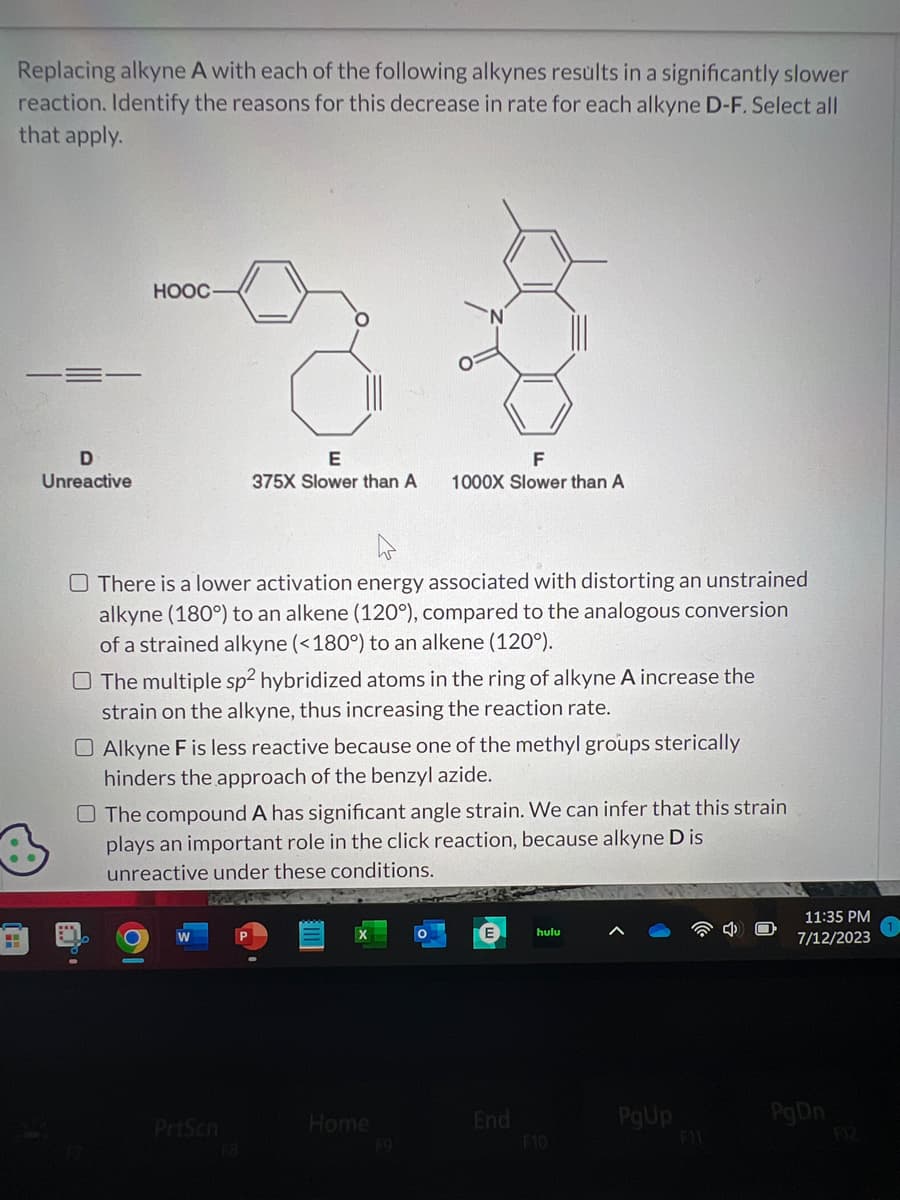
Replacing alkyne A with each of the following alkynes results in a significantly slower reaction. Identify the reasons for this decrease in rate for each alkyne D-F. Select all that apply.
Replacing alkyne A with each of the following alkynes results in a significantly slower reaction. Identify the reasons for this decrease in rate for each alkyne D-F. Select all that apply.
Chapter30: Orbitals And Organic Chemistry: Pericyclic Reactions
Section30.SE: Something Extra
Problem 14MP: Plastic photochromic sunglasses are based on the following reversible rearrangement of a dye inside...
Related questions
Question
100%
Replacing a kin, a word each of the following our kids results in a significantly lower reaction. Identify the reasons for this decrease in rate for each alkene D – F. Select all that apply.

Transcribed Image Text:H
Replacing alkyne A with each of the following alkynes results in a significantly slower
reaction. Identify the reasons for this decrease in rate for each alkyne D-F. Select all
that apply.
D
Unreactive
HỌỌC
E
375X Slower than A
There is a lower activation energy associated with distorting an unstrained
alkyne (180°) to an alkene (120°), compared to the analogous conversion
of a strained alkyne (<180°) to an alkene (120°).
O
5.
O The multiple sp2 hybridized atoms in the ring of alkyne A increase the
strain on the alkyne, thus increasing the reaction rate.
O Alkyne F is less reactive because one of the methyl groups sterically
hinders the approach of the benzyl azide.
PrtScn
F
1000X Slower than A
The compound A has significant angle strain. We can infer that this strain
plays an important role in the click reaction, because alkyne D is
unreactive under these conditions.
Home
O
E
End
hulu
F10
PgUp
11:35 PM
7/12/2023
PgDn
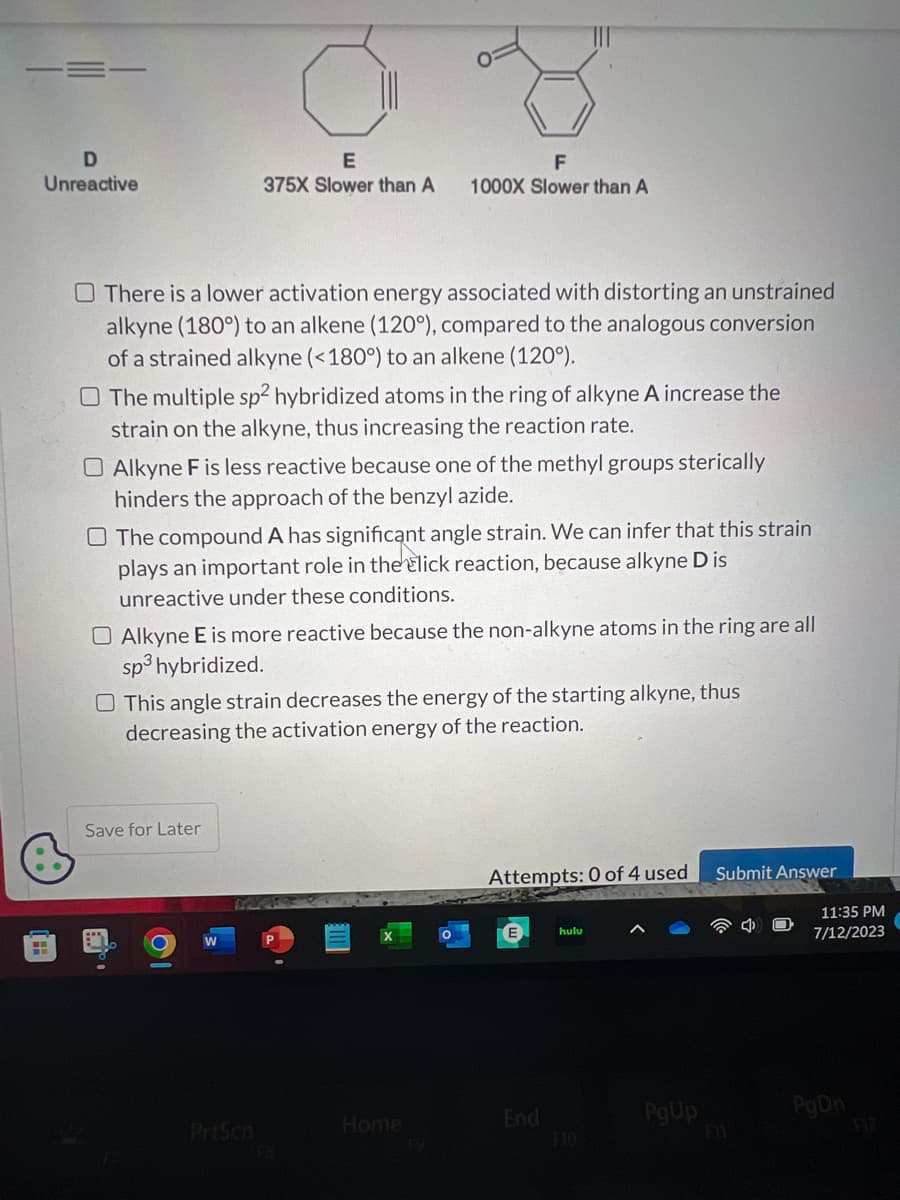
Transcribed Image Text:D
Unreactive
O There is a lower activation energy associated with distorting an unstrained
alkyne (180°) to an alkene (120°), compared to the analogous conversion
of a strained alkyne (<180°) to an alkene (120°).
E
375X Slower than A
O The multiple sp2 hybridized atoms in the ring of alkyne A increase the
strain on the alkyne, thus increasing the reaction rate.
O Alkyne F is less reactive because one of the methyl groups stericall
hinders the approach of the benzyl azide.
F
1000X Slower than A
O The compound A has significant angle strain. We can infer that this strain
plays an important role in the Elick reaction, because alkyne D is
unreactive under these conditions.
O Alkyne E is more reactive because the non-alkyne atoms in the ring are all
sp3 hybridized.
Save for Later
A
This angle strain decreases the energy of the starting alkyne, thus
decreasing the activation energy of the reaction.
PrtScn
Home
Attempts: 0 of 4 used
E
End
hulu
F10
PgUp
Submit Answer
11:35 PM
7/12/2023
PgDn
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning