Part A Which of the following statements best explains why a closed balloon filled with helium gas rises in air? Because the helium atoms are of lower mass than the average air molecule, the helium gas is less dense than air. The balloon thus weighs less than the air displaced by its volume. The average speed of helium atoms is higher than the average speed of air molecules, and the higher speed of collisions with the balloon walls propels the balloon upward. Because helium has a lower molar mass than the average air molecule, the helium atoms are in faster motion. This means that the temperature of the helium is higher than the air temperature. Hot gases tend to rise. Helium is a monatomic gas, whereas nearly all the molecules that make up air, such as nitrogen and oxygen, are diatomic. Submit Request Answer Next>
Part A Which of the following statements best explains why a closed balloon filled with helium gas rises in air? Because the helium atoms are of lower mass than the average air molecule, the helium gas is less dense than air. The balloon thus weighs less than the air displaced by its volume. The average speed of helium atoms is higher than the average speed of air molecules, and the higher speed of collisions with the balloon walls propels the balloon upward. Because helium has a lower molar mass than the average air molecule, the helium atoms are in faster motion. This means that the temperature of the helium is higher than the air temperature. Hot gases tend to rise. Helium is a monatomic gas, whereas nearly all the molecules that make up air, such as nitrogen and oxygen, are diatomic. Submit Request Answer Next>
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter10: Gases And Their Properties
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 105IL: You have a gas, one of the three known phosphorus-fluorine compounds (PF3, PF3, and P2F4). To find...
Related questions
Question
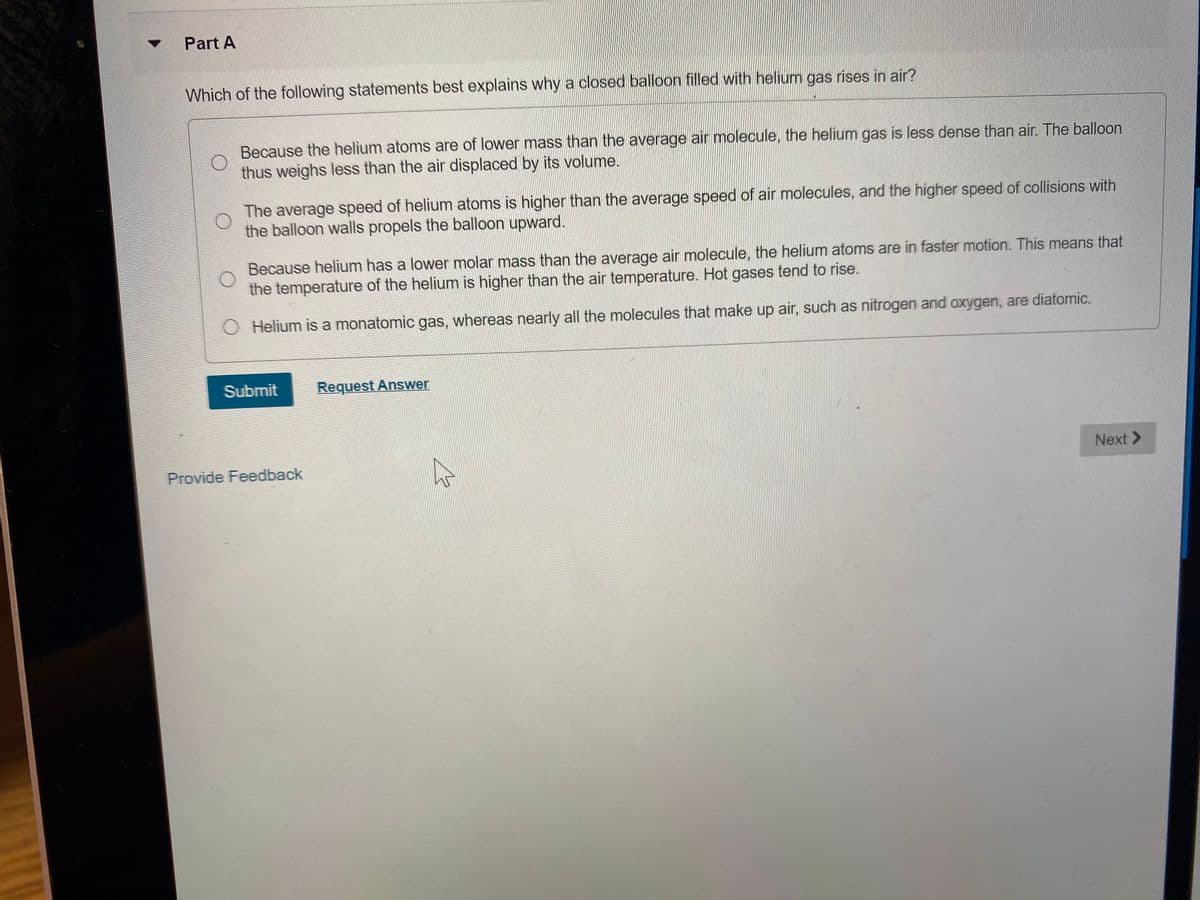
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
Which of the following statements best explains why a closed balloon filled with helium gas rises in air?
Because the helium atoms are of lower mass than the average air molecule, the helium gas is less dense than air. The balloon
thus weighs less than the air displaced by its volume.
The average speed of helium atoms is higher than the average speed of air molecules, and the higher speed of collisions with
the balloon walls propels the balloon upward.
Because helium has a lower molar mass than the average air molecule, the helium atoms are in faster motion. This means that
the temperature of the helium is higher than the air temperature. Hot gases tend to rise.
O Helium is a monatomic gas, whereas nearly all the molecules that make up air, such as nitrogen and oxygen, are diatomic.
Submit
Request Answer
Next >
Provide Feedback
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning