Nora is a runner looking for a new pair of running shoes. She found a pair that looks nice and fits well. However, Nora cannot determine the shoes' quality until they are too well worn to return. There is a 3/4 chance the pair is high-quality and worth $256 to her (256 = .75), and a 1/4 chance it is low-quality and worth only $36 to her (736 = .25). Nora's preferences over money (W)-or over the equivalent value represented by how much the shoes are worth to her-can be represented by the following utility function:
Nora is a runner looking for a new pair of running shoes. She found a pair that looks nice and fits well. However, Nora cannot determine the shoes' quality until they are too well worn to return. There is a 3/4 chance the pair is high-quality and worth $256 to her (256 = .75), and a 1/4 chance it is low-quality and worth only $36 to her (736 = .25). Nora's preferences over money (W)-or over the equivalent value represented by how much the shoes are worth to her-can be represented by the following utility function:
Chapter1: Making Economics Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1QTC
Related questions
Question
Can you help me solve this problem please?

Transcribed Image Text:Page
Nora is a runner looking for a new pair of running shoes. She found a pair that looks nice and fits
well. However, Nora cannot determine the shoes' quality until they are too well worn to return.
There is a 3/4 chance the pair is high-quality and worth $256 to her (256 = .75), and a 1/4
chance it is low-quality and worth only $36 to her (736 = .25).
Nora's preferences over money (W)-or over the equivalent value represented by how much the
shoes are worth to her-can be represented by the following utility function:
U(W) = √W
a. Calculate Nora's expected value of the pair of shoes and expected utility. Which is larger, her
expected utility or her utility of receiving the expected value with certainty?
b. What level of wealth (that means, money not spent on shoes) would make Nora indifferent
between purchasing or not these shoes? Why?
c. Using the graph below, label the following amounts:
i.
The expected value of the pair of shoes to Nora (on the horizontal axis).
ii.
Nora's utility with a gift card worth this expected value in dollars (on the vertical axis).
Nora's expected utility of buying these shoes (on the vertical axis).
iii.
iv.
The level of wealth that makes Nora indifferent between purchasing the shoes or not
(on the horizontal axis).
V.
The risk premium (a distance, or interval, on the horizontal axis).
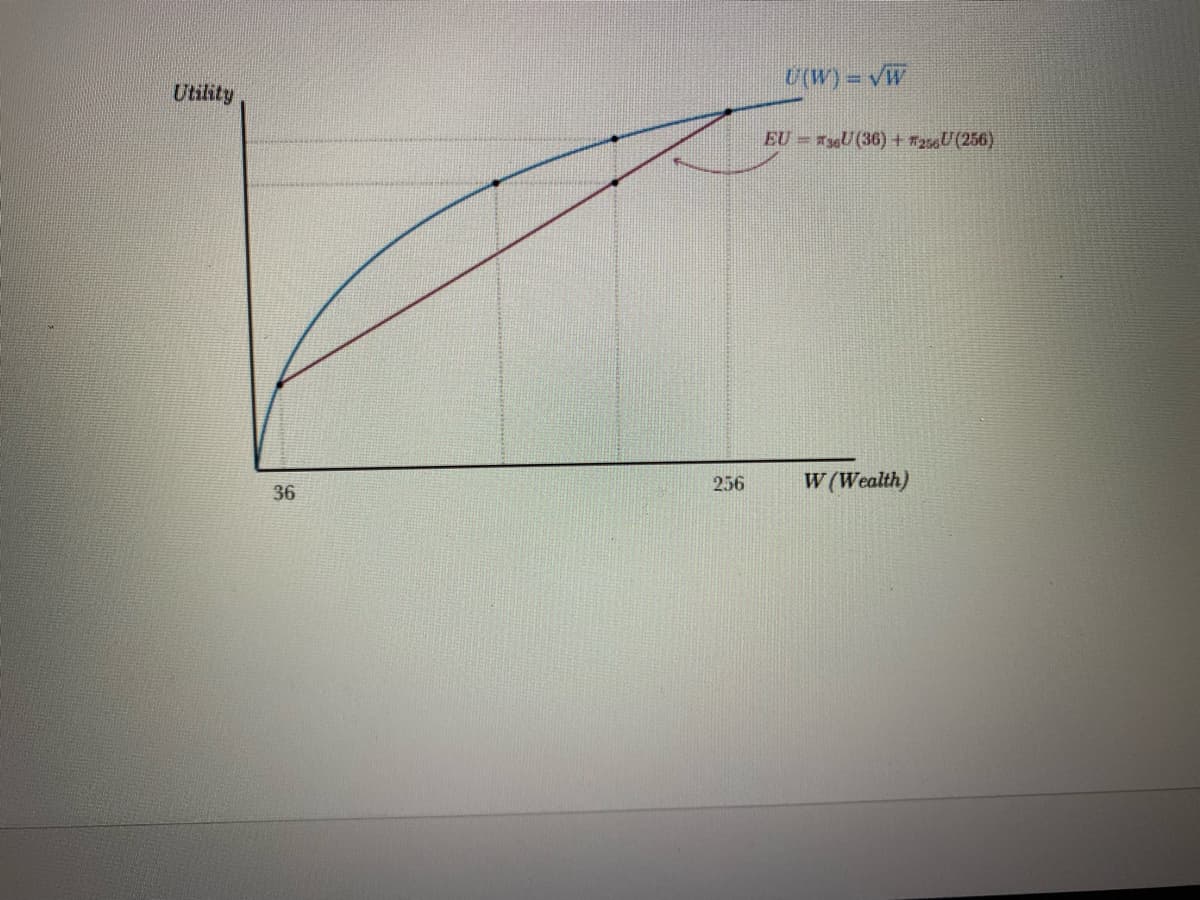
Transcribed Image Text:Utility
36
256
U(W) = √W
EU36U (36) + 7256U (256)
W (Wealth)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-…
Economics
ISBN:
9781259290619
Author:
Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education