Part B A container holds a sample of ideal gas in thermal equilibrium, as shown in the figure. (Figure 1) One end of the container is sealed with a piston whose head is perfectly free to move, unless it is locked in place. The walls of the container readily allow the transfer of energy via heat, unless the piston is insulated from its surroundings. Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas after the following process? "Immerse the container into a large water bath at the same temperature, and very slowly push the piston head further into the container." > View Available Hint(s) O point 1 O point 2 O point 3 O point 4 O point 5 O point 6 O point 7 O point 8 Submit Previous Answers X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining The volume of the gas cannot remain constant because the piston head has moved further into the container. Part C Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas after the following process? "Lock the piston head place and plunge the container into water that is colder than the gas." O point 1 O point 2 O point 3 O point 4 O point 5 O point 6 O point 7 O point 8 Submit Request Answer Part D Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas after the following process? "The piston is now insulated from its surroundings. Pull the piston head further out of the container." • View Available Hint(s) O point 1 Figure < 2 of 2 > O point 2 O point 3 Isotherms O point 4 O point 5 O point 6 O point 7 O point 8 Submit ol
Part B A container holds a sample of ideal gas in thermal equilibrium, as shown in the figure. (Figure 1) One end of the container is sealed with a piston whose head is perfectly free to move, unless it is locked in place. The walls of the container readily allow the transfer of energy via heat, unless the piston is insulated from its surroundings. Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas after the following process? "Immerse the container into a large water bath at the same temperature, and very slowly push the piston head further into the container." > View Available Hint(s) O point 1 O point 2 O point 3 O point 4 O point 5 O point 6 O point 7 O point 8 Submit Previous Answers X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining The volume of the gas cannot remain constant because the piston head has moved further into the container. Part C Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas after the following process? "Lock the piston head place and plunge the container into water that is colder than the gas." O point 1 O point 2 O point 3 O point 4 O point 5 O point 6 O point 7 O point 8 Submit Request Answer Part D Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas after the following process? "The piston is now insulated from its surroundings. Pull the piston head further out of the container." • View Available Hint(s) O point 1 Figure < 2 of 2 > O point 2 O point 3 Isotherms O point 4 O point 5 O point 6 O point 7 O point 8 Submit ol
Chapter3: The First Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 46P: A dilute gas is stored in the left chamber of a container whose walls are perfectly insulating (see...
Related questions
Question
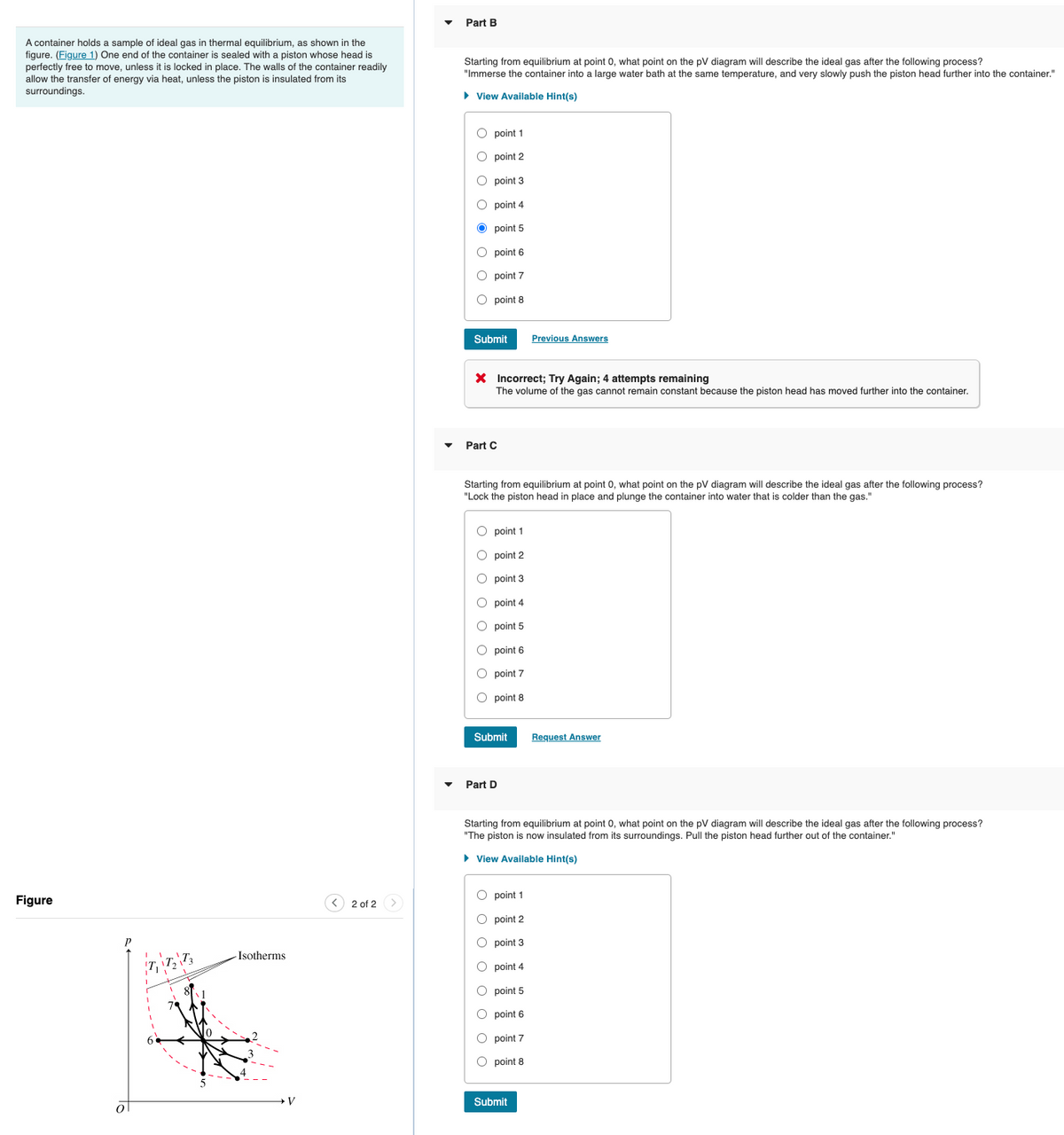
Transcribed Image Text:Part B
A container holds a sample of ideal gas in thermal equilibrium, as shown in the
figure. (Figure 1) One end of the container is sealed with a piston whose head is
perfectly free to move, unless it is locked in place. The walls of the container readily
allow the transfer of energy via heat, unless the piston is insulated from its
surroundings.
Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas after the following process?
"Immerse the container into a large water bath at the same temperature, and very slowly push the piston head further into the container."
• View Available Hint(s)
O point 1
O point 2
O point 3
O point 4
O point 5
O point 6
O point 7
O point 8
Submit
Previous Answers
X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
The volume of the gas cannot remain constant because the piston head has moved further into the container.
Part C
Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas after the following process?
"Lock the piston head in place and plunge the container into water that is colder than the gas."
O point 1
O point 2
O point 3
O point 4
O point 5
O point 6
O point 7
O point 8
Submit
Request Answer
Part D
Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas after the following process?
"The piston is now insulated from its surroundings. Pull the piston head further out of the container."
• View Available Hint(s)
O point 1
Figure
< 2 of 2 >
O point 2
O point 3
-Isotherms
O point 4
O point 5
O point 6
O point 7
O point 8
Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning