.01 1.00 13 0.53 0.68 23 0.41 0.53 4 0.95 0.99 14 0.53 0.66 24 0.40 0.52 0.88 0.96 15 0.51 0.64 25 0.40 0.51 6. 0.81 0.92 16 0.50 0.61 26 0.39 0.50 7 0.75 0.87 17 0.48 0.61 27 0.38 0.49 0.71 0.83 18 0.47 0.59 28 0.37 0.48 0.67 0.80 19 0.46 0.58 29 0.37 0.47 10 0.63 0.76 20 0.44 0.56 30 0.36 0.46 0.60 0.73 21 043 0.55 12 0.58 0.71 22 0.42 0.54 (a) Is a sample correlation coefficient p = 0.86 significant at the a = 0.01 level based on a sample size of n = 3 data pairs? What about n = 12 data pairs? (Select all that apply.) O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01. O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01. O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01. O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01. O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01. O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01. O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01. O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01. (b) Is a sample correlation coefficient p = 0.40 significant at the a = 0.05 level based on a sample size of n = 18 data pairs? What about n = 30 data pairs? (Select all that apply.) O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 30 and a = 0.05.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter4: Equations Of Linear Functions
Section4.5: Correlation And Causation
Problem 24PFA
Related questions
Question
In this problem, we use your critical values table to explore the significance of r based on different

Transcribed Image Text:(c) Is it true that in order to be significant, a p value must be larger than 0.90? larger than 0.70? larger than 0.50? What does sample size have to do with the significance of p? Explain your answer.
O Yes, a larger correlation coefficient of 0.90 means that the data will be significant.
O No, a larger sample size means that a smaller absolute value of the correlation coefficient might be significant.
O Yes, a larger correlation coefficient of 0.50 means that the data will be significant.
O No, sample size has no bearing on whether or not the correlation coefficient might be significant.
O Yes, a larger correlation coefficient of 0.70 means that the data will be significant.
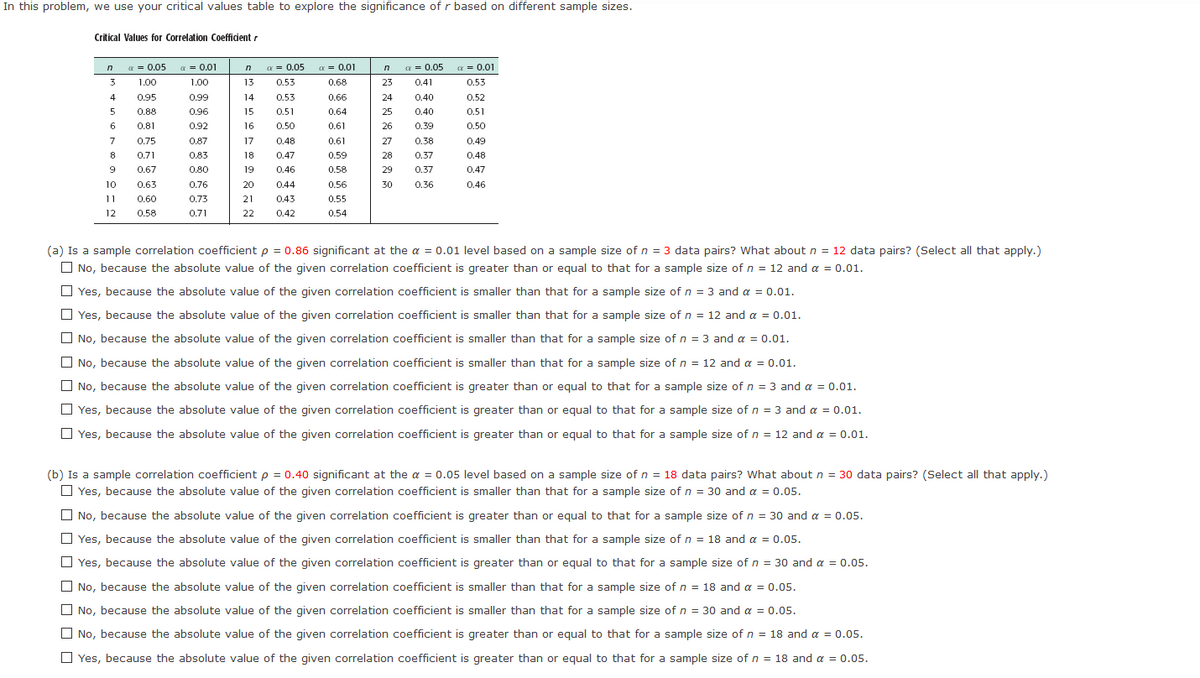
Transcribed Image Text:In this problem, we use your critical values table to explore the significance of r based on different sample sizes.
Critical Values for Correlation Coefficient r
a = 0.05
a = 0.01
a = 0.05
a = 0.01
a = 0.05
a = 0.01
n
n
3
1.00
1.00
13
0.53
0.68
23
0.41
0.53
4
0.95
0.99
14
0.53
0.66
24
0.40
0.52
0.88
0.96
15
0.51
0.64
25
0.40
0.51
0.81
0.92
16
0.50
0.61
26
0.39
0.50
7
0.75
0.87
17
0.48
0.61
27
0.38
0.49
8
0.71
0.83
18
0.47
0.59
28
0.37
0.48
0.67
0.80
19
0.46
0.58
29
0.37
0.47
10
0.63
0.76
20
0.44
0.56
30
0.36
0.46
11
0.60
0.73
21
0.43
0.55
12
0.58
0.71
22
0.42
0.54
(a) Is a sample correlation coefficient p = 0.86 significant at the a = 0.01 level based on a sample size of n = 3 data pairs? What about n = 12 data pairs? (Select all that apply.)
O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01.
O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01.
O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01.
O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size ofn = 3 and a = 0.01.
O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size ofn = 12 and a = 0.01.
No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01.
O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 3 and a = 0.01.
O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 12 and a = 0.01.
(b) Is a sample correlation coefficient p = 0.40 significant at the a = 0.05 level based on a sample size of n = 18 data pairs? What about n = 30 data pairs? (Select all that apply.)
O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 30 and a = 0.05.
O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 30 and a = 0.05.
O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 18 and a = 0.05.
O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 30 and a = 0.05.
O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size ofn = 18 and a = 0.05.
O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is smaller than that for a sample size of n = 30 and a = 0.05.
O No, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 18 and a = 0.05.
O Yes, because the absolute value of the given correlation coefficient is greater than or equal to that for a sample size of n = 18 and a = 0.05.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill