Quantity (in gallons) Total Price Revenue $8 $0 50 7 350 100 600 150 5 750 200 800 250 3 750 300 2 600 350 1 350 400 Imagine a small town in a remote area where only two residents, Maria and Miguel, own dairies that produce milk. Their respective dairies are equal in size. Each week Maria and Miguel work together to decide how many gallons of milk to produce and what price to charge. To keep things simple, suppose that Maria and Miguel can produce as much milk as they want without cost so that the marginal cost is zero and there are no fixed costs. The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for milk is shown in the table above. Suppose the town enacts new antitrust laws that prohibit Maria and Miguel from operating as a cartel. Assuming that each producer can only modify quantity in increments of 50, which of the following is consistent with the Nash equilibrium for this scenario? Maria will charge a price of $5 for each gallon. Miguel and Maria will each sell 150 gallons per week. The Nash equilibrium quantity is 200. Milk will sell for $4 per gallon.
Quantity (in gallons) Total Price Revenue $8 $0 50 7 350 100 600 150 5 750 200 800 250 3 750 300 2 600 350 1 350 400 Imagine a small town in a remote area where only two residents, Maria and Miguel, own dairies that produce milk. Their respective dairies are equal in size. Each week Maria and Miguel work together to decide how many gallons of milk to produce and what price to charge. To keep things simple, suppose that Maria and Miguel can produce as much milk as they want without cost so that the marginal cost is zero and there are no fixed costs. The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for milk is shown in the table above. Suppose the town enacts new antitrust laws that prohibit Maria and Miguel from operating as a cartel. Assuming that each producer can only modify quantity in increments of 50, which of the following is consistent with the Nash equilibrium for this scenario? Maria will charge a price of $5 for each gallon. Miguel and Maria will each sell 150 gallons per week. The Nash equilibrium quantity is 200. Milk will sell for $4 per gallon.
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305971493
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter17: Oligopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9PA
Related questions
Question
6
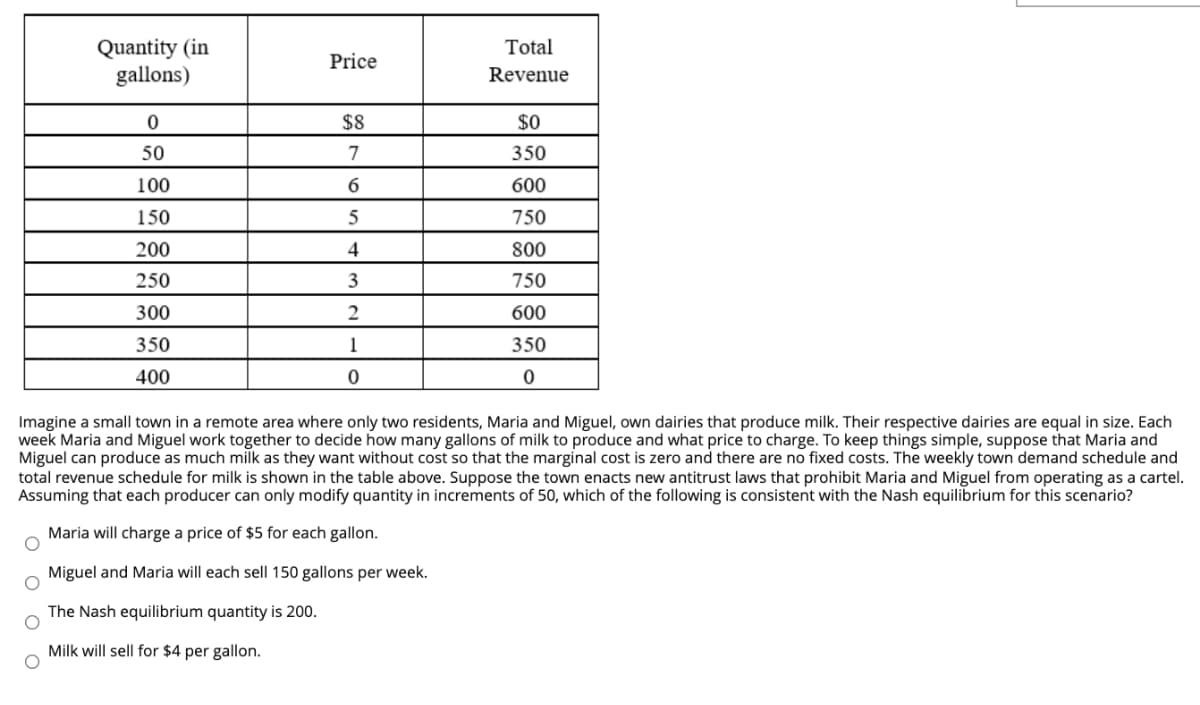
Transcribed Image Text:Quantity (in
gallons)
Total
Price
Revenue
$8
$0
50
7
350
100
600
150
750
200
4
800
250
3
750
300
2
600
350
1
350
400
Imagine a small town in a remote area where only two residents, Maria and Miguel, own dairies that produce milk. Their respective dairies are equal in size. Each
week Maria and Miguel work together to decide how many gallons of milk to produce and what price to charge. To keep things simple, suppose that Maria and
Miguel can produce as much milk as they want without cost so that the marginal cost is zero and there are no fixed costs. The weekly town demand schedule and
total revenue schedule for milk is shown in the table above. Suppose the town enacts new antitrust laws that prohibit Maria and Miguel from operating as a cartel.
Assuming that each producer can only modify quantity in increments of 50, which of the following is consistent with the Nash equilibrium for this scenario?
Maria will charge a price of $5 for each gallon.
Miguel and Maria will each sell 150 gallons per week.
The Nash equilibrium quantity is 200.
Milk will sell for $4 per gallon.

Transcribed Image Text:Samsung Expensive
Cheap
Apple
Expensive Cheap
2,6
3,3
4,4
6,2
Apple and Samsung control the majority of the Smart Phones. Suppose the diagram above represents their strategic options, either to offer an expensive or a
cheap phone in the market. If both firms offer an expensive phone, they will each earn 4 billion dollars. If Samsung offers a cheap phone, while Apple offers only
an expensive phone, Samsung will earn $6 billion and Apple will earn $2 billion, and vice versa. If they both offer a cheap phone, they will each earn $3 billion.
What is each firm's dominant strategy?
The dominant strategy for Apple is to offer an expensive phone, but Samsung does not have a dominant strategy.
The dominant strategy for Apple is to offer a cheap phone, but Samsung does not have a dominant strategy.
The dominant strategy for both firms is to offer a cheap phone.
The dominant strategy for both firms is to offer an expensive phone.
O O O O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc