Review | Constants I Periodie Table Entropy, denoted by the symbol S. is the thermodynamic property describing the amount of molecular randomness or disorder in a system. It is a state thermodynamic function, meaning that its value does not depend on the path used to arive at a specific set of conditions. Each system with a specified temperature, pressure, and composition has a unique entropy value. the temperature of a perfect crystal increases, the random vibrations of the molecules decrease. O At the melting point, the entropy of a system increases abruptly as the compound transforms into a liquid. The entropy change. A:S. is the difference in entropy between two states of a system, such as between the reactants and products of a reaction or between a flask before and after adding a mixture of gas Previous Answere v Correct The third law of thermodynamics deals with the entropy of a system and the chemical bonding in the molecules. Whenever there is a change in phase from a solid to a liquid or from a liquid to a gas, the vibrational and rotational motions of molecules increase; therefore, the entropy of the system increases as the phase changes. At absolute zero, the entropy of any perfect system becomes zero. • Part B Calculate the standard-state entropy for the follovwing reaction: 2NIS(s) + 30,(9)-→250;(9) + 2NIO(s) The standard entropy values are given in the table. s° Formula 1K-mol SO:(9) 248 NiO(a) 38.0 Nis(s) 53.0 O:(9) 205 Express your answer with the appropriate units > View Available Hint/s) empigtes Symbola undo regdo fesér keyboard shortcuts Help J A,S° = - 1479 mol •k
Review | Constants I Periodie Table Entropy, denoted by the symbol S. is the thermodynamic property describing the amount of molecular randomness or disorder in a system. It is a state thermodynamic function, meaning that its value does not depend on the path used to arive at a specific set of conditions. Each system with a specified temperature, pressure, and composition has a unique entropy value. the temperature of a perfect crystal increases, the random vibrations of the molecules decrease. O At the melting point, the entropy of a system increases abruptly as the compound transforms into a liquid. The entropy change. A:S. is the difference in entropy between two states of a system, such as between the reactants and products of a reaction or between a flask before and after adding a mixture of gas Previous Answere v Correct The third law of thermodynamics deals with the entropy of a system and the chemical bonding in the molecules. Whenever there is a change in phase from a solid to a liquid or from a liquid to a gas, the vibrational and rotational motions of molecules increase; therefore, the entropy of the system increases as the phase changes. At absolute zero, the entropy of any perfect system becomes zero. • Part B Calculate the standard-state entropy for the follovwing reaction: 2NIS(s) + 30,(9)-→250;(9) + 2NIO(s) The standard entropy values are given in the table. s° Formula 1K-mol SO:(9) 248 NiO(a) 38.0 Nis(s) 53.0 O:(9) 205 Express your answer with the appropriate units > View Available Hint/s) empigtes Symbola undo regdo fesér keyboard shortcuts Help J A,S° = - 1479 mol •k
Chemistry for Engineering Students
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781285199023
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter10: Entropy And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.29PAE
Related questions
Question
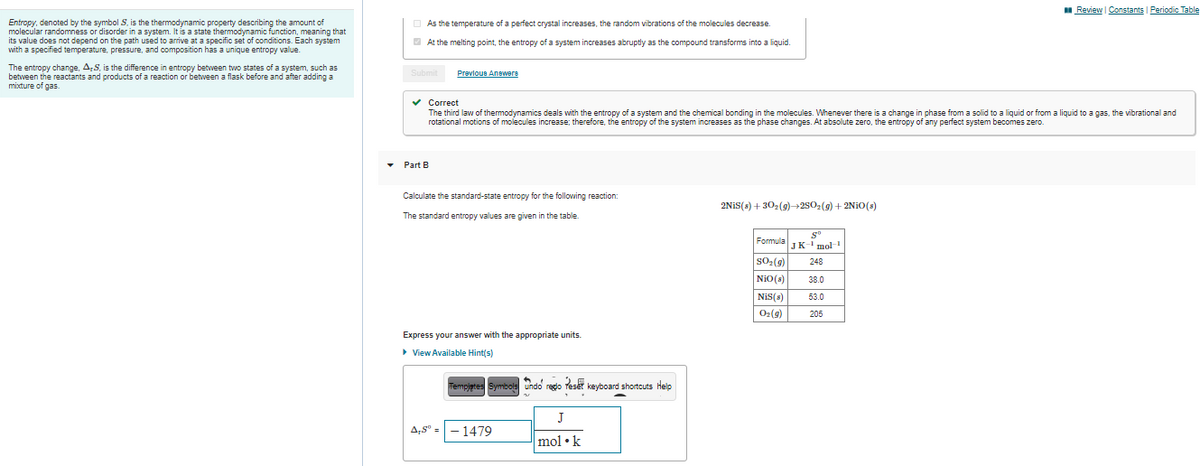
Transcribed Image Text:I Review Constants | Periodic Table
O As the temperature of a perfect crystal increases, the random vibrations of the molecules decrease.
Entropy, denoted by the symbol S, is the thermodynamic property describing the amount of
molecular randomness or disorder in a system. It is a state thermodynamic function, meaning that
its value does not depend on the path used to arrive at a specific set of conditions. Each system
with a specified temperature, pressure, and composition has a unique entropy value.
O At the melting point, the entropy of a system increases abruptly as the compound transforms into a liquid.
The entropy change, A:S, is the difference in entropy between two states of a system, such as
between the reactants and products of a reaction or between a flask before and after adding a
mixture of gas.
Prevlous Answera
v Correct
The third law of thermodynamics deals with the entropy of a system and the chemical bonding in the molecules. Whenever there is a change in phase from a solid to a liquid or from a liquid to a gas, the vibrational and
rotational motions of molecules increase; therefore, the entropy of the system increases as the phase changes. At absolute zero, the entropy of any perfect system becomes zero.
• Part B
Calculate the standard-state entropy for the following reaction:
2NIS(s) + 302(9)250(9) + 2NIO(s)
The standard entropy values are given in the table.
Formula
JK-' mol-
sO2(9)
248
NiO(s)
38.0
NIS(s)
53.0
Oz(9)
205
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
• View Available Hint(s)
Tempjates Symbols undo redo reser keyboard shortcuts Help
J
A,S° =
1479
mol •k
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning