Learning Goal: To learn the restrictions on each quantum number. Quantum numbers can be thought of as labels for an electron. Every electron in an atom has a unique set of four quantum numbers. The principal quantum number n corresponds to the shell in which the electron is located. Thus n can therefore be any integer. For example, an electron in the 2p subshell has a principal quantum number of n = 2 because 2p is in the second shell. The azimuthal or angular momentum quantum number & corresponds to the subshell in which the electron is located. s subshells are coded as 0, p subshells as 1, das 2, and fas 3. For example, an electron in the 2p subshell has l = 1. As a rule, l can have integer values ranging from 0 to n 1. The magnetic quantum number me corresponds to the orbital in which the electron is located. Instead of 2px, 2py, and 2p%, the three 2p orbitals can be labeled 1, 0, and 1, but not necessarily respectively. As a rule, me can have integer values ranging from -l to +l. ▼ Part A What is the only possible value of me for an electron in an s orbital? Express your answer numerically. ► View Available Hint(s) Submit Part B What are the possible values of me for an electron in a d orbital? Express your answer numerically with sequential values separated by commas. ► View Available Hint(s)
Learning Goal: To learn the restrictions on each quantum number. Quantum numbers can be thought of as labels for an electron. Every electron in an atom has a unique set of four quantum numbers. The principal quantum number n corresponds to the shell in which the electron is located. Thus n can therefore be any integer. For example, an electron in the 2p subshell has a principal quantum number of n = 2 because 2p is in the second shell. The azimuthal or angular momentum quantum number & corresponds to the subshell in which the electron is located. s subshells are coded as 0, p subshells as 1, das 2, and fas 3. For example, an electron in the 2p subshell has l = 1. As a rule, l can have integer values ranging from 0 to n 1. The magnetic quantum number me corresponds to the orbital in which the electron is located. Instead of 2px, 2py, and 2p%, the three 2p orbitals can be labeled 1, 0, and 1, but not necessarily respectively. As a rule, me can have integer values ranging from -l to +l. ▼ Part A What is the only possible value of me for an electron in an s orbital? Express your answer numerically. ► View Available Hint(s) Submit Part B What are the possible values of me for an electron in a d orbital? Express your answer numerically with sequential values separated by commas. ► View Available Hint(s)
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter4: Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 39P: Chapter 3 introduced the concept of a double bond between carbon atoms, represented by C=C , with a...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Part C
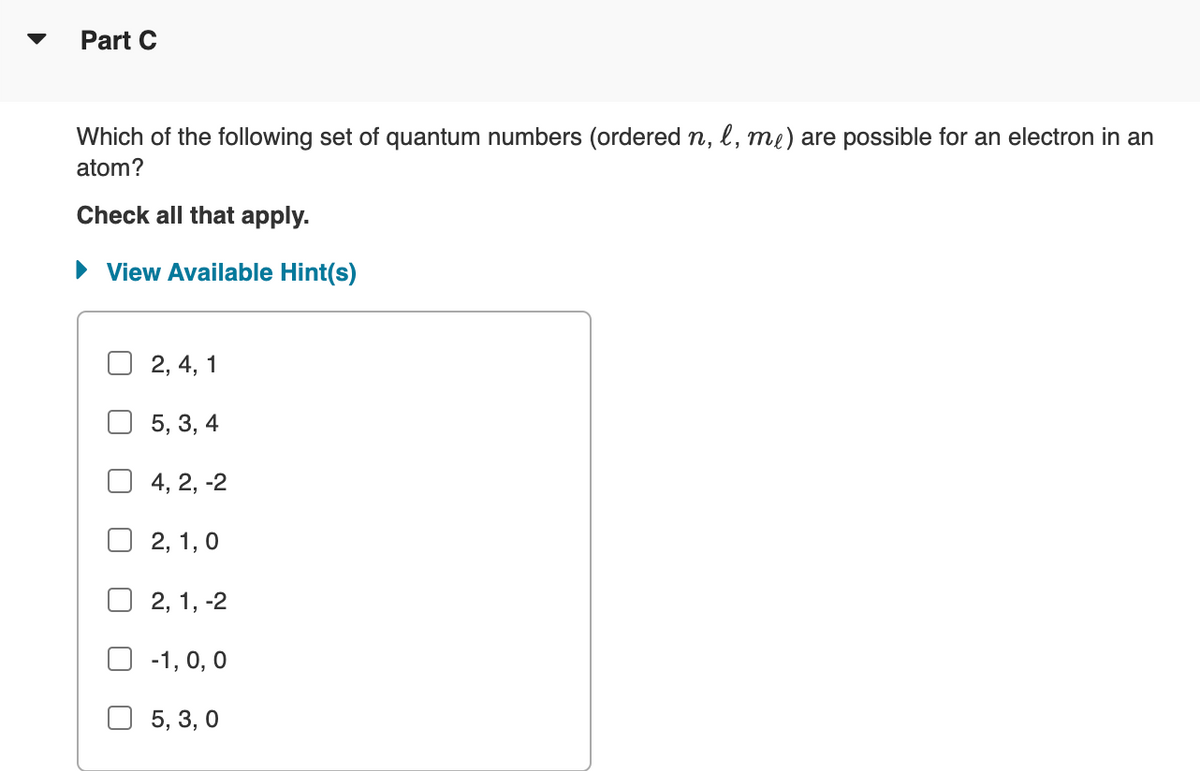
Which of the following set of quantum numbers (ordered n, l, me) are possible for an electron in an
atom?
Check all that apply.
View Available Hint(s)
2, 4, 1
5, 3, 4
4, 2, -2
2, 1, 0
2, 1, -2
☐ -1, 0, 0
5, 3, 0
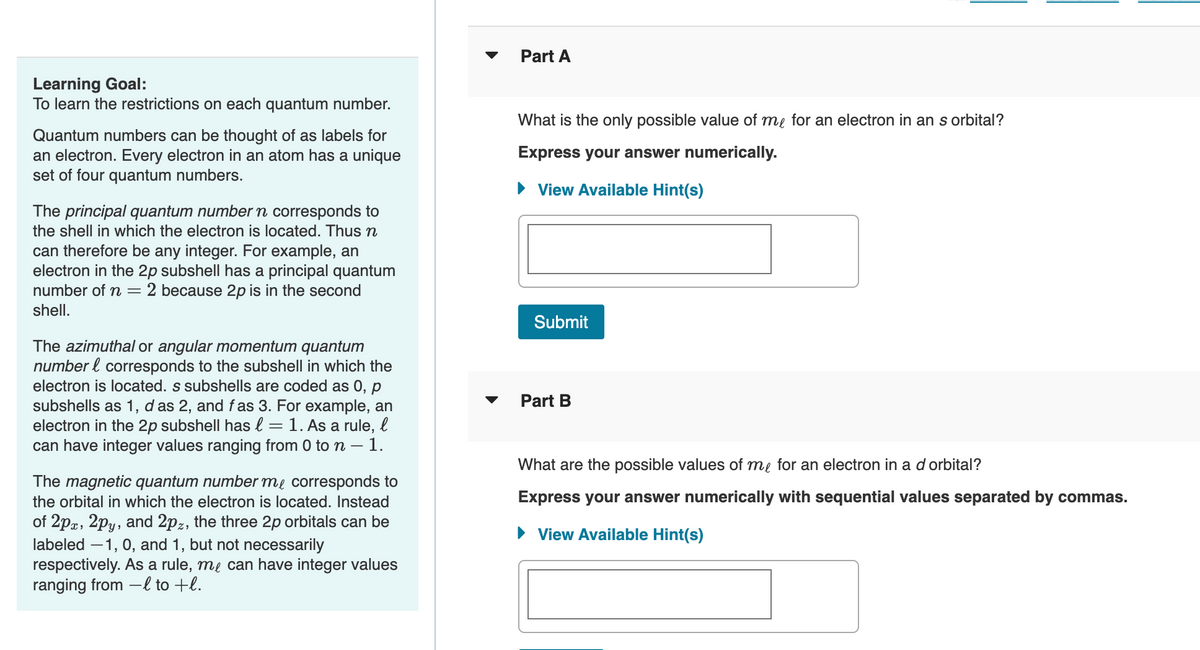
Transcribed Image Text:Learning Goal:
To learn the restrictions on each quantum number.
Quantum numbers can be thought of as labels for
an electron. Every electron in an atom has a unique
set of four quantum numbers.
The principal quantum number n corresponds to
the shell in which the electron is located. Thus n
can therefore be any integer. For example, an
electron in the 2p subshell has a principal quantum
number of n = 2 because 2p is in the second
shell.
The azimuthal or angular momentum quantum
number & corresponds to the subshell in which the
electron is located. s subshells are coded as 0, p
subshells as 1, das 2, and fas 3. For example, an
electron in the 2p subshell has l = 1. As a rule, l
can have integer values ranging from 0 to n - 1.
-
The magnetic quantum number me corresponds to
the orbital in which the electron is located. Instead
of 2px, 2py, and 2pz, the three 2p orbitals can be
labeled -1, 0, and 1, but not necessarily
respectively. As a rule, me can have integer values
ranging from -l to +l.
Part A
What is the only possible value of me for an electron in an s orbital?
Express your answer numerically.
► View Available Hint(s)
Submit
Part B
What are the possible values of me for an electron in a d orbital?
Express your answer numerically with sequential values separated by commas.
► View Available Hint(s)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning