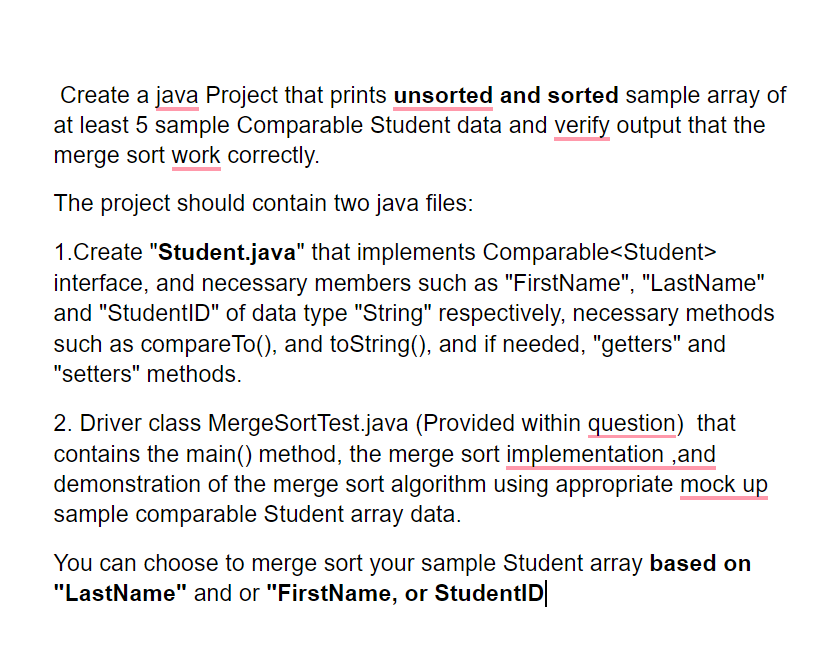
// MergeSortTest.java // Sorting an array with merge sort. import java.security.SecureRandom; import java.util.Arrays; public class MergeSortTest { // calls recursive sortArray method to begin merge sorting public static void mergeSort(int[] data) { sortArray(data, 0, data.length - 1); // sort entire array } // splits array, sorts subarrays and merges subarrays into sorted array private static void sortArray(int[] data, int low, int high) { // test base case; size of array equals 1 if ((high - low) >= 1) { // if not base case int middle1 = (low + high) / 2; // calculate middle of array int middle2 = middle1 + 1; // calculate next element over // split array in half; sort each half (recursive calls) sortArray(data, low, middle1); // first half of array sortArray(data, middle2, high); // second half of array // merge two sorted arrays after split calls return merge (data, low, middle1, middle2, high); } } // merge two sorted subarrays into one sorted subarray private static void merge(int[] data, int left, int middle1, int middle2, int right) { int leftIndex = left; // index into left subarray int rightIndex = middle2; // index into right subarray int combinedIndex = left; // index into temporary working array int[] combined = new int[data.length]; // working array // merge arrays until reaching end of either while (leftIndex <= middle1 && rightIndex <= right) { // place smaller of two current elements into result // and move to next space in arrays if (data[leftIndex] <= data[rightIndex]) { combined[combinedIndex++] = data[leftIndex++]; } else { combined[combinedIndex++] = data[rightIndex++]; } } // if left array is empty if (leftIndex == middle2) { // copy in rest of right array while (rightIndex <= right) { combined[combinedIndex++] = data[rightIndex++]; } } else { // right array is empty // copy in rest of left array while (leftIndex <= middle1) { combined[combinedIndex++] = data[leftIndex++]; } } // copy values back into original array for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) { data[i] = combined[i]; } // output merged array } // method to output certain values in array public static void main(String[] args) { SecureRandom generator = new SecureRandom(); // create unordered array of 10 random ints int[] data = generator.ints(10, 10, 91).toArray(); System.out.printf("Unsorted array: %s%n%n", Arrays.toString(data)); mergeSort(data); // sort array System.out.printf("Sorted array: %s%n", Arrays.toString(data)); } } //we get 2000 - 2001 = -1... A Negative number, that means m1 < m2. //If we get a positive number then m
// MergeSortTest.java
// Sorting an array with merge sort.
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeSortTest {
// calls recursive sortArray method to begin merge sorting
public static void mergeSort(int[] data) {
sortArray(data, 0, data.length - 1); // sort entire array
}
// splits array, sorts subarrays and merges subarrays into sorted array
private static void sortArray(int[] data, int low, int high) {
// test base case; size of array equals 1
if ((high - low) >= 1) { // if not base case
int middle1 = (low + high) / 2; // calculate middle of array
int middle2 = middle1 + 1; // calculate next element over
// split array in half; sort each half (recursive calls)
sortArray(data, low, middle1); // first half of array
sortArray(data, middle2, high); // second half of array
// merge two sorted arrays after split calls return
merge (data, low, middle1, middle2, high);
}
}
// merge two sorted subarrays into one sorted subarray
private static void merge(int[] data, int left, int middle1,
int middle2, int right) {
int leftIndex = left; // index into left subarray
int rightIndex = middle2; // index into right subarray
int combinedIndex = left; // index into temporary working array
int[] combined = new int[data.length]; // working array
// merge arrays until reaching end of either
while (leftIndex <= middle1 && rightIndex <= right) {
// place smaller of two current elements into result
// and move to next space in arrays
if (data[leftIndex] <= data[rightIndex]) {
combined[combinedIndex++] = data[leftIndex++];
}
else {
combined[combinedIndex++] = data[rightIndex++];
}
}
// if left array is empty
if (leftIndex == middle2) {
// copy in rest of right array
while (rightIndex <= right) {
combined[combinedIndex++] = data[rightIndex++];
}
}
else { // right array is empty
// copy in rest of left array
while (leftIndex <= middle1) {
combined[combinedIndex++] = data[leftIndex++];
}
}
// copy values back into original array
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
data[i] = combined[i];
}
// output merged array
}
// method to output certain values in array
public static void main(String[] args) {
SecureRandom generator = new SecureRandom();
// create unordered array of 10 random ints
int[] data = generator.ints(10, 10, 91).toArray();
System.out.printf("Unsorted array: %s%n%n", Arrays.toString(data));
mergeSort(data); // sort array
System.out.printf("Sorted array: %s%n", Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
//we get 2000 - 2001 = -1... A Negative number, that means m1 < m2.
//If we get a positive number then m
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images









