P5B.1 Potassium fluoride is very soluble in glacial acetic acid (ethanoic acid) and the solutions have a number of unusual properties. In an attempt to understand them, freezing-point depression data were obtained by taking a solution of known molality and then diluting it several times (J. Emsley, J. Chem. Soc. A, 2702 (1971)). The following data were obtained: b/(mol kg") 0.015 0.037 0.077 0.295 0.602 ΔΤΙΚ 0.115 0.295 0.470 1.381 2.67 Calculate the apparent molar mass of the solute and suggest an interpretation. Use AfH= 11.4kJ mol™ and T;* = 290 K for glacial acetic acid. lus
P5B.1 Potassium fluoride is very soluble in glacial acetic acid (ethanoic acid) and the solutions have a number of unusual properties. In an attempt to understand them, freezing-point depression data were obtained by taking a solution of known molality and then diluting it several times (J. Emsley, J. Chem. Soc. A, 2702 (1971)). The following data were obtained: b/(mol kg") 0.015 0.037 0.077 0.295 0.602 ΔΤΙΚ 0.115 0.295 0.470 1.381 2.67 Calculate the apparent molar mass of the solute and suggest an interpretation. Use AfH= 11.4kJ mol™ and T;* = 290 K for glacial acetic acid. lus
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
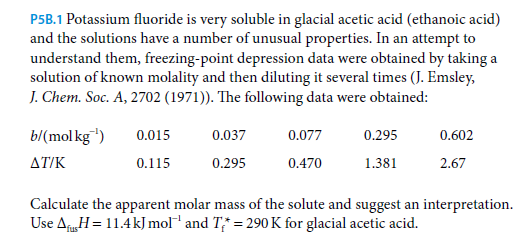
Transcribed Image Text:P5B.1 Potassium fluoride is very soluble in glacial acetic acid (ethanoic acid)
and the solutions have a number of unusual properties. In an attempt to
understand them, freezing-point depression data were obtained by taking a
solution of known molality and then diluting it several times (J. Emsley,
J. Chem. Soc. A, 2702 (1971)). The following data were obtained:
b/(mol kg")
0.015
0.037
0.077
0.295
0.602
ΔΤΙΚ
0.115
0.295
0.470
1.381
2.67
Calculate the apparent molar mass of the solute and suggest an interpretation.
Use AfH= 11.4kJ mol™ and T;* = 290 K for glacial acetic acid.
lus
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 9 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY