(KEY QUESTION) Consider the following strategic interaction between two Australia telecommuncation companies deciding to set the prices of their 'unlimited calls' mobile package. Optus Medium High 17,-8 15, 3 11,9 Low Low Medium 2,3 1, 10 13, 1 10, 8 3,16 Telstra High -10, 19 a. Put yourself in the shoes of a CEO of these companies. Try to explain the business reasons behind the relationships between the various payoffs (obviously, this is just an example, they may differ in the real world and change over time). For example, why is Low in the payoff matrix the best response to the opponent playing High? Why is the payoff from (High, High) higher for both players than from (Medium, Medium)? b. State all the dominated strategies in the game, by which strategy they are dominated, and whether weakly or strictly. What is the equilibrium outcome by dominance, if any? c. What are the pure-strategy Nash equilibria of this game? d. In the simultaneous game, is there anything interesting or surprising in this game? Does it remind you a different game we have examined? Explain. e. Now assume Telstra is the leader (first mover), what is the equilibrium outcome? Is Telstra's leadership an advantage or disadvantage for Telstra compared to the simultaneous game? Is Telstra's leadership an advantage or disadvantage for Optus compared to the simultaneous game? Explain.
(KEY QUESTION) Consider the following strategic interaction between two Australia telecommuncation companies deciding to set the prices of their 'unlimited calls' mobile package. Optus Medium High 17,-8 15, 3 11,9 Low Low Medium 2,3 1, 10 13, 1 10, 8 3,16 Telstra High -10, 19 a. Put yourself in the shoes of a CEO of these companies. Try to explain the business reasons behind the relationships between the various payoffs (obviously, this is just an example, they may differ in the real world and change over time). For example, why is Low in the payoff matrix the best response to the opponent playing High? Why is the payoff from (High, High) higher for both players than from (Medium, Medium)? b. State all the dominated strategies in the game, by which strategy they are dominated, and whether weakly or strictly. What is the equilibrium outcome by dominance, if any? c. What are the pure-strategy Nash equilibria of this game? d. In the simultaneous game, is there anything interesting or surprising in this game? Does it remind you a different game we have examined? Explain. e. Now assume Telstra is the leader (first mover), what is the equilibrium outcome? Is Telstra's leadership an advantage or disadvantage for Telstra compared to the simultaneous game? Is Telstra's leadership an advantage or disadvantage for Optus compared to the simultaneous game? Explain.
ChapterP7: Money, Banking, And Monetary Policy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7KC
Related questions
Question
100%
subpart d. and e. required
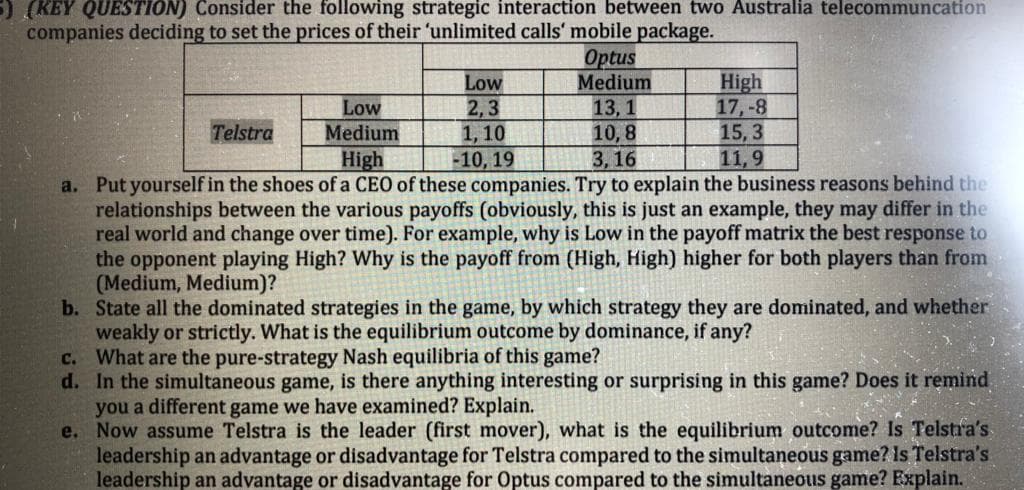
Transcribed Image Text:(KEY QUESTION) Consider the following strategic interaction between two Australia telecommuncation
companies deciding to set the prices of their 'unlimited calls' mobile package.
Optus
Medium
High
17,-8
15, 3
11,9
Low
Low
Medium
2,3
1, 10
13, 1
10, 8
3,16
Telstra
High
-10, 19
a. Put yourself in the shoes of a CEO of these companies. Try to explain the business reasons behind the
relationships between the various payoffs (obviously, this is just an example, they may differ in the
real world and change over time). For example, why is Low in the payoff matrix the best response to
the opponent playing High? Why is the payoff from (High, High) higher for both players than from
(Medium, Medium)?
b. State all the dominated strategies in the game, by which strategy they are dominated, and whether
weakly or strictly. What is the equilibrium outcome by dominance, if any?
c. What are the pure-strategy Nash equilibria of this game?
d. In the simultaneous game, is there anything interesting or surprising in this game? Does it remind
you a different game we have examined? Explain.
e. Now assume Telstra is the leader (first mover), what is the equilibrium outcome? Is Telstra's
leadership an advantage or disadvantage for Telstra compared to the simultaneous game? Is Telstra's
leadership an advantage or disadvantage for Optus compared to the simultaneous game? Explain.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you








Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning