Problem A single-line diagram of the power system is shown in the figure below, where negative- and zero- sequence reactances are also given. The neutrals of the generator and D-Y transformers are solidly grounded. The motor neutral is grounded through a reactance X = 0.05 per unit on the motor base. Part I: Manually Calculated 1. Draw the per-unit zero-, positive-, and negative sequence networks on a 100-MVA, 13.8-kV base in the zone of the generator. 2. Draw Thevenin equivalents of the sequence networks for the assigned fault locations according to your number as In question 3 3. Use Thevenin equivalents of the sequence networks to compute the fault current for the following faults as assigned to each student: (a) A balanced three-phase solid fault. Fault at BUS4 (b) A single line-to-ground solid fault Fault at BUS1 (c) A double line-to-ground solid fault Fault at BUS1 (d) A line-to-line solid fault Fault at BUS4 Part II: MATLAB Calculated 4. Using the SYMFAULT, IGFAULT, LLFAULT, AND DLGFAULT Matlab functions, compute the fault current, bus voltages and line currents during the calculated faults in part 3. T T₁ Τι G 1 3 4 Line 2 2 M A 100 MVA 13.8 kV X 0.15 X₂ = 0.17 X₁ = X₂ = 20 N X-600 100 MVA 13.8-kVA/138-kVY X=0.10 per unit X=0.05 per unit 100 MVA 138-kV Y/13.8-kVA X 0.10 per unit 100 MVA 13.8 kV X-0.20 X₂ = 0.21 X-0.10 X, 0.05 per unit
Problem A single-line diagram of the power system is shown in the figure below, where negative- and zero- sequence reactances are also given. The neutrals of the generator and D-Y transformers are solidly grounded. The motor neutral is grounded through a reactance X = 0.05 per unit on the motor base. Part I: Manually Calculated 1. Draw the per-unit zero-, positive-, and negative sequence networks on a 100-MVA, 13.8-kV base in the zone of the generator. 2. Draw Thevenin equivalents of the sequence networks for the assigned fault locations according to your number as In question 3 3. Use Thevenin equivalents of the sequence networks to compute the fault current for the following faults as assigned to each student: (a) A balanced three-phase solid fault. Fault at BUS4 (b) A single line-to-ground solid fault Fault at BUS1 (c) A double line-to-ground solid fault Fault at BUS1 (d) A line-to-line solid fault Fault at BUS4 Part II: MATLAB Calculated 4. Using the SYMFAULT, IGFAULT, LLFAULT, AND DLGFAULT Matlab functions, compute the fault current, bus voltages and line currents during the calculated faults in part 3. T T₁ Τι G 1 3 4 Line 2 2 M A 100 MVA 13.8 kV X 0.15 X₂ = 0.17 X₁ = X₂ = 20 N X-600 100 MVA 13.8-kVA/138-kVY X=0.10 per unit X=0.05 per unit 100 MVA 138-kV Y/13.8-kVA X 0.10 per unit 100 MVA 13.8 kV X-0.20 X₂ = 0.21 X-0.10 X, 0.05 per unit
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Chapter9: Unsymmetrical Faults
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.55P
Related questions
Question
solve all qestio
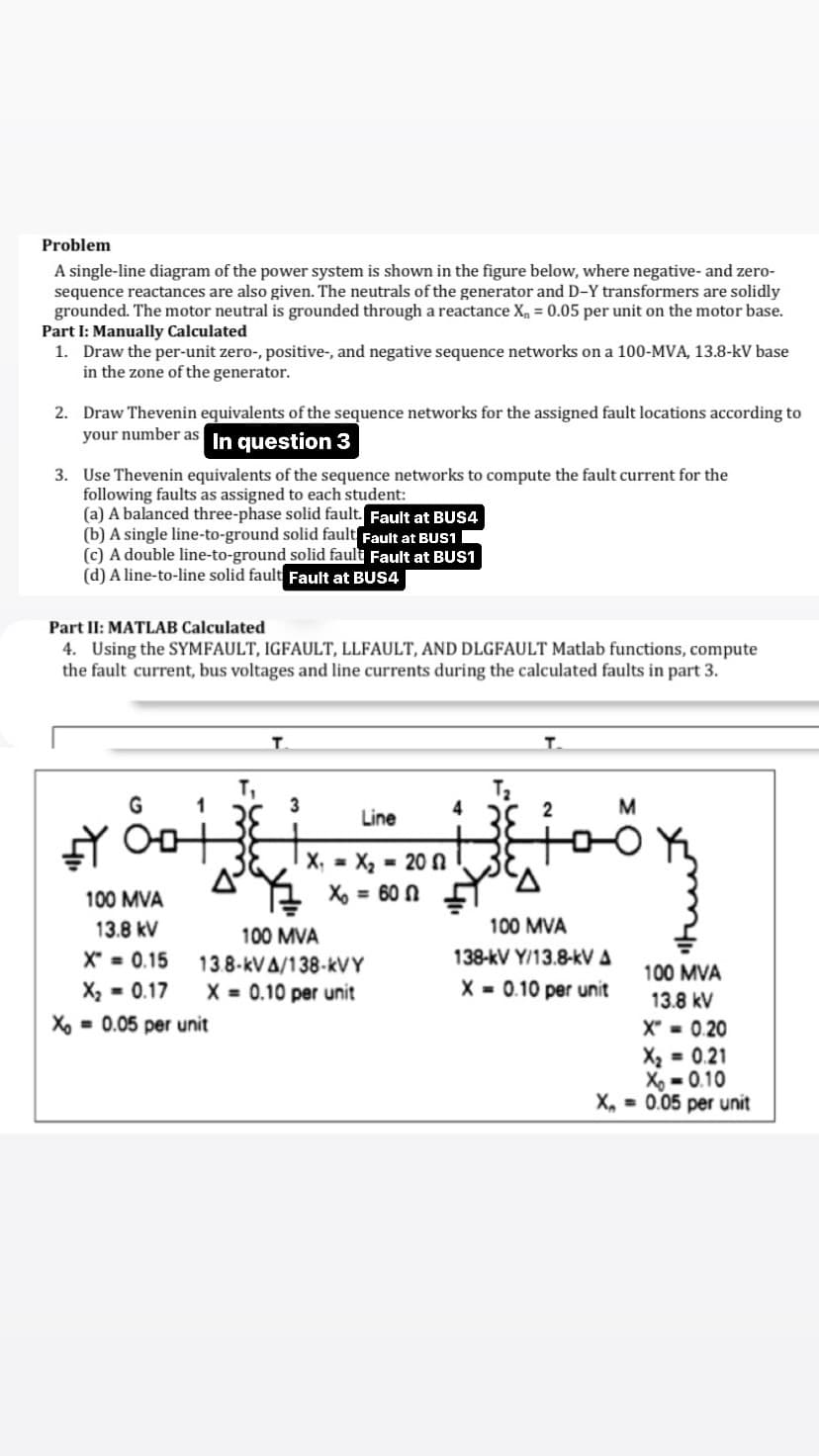
Transcribed Image Text:Problem
A single-line diagram of the power system is shown in the figure below, where negative- and zero-
sequence reactances are also given. The neutrals of the generator and D-Y transformers are solidly
grounded. The motor neutral is grounded through a reactance X = 0.05 per unit on the motor base.
Part I: Manually Calculated
1. Draw the per-unit zero-, positive-, and negative sequence networks on a 100-MVA, 13.8-kV base
in the zone of the generator.
2. Draw Thevenin equivalents of the sequence networks for the assigned fault locations according to
your number as In question 3
3. Use Thevenin equivalents of the sequence networks to compute the fault current for the
following faults as assigned to each student:
(a) A balanced three-phase solid fault. Fault at BUS4
(b) A single line-to-ground solid fault Fault at BUS1
(c) A double line-to-ground solid fault Fault at BUS1
(d) A line-to-line solid fault Fault at BUS4
Part II: MATLAB Calculated
4. Using the SYMFAULT, IGFAULT, LLFAULT, AND DLGFAULT Matlab functions, compute
the fault current, bus voltages and line currents during the calculated faults in part 3.
T
T₁
Τι
G
1
3
4
Line
2
2
M
A
100 MVA
13.8 kV
X 0.15
X₂ = 0.17
X₁ = X₂ = 20 N
X-600
100 MVA
13.8-kVA/138-kVY
X=0.10 per unit
X=0.05 per unit
100 MVA
138-kV Y/13.8-kVA
X 0.10 per unit
100 MVA
13.8 kV
X-0.20
X₂ = 0.21
X-0.10
X, 0.05 per unit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course …
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305632134
Author:
J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course …
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305632134
Author:
J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:
Cengage Learning