Q2. Under the Examples" column in Table 2, Place the letters, a thru j, from the reactions from Q2 that identi fies each reaction type. Table 2. Four Types of Chemical Reaction |Type of Reaction Description USE EACH LETTER a thur Examples (from Q1) Format Combination Two reactants combine to A+B → C give the product. One reactant breaks down | A→B+C Decomposition into two or more products. One reactant replaces a part of the second |reactant. Two reactants "switch" Single Replacement A +BX →B +AX Double AX+BY → AY+BX Replacement partners with each other. III. FURTHER STUDIES To identify the type of rxn use: C composition DE decomposition SR single replacement DR double replacement Q3. Balance the foll owing chemical equations and classify each as to type listed on Table 2. (a) This is an explosive reaction occurring when ammonium nitrate (NH,NO3, a fertilizer) is heated. - NH,NO; → N2 + 0 + H2O Туре: (b) This is an exothermic reaction in which sulfuric acid (H2SO2) is neutralized by lye (NaOH). H2SO4 + NAOH → Na2SO4 + H2O Туре: (c) This exothermic reaction occurs when nitric acid (HNO;) neutralizes magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2. HNO; + _Mg(OH)2 Mg(NO:)2 + H2O Туре: (d) Scrap iron (Fe) reacts with stibnite (Sb2S3, a black mineral) to produce pure antimony (Sb). Fe +Sb,S; →_ Fes +_ Sb Туре: — (e) Charcoal (C) burms with insufficient oxygen (O) to produce carbon monoxide (CO), a toxic gas. C + CO Туре: (f) A precipitation reaction in which a black precipitate (CuS) is formed. _Cu(NO3)2 + NazS Cus NANO; Туре: (g) An exothermic reacti on in which sulfuric acid (H2SO4) neutralizes aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH);). _Al(ОН)з + H2 SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + H2O Туре: An endothermic reaction in which limestone (CaCO;) is converted to quicklime (CaO) in a 800°C kiln. Сао + CO2 СаСОз Copper (Cu, a cheap metal) reacts with silver nitrate (AGNO3, a silver-containing mineral) to yield metallic silver (Ag, a precious metal). Туре: A NO; + Ag + Cu(NO3)2 Туре: Cu →
Q2. Under the Examples" column in Table 2, Place the letters, a thru j, from the reactions from Q2 that identi fies each reaction type. Table 2. Four Types of Chemical Reaction |Type of Reaction Description USE EACH LETTER a thur Examples (from Q1) Format Combination Two reactants combine to A+B → C give the product. One reactant breaks down | A→B+C Decomposition into two or more products. One reactant replaces a part of the second |reactant. Two reactants "switch" Single Replacement A +BX →B +AX Double AX+BY → AY+BX Replacement partners with each other. III. FURTHER STUDIES To identify the type of rxn use: C composition DE decomposition SR single replacement DR double replacement Q3. Balance the foll owing chemical equations and classify each as to type listed on Table 2. (a) This is an explosive reaction occurring when ammonium nitrate (NH,NO3, a fertilizer) is heated. - NH,NO; → N2 + 0 + H2O Туре: (b) This is an exothermic reaction in which sulfuric acid (H2SO2) is neutralized by lye (NaOH). H2SO4 + NAOH → Na2SO4 + H2O Туре: (c) This exothermic reaction occurs when nitric acid (HNO;) neutralizes magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2. HNO; + _Mg(OH)2 Mg(NO:)2 + H2O Туре: (d) Scrap iron (Fe) reacts with stibnite (Sb2S3, a black mineral) to produce pure antimony (Sb). Fe +Sb,S; →_ Fes +_ Sb Туре: — (e) Charcoal (C) burms with insufficient oxygen (O) to produce carbon monoxide (CO), a toxic gas. C + CO Туре: (f) A precipitation reaction in which a black precipitate (CuS) is formed. _Cu(NO3)2 + NazS Cus NANO; Туре: (g) An exothermic reacti on in which sulfuric acid (H2SO4) neutralizes aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH);). _Al(ОН)з + H2 SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + H2O Туре: An endothermic reaction in which limestone (CaCO;) is converted to quicklime (CaO) in a 800°C kiln. Сао + CO2 СаСОз Copper (Cu, a cheap metal) reacts with silver nitrate (AGNO3, a silver-containing mineral) to yield metallic silver (Ag, a precious metal). Туре: A NO; + Ag + Cu(NO3)2 Туре: Cu →
Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305264434
Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Chapter21: Rates Of Chemical Reactions, Ii. A Clock Reaction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1ASA
Related questions
Question
100%
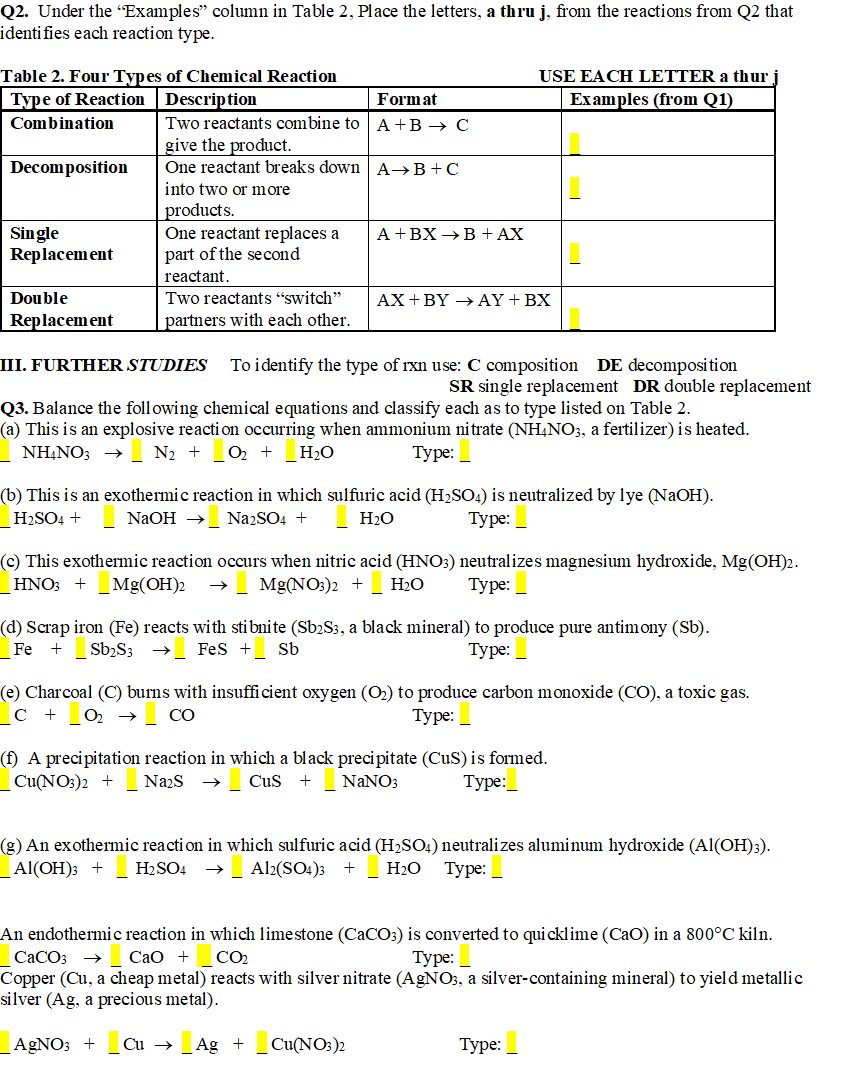
Transcribed Image Text:Q2. Under the Examples" column in Table 2, Place the letters, a thru j, from the reactions from Q2 that
identi fies each reaction type.
Table 2. Four Types of Chemical Reaction
|Type of Reaction Description
USE EACH LETTER a thur
Examples (from Q1)
Format
Combination
Two reactants combine to A+B → C
give the product.
One reactant breaks down | A→B+C
Decomposition
into two or more
products.
One reactant replaces a
part of the second
|reactant.
Two reactants "switch"
Single
Replacement
A +BX →B +AX
Double
AX+BY → AY+BX
Replacement
partners with each other.
III. FURTHER STUDIES
To identify the type of rxn use: C composition DE decomposition
SR single replacement DR double replacement
Q3. Balance the foll owing chemical equations and classify each as to type listed on Table 2.
(a) This is an explosive reaction occurring when ammonium nitrate (NH,NO3, a fertilizer) is heated.
- NH,NO; →
N2 + 0 +
H2O
Туре:
(b) This is an exothermic reaction in which sulfuric acid (H2SO2) is neutralized by lye (NaOH).
H2SO4 +
NAOH → Na2SO4 +
H2O
Туре:
(c) This exothermic reaction occurs when nitric acid (HNO;) neutralizes magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2.
HNO; + _Mg(OH)2
Mg(NO:)2 +
H2O
Туре:
(d) Scrap iron (Fe) reacts with stibnite (Sb2S3, a black mineral) to produce pure antimony (Sb).
Fe +Sb,S; →_ Fes +_ Sb
Туре: —
(e) Charcoal (C) burms with insufficient oxygen (O) to produce carbon monoxide (CO), a toxic gas.
C +
CO
Туре:
(f) A precipitation reaction in which a black precipitate (CuS) is formed.
_Cu(NO3)2 +
NazS
Cus
NANO;
Туре:
(g) An exothermic reacti on in which sulfuric acid (H2SO4) neutralizes aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH);).
_Al(ОН)з +
H2 SO4
→ Al2(SO4)3
+ H2O
Туре:
An endothermic reaction in which limestone (CaCO;) is converted to quicklime (CaO) in a 800°C kiln.
Сао +
CO2
СаСОз
Copper (Cu, a cheap metal) reacts with silver nitrate (AGNO3, a silver-containing mineral) to yield metallic
silver (Ag, a precious metal).
Туре:
A NO; +
Ag +
Cu(NO3)2
Туре:
Cu →
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305264434
Author:
Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305264434
Author:
Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
