Question 1: Visitors to a Skee-Ball booth attempt to roll a ball into a central target. Define the discrete random variable C: the number of times a customer rolls the ball into the central target in three attempts. The discrete random variable C reflects the customer's score. The PDF of C is as follows: P(C = c) 0.6 c=0 0 1 0.3 c=1 0.15 c=2 0.05 a) Sketch the CDF of C. What proportion of customers roll the ball into the central target at least twice in three attempts? $0 $3.00 $5.00 $7.00 c=3 b) It costs $2.00 to play a single game of Skee-Ball (three attempts) at this booth. Customer winnings (W) are outlined in the table below, alongside the booth's profit (P= W-$2.00) for each possible outcome of the customer's score (C). Customer Score (C) Customer Winnings (W) Booth's Profit (P) +$2.00 -$1.00 2 -$3.00 3 $5.00 Compute E(P), the expected booth's profit for a single game of Skee-Ball. c) How much should the booth charge for a single game of Skee-Ball in order to achieve an expected profit of 40 cents per game? Assume customer winnings amounts remain the same, but the booth's profit (P) will reflect the new price. d) How can the booth achieve an expected profit of 40 cents per game by adjusting customer winnings amounts, while keeping the cost per game equal to $2.00? Note: There is more than one correct answer.
Question 1: Visitors to a Skee-Ball booth attempt to roll a ball into a central target. Define the discrete random variable C: the number of times a customer rolls the ball into the central target in three attempts. The discrete random variable C reflects the customer's score. The PDF of C is as follows: P(C = c) 0.6 c=0 0 1 0.3 c=1 0.15 c=2 0.05 a) Sketch the CDF of C. What proportion of customers roll the ball into the central target at least twice in three attempts? $0 $3.00 $5.00 $7.00 c=3 b) It costs $2.00 to play a single game of Skee-Ball (three attempts) at this booth. Customer winnings (W) are outlined in the table below, alongside the booth's profit (P= W-$2.00) for each possible outcome of the customer's score (C). Customer Score (C) Customer Winnings (W) Booth's Profit (P) +$2.00 -$1.00 2 -$3.00 3 $5.00 Compute E(P), the expected booth's profit for a single game of Skee-Ball. c) How much should the booth charge for a single game of Skee-Ball in order to achieve an expected profit of 40 cents per game? Assume customer winnings amounts remain the same, but the booth's profit (P) will reflect the new price. d) How can the booth achieve an expected profit of 40 cents per game by adjusting customer winnings amounts, while keeping the cost per game equal to $2.00? Note: There is more than one correct answer.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.1: Measures Of Center
Problem 9PPS
Related questions
Question
Please no written by hand solution and no img
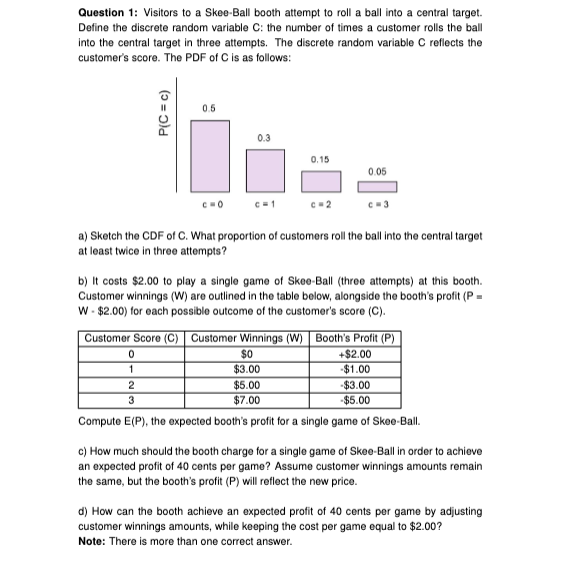
Transcribed Image Text:Question 1: Visitors to a Skee-Ball booth attempt to roll a ball into a central target.
Define the discrete random variable C: the number of times a customer rolls the ball
into the central target in three attempts. The discrete random variable C reflects the
customer's score. The PDF of C is as follows:
P(C = c)
0.5
c=0
0
1
0.3
c=1
0.15
c=2
a) Sketch the CDF of C. What proportion of customers roll the ball into the central target
at least twice in three attempts?
0.05
b) It costs $2.00 to play a single game of Skee-Ball (three attempts) at this booth.
Customer winnings (W) are outlined in the table below, alongside the booth's profit (P =
W-$2.00) for each possible outcome of the customer's score (C).
$0
$3.00
$5.00
$7.00
Customer Score (C) | Customer Winnings (W) Booth's Profit (P)
+$2.00
-$1.00
-$3.00
-$5.00
2
3
Compute E(P), the expected booth's profit for a single game of Skee-Ball.
c) How much should the booth charge for a single game of Skee-Ball in order to achieve
an expected profit of 40 cents per game? Assume customer winnings amounts remain
the same, but the booth's profit (P) will reflect the new price.
d) How can the booth achieve an expected profit of 40 cents per game by adjusting
customer winnings amounts, while keeping the cost per game equal to $2.00?
Note: There is more than one correct answer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 9 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage