mm. a) Determine the displacement in -y direction of end D by using Castigliano's second theorem. b) Determine the rotation about x'axis of end D by using Castigliano's second theorem. c) Without any calculation, explain whether the rotation about x' axis of end D increases if the applied load is increased from 10 kN to 20 kN. Consider the strain energy due to axial, bending and torsion only. Neglect the strain energy đue to transverse shear. B D
mm. a) Determine the displacement in -y direction of end D by using Castigliano's second theorem. b) Determine the rotation about x'axis of end D by using Castigliano's second theorem. c) Without any calculation, explain whether the rotation about x' axis of end D increases if the applied load is increased from 10 kN to 20 kN. Consider the strain energy due to axial, bending and torsion only. Neglect the strain energy đue to transverse shear. B D
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter2: Axially Loaded Members
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.2.13P: Two rigid bars are connected to each other by two linearly elastic springs. Before loads are...
Related questions
Question
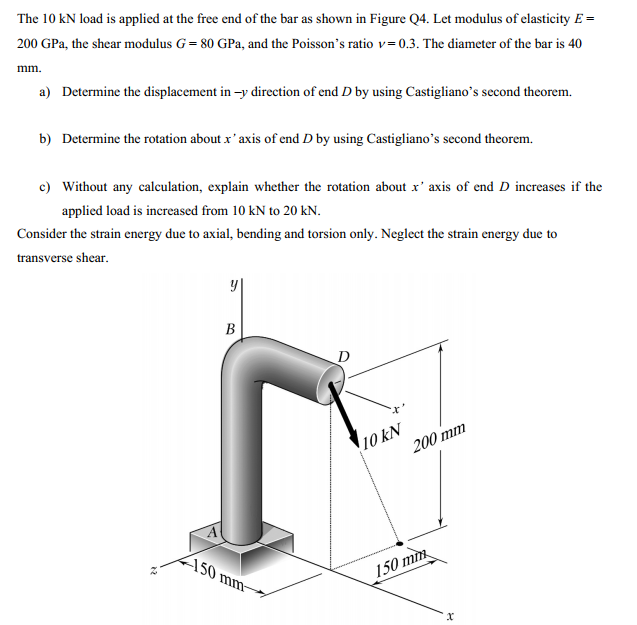
Transcribed Image Text:The 10 kN load is applied at the free end of the bar as shown in Figure Q4. Let modulus of elasticity E =
200 GPa, the shear modulus G= 80 GPa, and the Poisson's ratio v=0.3. The diameter of the bar is 40
mm.
a) Determine the displacement in -y direction of end D by using Castigliano's second theorem.
b) Determine the rotation about x' axis of end D by using Castigliano's second theorem.
c) Without any calculation, explain whether the rotation about x' axis of end D increases if the
applied load is increased from 10 kN to 20 kN.
Consider the strain energy due to axial, bending and torsion only. Neglect the strain energy due to
transverse shear.
B
D
10 kN
200 mm
150 mm-
150 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning