ne the null and alternative hypotheses. ine the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) ine the P-value of the test statistic. -=(Round to three decimal places as needed.) results suggest that texting while driving and driving while drinking are related? Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that texting while driving happens 95% of the time when driving while dri Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence at a 0.05 significance level to warrant rejection of the claim of independence between texting w not related. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence at a 0.05 significance level to warrant rejection of the claim of independence between texting while drivin somehow related.
ne the null and alternative hypotheses. ine the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) ine the P-value of the test statistic. -=(Round to three decimal places as needed.) results suggest that texting while driving and driving while drinking are related? Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that texting while driving happens 95% of the time when driving while dri Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence at a 0.05 significance level to warrant rejection of the claim of independence between texting w not related. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence at a 0.05 significance level to warrant rejection of the claim of independence between texting while drivin somehow related.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter4: Equations Of Linear Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8SGR
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:In a study of high school students at least 16 years of age, researchers obtained survey results summarized in the accompanying table. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim of independence between texting while driving and driving
when drinking alcohol. Are those two risky behaviors independent of each other?
Click the icon to view the table of survey results.
Determine the null and alternative hypotheses.
Ho:
H₁:
Determine the test statistic.
x² =
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Determine the P-value of the test statistic.
P-value= (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Do the results suggest that texting while driving and driving while drinking are related?
C
O A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that texting while driving happens 95% of the time when driving while drinking alcohol.
O B. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence at a 0.05 significance level to warrant rejection of the claim of independence between texting while driving and driving while drinking alcohol. Those two risky behaviors are
not related.
O C. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence at a 0.05 significance level to warrant rejection of the claim of independence between texting while driving and driving while drinking alcohol. Those two risky behaviors appear to be
somehow related.
O D. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that texting while driving happens 95% of the time when driving while drinking alcohol.
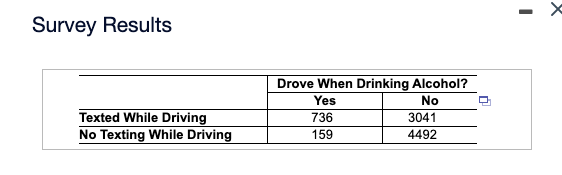
Transcribed Image Text:Survey Results
Texted While Driving
No Texting While Driving
Drove When Drinking Alcohol?
Yes
No
736
159
3041
4492
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning