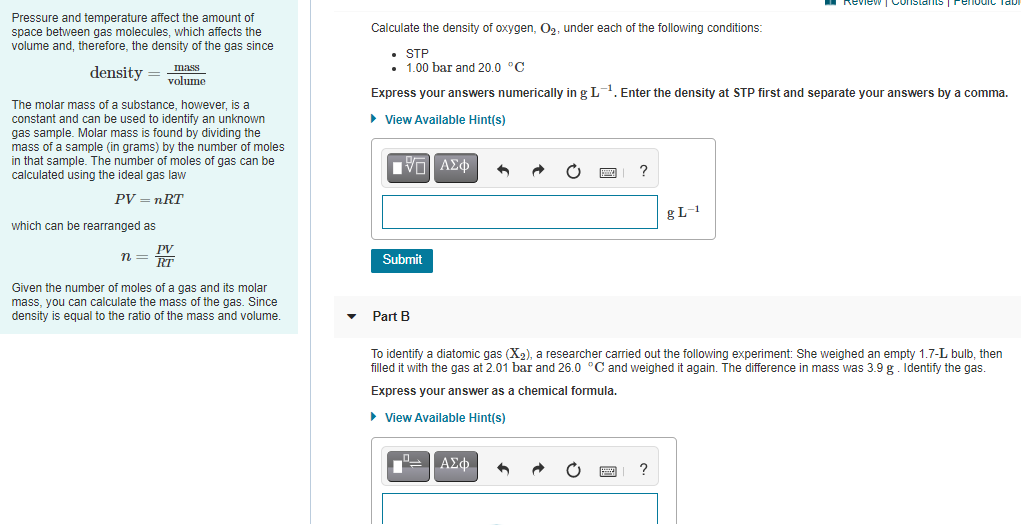
Pressure and temperature affect the amount of space between gas molecules, which affects the volume and, therefore, the density of the gas since Calculate the density of oxygen, O2, under each of the following conditions: • STP 1.00 bar and 20.0 °C density = mass volume Express your answers numerically in g L-1. Enter the density at STP first and separate your answers by a comma. The molar mass of a substance, however, is a constant and can be used to identify an unknown gas sample. Molar mass is found by dividing the mass of a sample (in grams) by the number of moles in that sample. The number of moles of gas can be calculated using the ideal gas law > View Available Hint(s) ? PV – nRT which can be rearranged as PV n = ir Submit Given the number of moles of a gas and its molar mass, you can calculate the mass of the gas. Since density is equal to the ratio of the mass and volume. • Part B To identify a diatomic gas (X2), a researcher carried out the following experiment: She weighed an empty 1.7-L bulb, then filled it with the gas at 2.01 bar and 26.0 °C and weighed it again. The difference in mass was 3.9 g. Identify the gas. Express your answer as a chemical formula.
Pressure and temperature affect the amount of space between gas molecules, which affects the volume and, therefore, the density of the gas since Calculate the density of oxygen, O2, under each of the following conditions: • STP 1.00 bar and 20.0 °C density = mass volume Express your answers numerically in g L-1. Enter the density at STP first and separate your answers by a comma. The molar mass of a substance, however, is a constant and can be used to identify an unknown gas sample. Molar mass is found by dividing the mass of a sample (in grams) by the number of moles in that sample. The number of moles of gas can be calculated using the ideal gas law > View Available Hint(s) ? PV – nRT which can be rearranged as PV n = ir Submit Given the number of moles of a gas and its molar mass, you can calculate the mass of the gas. Since density is equal to the ratio of the mass and volume. • Part B To identify a diatomic gas (X2), a researcher carried out the following experiment: She weighed an empty 1.7-L bulb, then filled it with the gas at 2.01 bar and 26.0 °C and weighed it again. The difference in mass was 3.9 g. Identify the gas. Express your answer as a chemical formula.
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter8: Properties Of Gases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 122QRT
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Review | Constants
Fenodic
Pressure and temperature affect the amount of
space between gas molecules, which affects the
volume and, therefore, the density of the gas since
Calculate the density of oxygen, O2, under each of the following conditions:
• STP
• 1.00 bar and 20.0 °C
Imass
density = volume
Express your answers numerically in g L. Enter the density at STP first and separate your answers by a comma.
The molar mass of a substance, however, is a
constant and can be used to identify an unknown
gas sample. Molar mass is found by dividing the
mass of a sample (in grams) by the number of moles
in that sample. The number of moles of gas can be
calculated using the ideal gas law
• View Available Hint(s)
Πνα ΑΣφ
PV — пRT
gL-1
which can be rearranged as
PV
RT
n =
Submit
Given the number of moles of a gas and its molar
mass, you can calculate the mass of the gas. Since
density is equal to the ratio of the mass and volume.
Part B
To identify a diatomic gas (X2), a researcher carried out the following experiment: She weighed an empty 1.7-L bulb, then
filled it with the gas at 2.01 bar and 26.0 °C and weighed it again. The difference in mass was 3.9 g. Identify the gas.
Express your answer as a chemical formula.
• View Available Hint(s)
.-ΑΣφ.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning