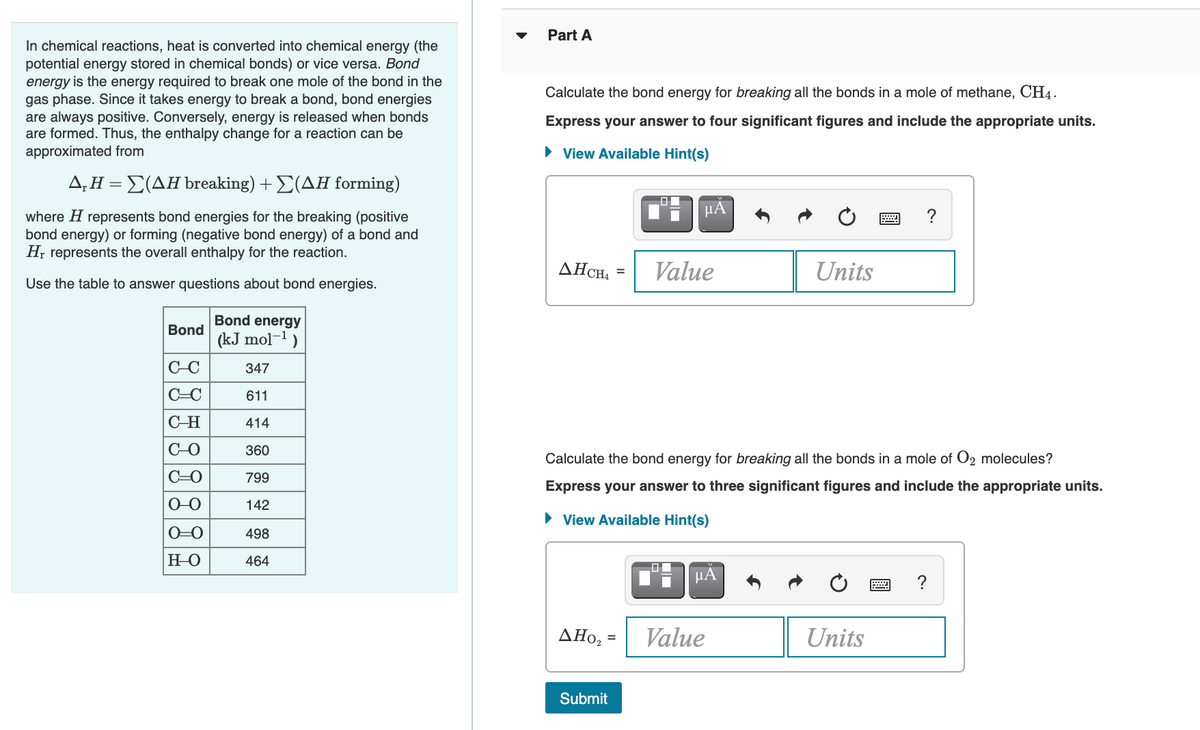
Part A In chemical reactions, heat is converted into chemical energy (the potential energy stored in chemical bonds) or vice versa. Bond energy is the energy required to break one mole of the bond in the gas phase. Since it takes energy to break a bond, bond energies are always positive. Conversely, energy is released when bonds are formed. Thus, the enthalpy change for a reaction can be approximated from Calculate the bond energy for breaking all the bonds in a mole of methane, CH4. Express your answer to four significant figures and include the appropriate units. • View Available Hint(s) Δ.ΗΣ(ΔΗ breaking) + Σ(ΔΗ forming) HA where H represents bond energies for the breaking (positive bond energy) or forming (negative bond energy) of a bond and H; represents the overall enthalpy for the reaction. ? AHCH, = Value Units Use the table to answer questions about bond energies. Bond energy Bond (kJ mol-1) C-C 347 C=C 611 C-H 414 C-O 360 Calculate the bond energy for breaking all the bonds in a mole of O2 molecules? C-O 799 Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 142 • View Available Hint(s) O-0 498 HO 464 HA ΔΗo, - Value Units Submit
Types of Chemical Bonds
The attractive force which has the ability of holding various constituent elements like atoms, ions, molecules, etc. together in different chemical species is termed as a chemical bond. Chemical compounds are dependent on the strength of chemical bonds between its constituents. Stronger the chemical bond, more will be the stability in the chemical compounds. Hence, it can be said that bonding defines the stability of chemical compounds.
Polarizability In Organic Chemistry
Polarizability refers to the ability of an atom/molecule to distort the electron cloud of neighboring species towards itself and the process of distortion of electron cloud is known as polarization.
Coordinate Covalent Bonds
A coordinate covalent bond is also known as a dative bond, which is a type of covalent bond. It is formed between two atoms, where the two electrons required to form the bond come from the same atom resulting in a semi-polar bond. The study of coordinate covalent bond or dative bond is important to know about the special type of bonding that leads to different properties. Since covalent compounds are non-polar whereas coordinate bonds results always in polar compounds due to charge separation.
Please answer both questions as they are calculated together but just a heads up they are different questions. Thank you for helping me
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









