Part 1 A steel pipe with an outside diameter of 115 mm and an inside diameter of 105 mm supports the loadings shown. Assume a = 510 mm, b = 230 mm, Px = 20 kN, Py = 16 kN, and P; = 11 kN. (a) Determine the normal and shear stresses on the top surface of the pipe at point H. (b)Determine the principal stresses and maximum in-plane shear stress magnitude at point Hand show the orientation of these stresses on an appropriate sketch. y H K b (a) Determine the statically equivalent forces acting on a section at point H. Answers: Fx* i kN, Fy= kN, Fz = i kN.
Part 1 A steel pipe with an outside diameter of 115 mm and an inside diameter of 105 mm supports the loadings shown. Assume a = 510 mm, b = 230 mm, Px = 20 kN, Py = 16 kN, and P; = 11 kN. (a) Determine the normal and shear stresses on the top surface of the pipe at point H. (b)Determine the principal stresses and maximum in-plane shear stress magnitude at point Hand show the orientation of these stresses on an appropriate sketch. y H K b (a) Determine the statically equivalent forces acting on a section at point H. Answers: Fx* i kN, Fy= kN, Fz = i kN.
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter7: Analysis Of Stress And Strain
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.3.1P: The stresses acting on an element are x= 750 psi, y= 600 psi, and xy = 400 psi. Determine the...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Part 2
(a) Determine the statically equivalent moments acting on a section at point H.
Answers:
Mx = i
kN-m,
My = i
kN-m,
M, = i
kN-m.
eTextbook and Media
Attempts: 0 of 5 used Submit Answer
Save for Later
Part 3
(a) Determine the section properties needed to calculate the stresses.
Answers:
A =
i
mm?.
J = i
mm“.
Ix = ly = i
mm“.
Q =
mm3.
eTextbook and Media
Save for Later
Attempts: 0 of 5 used Submit Answer
Transcribed Image Text:Part 1
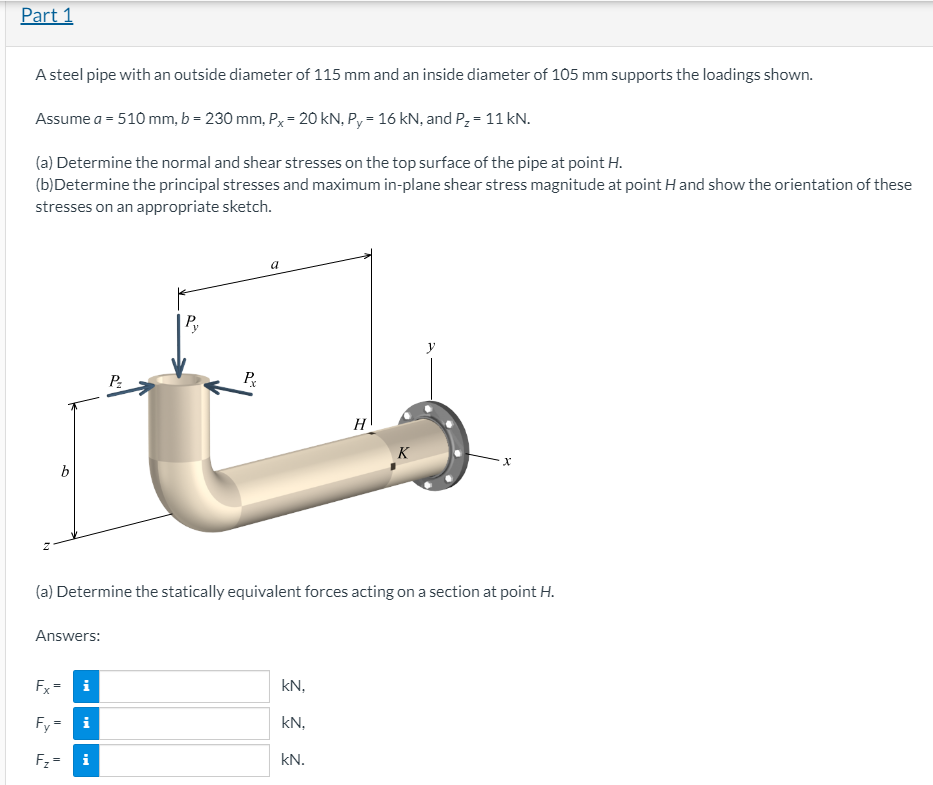
A steel pipe with an outside diameter of 115 mm and an inside diameter of 105 mm supports the loadings shown.
Assume a = 510 mm, b = 230 mm, P = 20 kN, P, = 16 kN, and P, = 11 kN.
(a) Determine the normal and shear stresses on the top surface of the pipe at point H.
(b)Determine the principal stresses and maximum in-plane shear stress magnitude at point H and show the orientation of these
stresses on an appropriate sketch.
a
P.
P
H
K
b
(a) Determine the statically equivalent forces acting on a section at point H.
Answers:
Fx
kN,
Fy=
kN,
Fz =
kN.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning