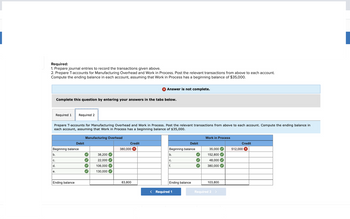
The Polaris Company uses a job-order costing system. The following transactions occurred in October: a. Raw materials purchased on account, $209,000. b. Raw materials used in production, $191,000 ($152,800 direct materials and $38,200 indirect materials). c. Accrued direct labor cost of $48,000 and indirect labor cost of $22,000. d. Depreciation recorded on factory equipment, $106,000. e. Other manufacturing overhead costs accrued during October, $130,000. f. The company applies manufacturing overhead cost to production using a predetermined rate of $5 per machine-hour. A total of 76,000 machine-hours were used in October. g. Jobs costing $512,000 according to their job cost sheets were completed during October and transferred to Finished Goods. h. Jobs that had cost $447,000 to complete according to their job cost sheets were shipped to customers during the month. These jobs were sold on account at 36% above cost. Required: 1. Prepare journal entries to record the transactions given above. 2. Prepare T-accounts for Manufacturing Overhead and Work in Process. Post the relevant transactions from above to each account. Compute the ending balance in each account, assuming that Work in Process has a beginning balance of $35,000. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Prepare T-accounts for Manufacturing Overhead and Work in Process. Post the relevant transactions from above to each account. Compute the ending balance in each account, assuming that Work in Process has a beginning balance of $35,000. Manufacturing Overhead Debit Beginning balance Credit Debit Beginning balance Work in Process Credit
Process Costing
Process costing is a sort of operation costing which is employed to determine the value of a product at each process or stage of producing process, applicable where goods produced from a series of continuous operations or procedure.
Job Costing
Job costing is adhesive costs of each and every job involved in the production processes. It is an accounting measure. It is a method which determines the cost of specific jobs, which are performed according to the consumer’s specifications. Job costing is possible only in businesses where the production is done as per the customer’s requirement. For example, some customers order to manufacture furniture as per their needs.
ABC Costing
Cost Accounting is a form of managerial accounting that helps the company in assessing the total variable cost so as to compute the cost of production. Cost accounting is generally used by the management so as to ensure better decision-making. In comparison to financial accounting, cost accounting has to follow a set standard ad can be used flexibly by the management as per their needs. The types of Cost Accounting include – Lean Accounting, Standard Costing, Marginal Costing and Activity Based Costing.
In the accounting books of the business organizations the journal entry served as a record of its financial activities. The business entities provide the journal entries so as to get the records of all the business transactions occurs in chronological order.
Journal entry types:
- Transfer entries
- Closing entries
- Adjusting entries
- Compound entries
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images