Part 2 -. Now, let's apply the terms in Part 1 in a more visual way. Use the numbers 1-7 listed above to label the image below (#1, deamination has been done for you). If you are not able to insert the numbers into the boxes, insert them in the statements below the diagram. Glycogen Triglycerides Protein Glucose Amino Acids Fatty Acids Citric Acid Cycle NADH & FADH, for the electron transport chain
Part 2 -. Now, let's apply the terms in Part 1 in a more visual way. Use the numbers 1-7 listed above to label the image below (#1, deamination has been done for you). If you are not able to insert the numbers into the boxes, insert them in the statements below the diagram. Glycogen Triglycerides Protein Glucose Amino Acids Fatty Acids Citric Acid Cycle NADH & FADH, for the electron transport chain
Anatomy & Physiology
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Chapter24: Metabolism And Nutrition
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: A monosaccharide is formed from a polysaccharide in what kind of reaction? oxidation-reduction...
Related questions
Question
100%
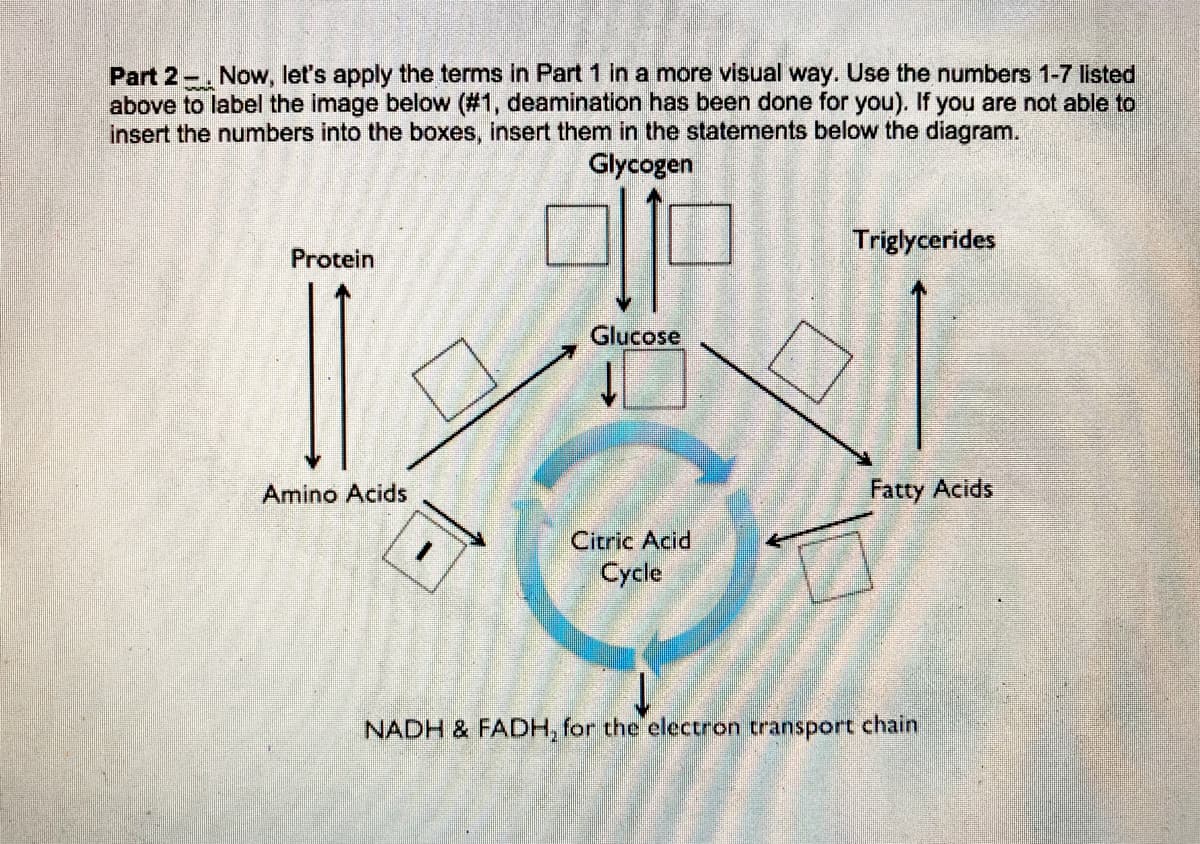
Transcribed Image Text:Part 2-. Now, let's apply the terms in Part 1 in a more visual way. Use the numbers 1-7 listed
above to label the image below (#1, deamination has been done for you). If you are not able to
insert the numbers into the boxes, insert them in the statements below the diagram.
Glycogen
Triglycerides
Protein
Glucose
Amino Acids
Fatty Acids
Citric Acid
Cycle
NADH & FADH, for the electron transport chain
Expert Solution
Step 1
Note: Since numbers for the labels are not mentioned in the image provided, numbers have been allotted for the boxes and labeled in the solution accordingly.
At any given point in time, a number of chemical reactions take place within a cell. The reactants, products and intermediates of metabolic pathways are known as metabolites and they are often interlinked as a network to allow proper cellular metabolic functions to occur. Metabolism can be of two major types, anabolism or catabolism. Anabolic pathways utilize energy to synthesize metabolites and important biomolecules, while catabolic pathways generate energy through breakdown of complex molecules.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College