ReplenAde produced 15.000 cases of powdered drink mix and sold 12.000 cases in April. The sales price was $26, variable costs were $11 per case ($8 manufacturing and $3 selling and administrative), and total fixed costs were $70,000 ($45,000 manufacturing overhead and $25,000 selling and administrative). The company had no beginning Finished Goods Inventory. ReplenAde calculated the cost per unit and the total cost of the 3,000 cases in Finished Goods Inventory as of April 30 using both the absorption and variable costing methods. The calculations are presented below. (Click the icon to view the calculations using the absortion and variable costing methods.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Which costing method produces the highest operating income? Explain why. The cost method produces the highest operating income. The primary reason for this is that the unit cost. Under the absorption costing method, are distributed across the entire production run as part of of fixed manufacturing costs are Under the variable costing method, this amount is Reference Variable manufacturing cost per case Fixed manufacturing overhead per case + = Total product cost per case x Number of cases in Finished Goods Inventory = Total cost of Finished Goods Inventory Print Done April 30 Absorption Variable costing costing $ $ $ 8 $ 3 11 S 3,000 33,000 $ - X 8 X 8 3,000 24,000 Requirements 1. Which costing method produces the highest operating income? Explain why. 2. Which costing method produces the highest April 30 balance in Finished Goods Inventory? Explain why. Print Done - X
ReplenAde produced 15.000 cases of powdered drink mix and sold 12.000 cases in April. The sales price was $26, variable costs were $11 per case ($8 manufacturing and $3 selling and administrative), and total fixed costs were $70,000 ($45,000 manufacturing overhead and $25,000 selling and administrative). The company had no beginning Finished Goods Inventory. ReplenAde calculated the cost per unit and the total cost of the 3,000 cases in Finished Goods Inventory as of April 30 using both the absorption and variable costing methods. The calculations are presented below. (Click the icon to view the calculations using the absortion and variable costing methods.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Which costing method produces the highest operating income? Explain why. The cost method produces the highest operating income. The primary reason for this is that the unit cost. Under the absorption costing method, are distributed across the entire production run as part of of fixed manufacturing costs are Under the variable costing method, this amount is Reference Variable manufacturing cost per case Fixed manufacturing overhead per case + = Total product cost per case x Number of cases in Finished Goods Inventory = Total cost of Finished Goods Inventory Print Done April 30 Absorption Variable costing costing $ $ $ 8 $ 3 11 S 3,000 33,000 $ - X 8 X 8 3,000 24,000 Requirements 1. Which costing method produces the highest operating income? Explain why. 2. Which costing method produces the highest April 30 balance in Finished Goods Inventory? Explain why. Print Done - X
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Chapter18: Pricing And Profitability Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3CE: Pattison Products, Inc., began operations in October and manufactured 40,000 units during the month...
Related questions
Question
Complete all requirements
<><>
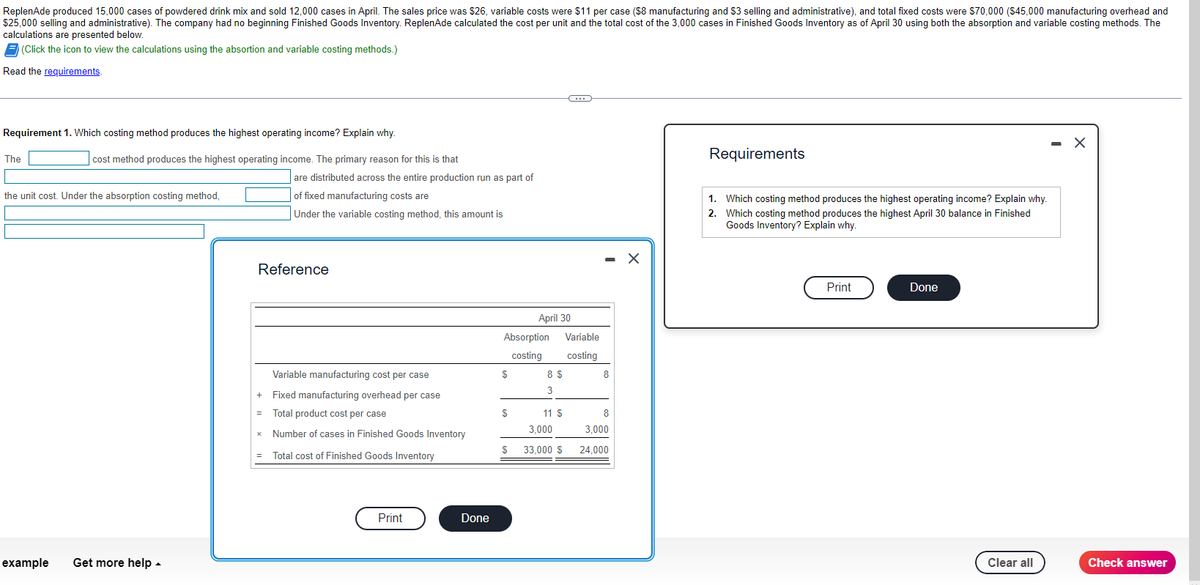
Transcribed Image Text:ReplenAde produced 15,000 cases of powdered drink mix and sold 12,000 cases in April. The sales price was $26, variable costs were $11 per case ($8 manufacturing and $3 selling and administrative), and total fixed costs were $70,000 ($45,000 manufacturing overhead and
$25,000 selling and administrative). The company had no beginning Finished Goods Inventory. ReplenAde calculated the cost per unit and the total cost of the 3,000 cases in Finished Goods Inventory as of April 30 using both the absorption and variable costing methods. The
calculations are presented below.
(Click the icon to view the calculations using the absortion and variable costing methods.)
Read the requirements.
Requirement 1. Which costing method produces the highest operating income? Explain why.
The
cost method produces the highest operating income. The primary reason for this is that
the unit cost. Under the absorption costing method,
example Get more help.
are distributed across the entire production run as part of
of fixed manufacturing costs are
Under the variable costing method, this amount is
Reference
Variable manufacturing cost per case
Fixed manufacturing overhead per case
+
= Total product cost per case
x
Number of cases in Finished Goods Inventory
=
Total cost of Finished Goods Inventory
Print
Done
April 30
Absorption Variable
costing costing
$
$
$
8 $
3
C
11 S
3,000
33,000 $
- X
8
8
3,000
24,000
Requirements
1. Which costing method produces the highest operating income? Explain why.
2. Which costing method produces the highest April 30 balance in Finished
Goods Inventory? Explain why.
Print
Done
Clear all
X
Check answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,