IV. APPLICATION AND ANALYSIS ON QUEUING THEORY. Direction: Given the following assumptions, derive the answer/s for each question. In answering the questions, copy the questions into the Output Area and write your answers after each question. Assumptions: Mean Arrival Rate (2) = 3 customers/hour Number of Ser ver s (C ) = 1 Mean Service Rate (U) = 4 customers/hour %3D 1. Calculate and determine the Occupation Rate. (p) 2. What is the average number in system average (L)? 3. Determine the average system in system (W).
IV. APPLICATION AND ANALYSIS ON QUEUING THEORY. Direction: Given the following assumptions, derive the answer/s for each question. In answering the questions, copy the questions into the Output Area and write your answers after each question. Assumptions: Mean Arrival Rate (2) = 3 customers/hour Number of Ser ver s (C ) = 1 Mean Service Rate (U) = 4 customers/hour %3D 1. Calculate and determine the Occupation Rate. (p) 2. What is the average number in system average (L)? 3. Determine the average system in system (W).
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.6: The Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Problem 92E
Related questions
Question
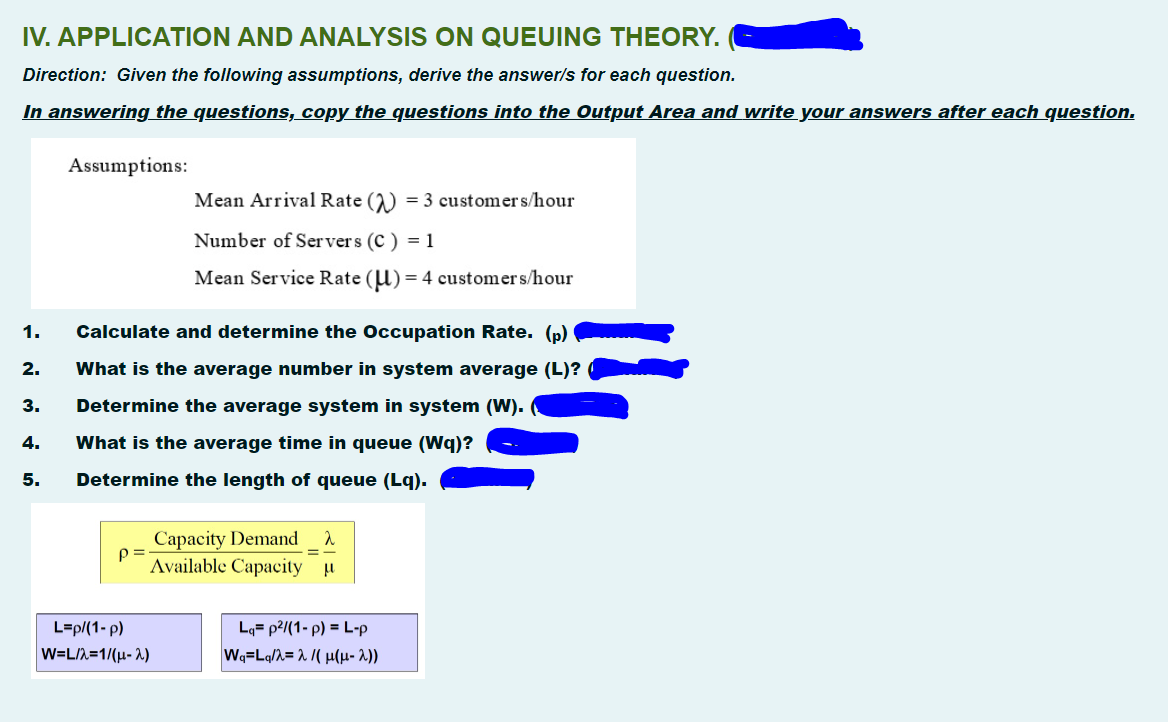
Transcribed Image Text:IV. APPLICATION AND ANALYSIS ON QUEUING THEORY.
Direction: Given the following assumptions, derive the answer/s for each question.
In answering the questions, copy the questions into the Output Area and write your answers after each question.
Assumptions:
Mean Arrival Rate (2) = 3 customers/hour
Number of Ser vers (C ) = 1
Mean Service Rate (U) = 4 customer s/hour
1.
Calculate and determine the Occupation Rate. (p)
2.
What is the average number in system average (L)?
3.
Determine the average system in system (W).
4.
What is the average time in queue (Wq)?
5.
Determine the length of queue (Lq).
Capacity Demand
p =
Available Capacity u
=-
L=p/(1- p)
Lq= p2/(1- p) = L-p
W=LA=1/(u- 2)
We-Lψλ- λ( μ(μ- λ)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning