"Select the most suitable complement among listed options for the 10 items: T) Real fluids (a) are viscous (b) possess surface tension (c) are compressible (d) possess all the above properties (e) possess none of the above properties. 2) In a static fluid (a) resistance to shear stress is small (b) fluid pressure is zero (c) linear deformation is small (e) viscosity is nil. (d) only normal stresses can exist 3) When the flow parameters at any given instant remain same at every point, then flow is said to be (d) uniform (e) Static. (a) Turbulent (b) Steady state (c) laminar 4) The increase of temperature results in (a) increase in viscosity of gas (b) increase in viscosity of liquid (c)decrease in viscosity of ga (d) decrease in viscosity of liquid (e) (a) and (d) above. 5) Consider the flow in pipe in figure. If P₁ -AP/y. b) The ow direction is from 2 to 1 if AZ <-AP/y. c) T flow is zero if AZ = -AP/y. d) The flow is zero if AZ = AP/y. Q 6) Air flow though the device shown in figure. Select which set of the following conditions is TRUE assuming incompressible non-viscous steady flow ½-1 2 (a) p4 v3 (b) p3> pl; vl > v3 (c) p2 p3; v2> v3 (d) p4 vl (e) p4> pl; v4
"Select the most suitable complement among listed options for the 10 items: T) Real fluids (a) are viscous (b) possess surface tension (c) are compressible (d) possess all the above properties (e) possess none of the above properties. 2) In a static fluid (a) resistance to shear stress is small (b) fluid pressure is zero (c) linear deformation is small (e) viscosity is nil. (d) only normal stresses can exist 3) When the flow parameters at any given instant remain same at every point, then flow is said to be (d) uniform (e) Static. (a) Turbulent (b) Steady state (c) laminar 4) The increase of temperature results in (a) increase in viscosity of gas (b) increase in viscosity of liquid (c)decrease in viscosity of ga (d) decrease in viscosity of liquid (e) (a) and (d) above. 5) Consider the flow in pipe in figure. If P₁ -AP/y. b) The ow direction is from 2 to 1 if AZ <-AP/y. c) T flow is zero if AZ = -AP/y. d) The flow is zero if AZ = AP/y. Q 6) Air flow though the device shown in figure. Select which set of the following conditions is TRUE assuming incompressible non-viscous steady flow ½-1 2 (a) p4 v3 (b) p3> pl; vl > v3 (c) p2 p3; v2> v3 (d) p4 vl (e) p4> pl; v4
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter5: Analysis Of Convection Heat Transfer
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.9P: When a sphere falls freely through a homogeneous fluid, it reaches a terminal velocity at which the...
Related questions
Question
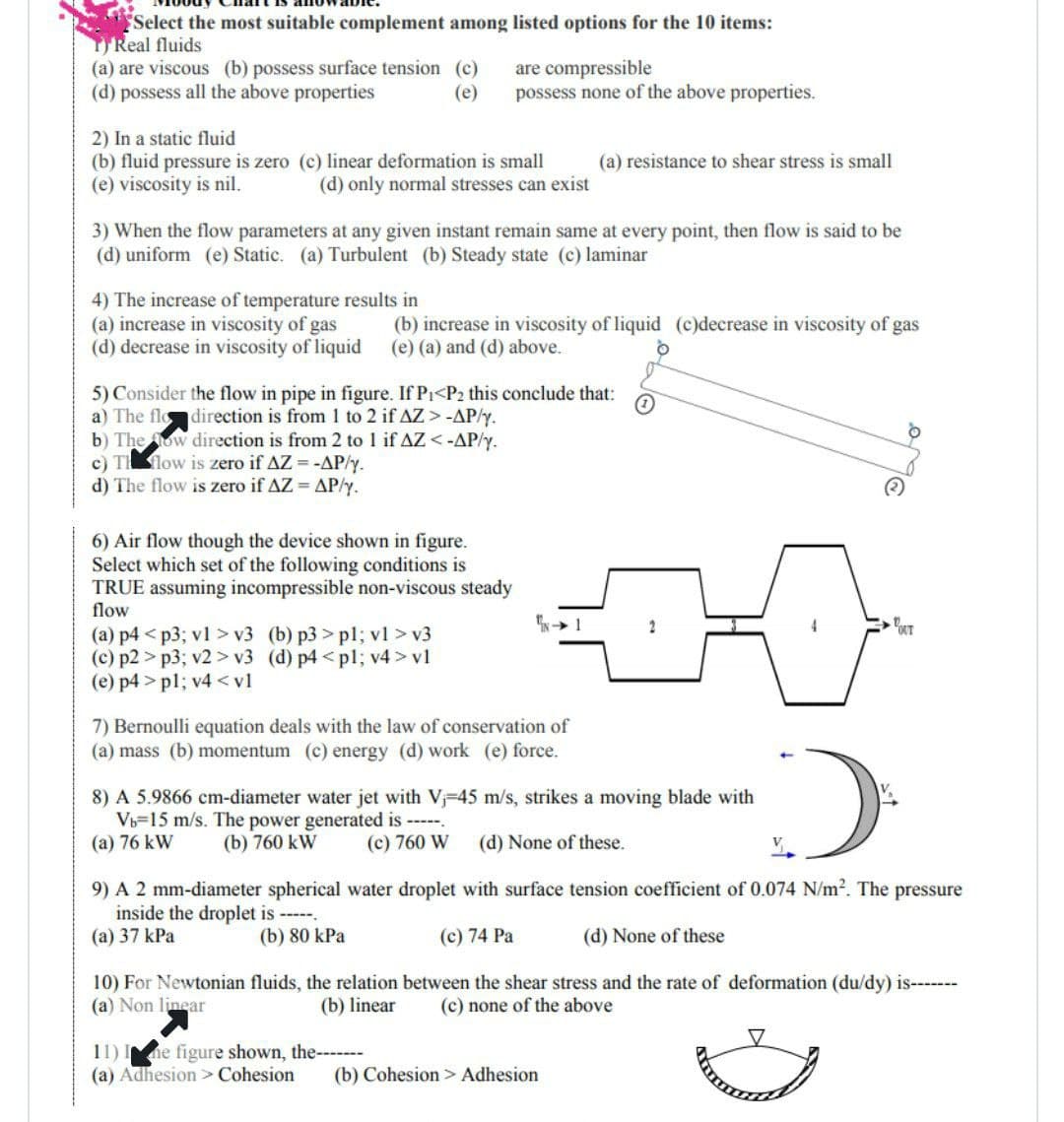
Transcribed Image Text:"Select the most suitable complement among listed options for the 10 items:
TReal fluids
(a) are viscous (b) possess surface tension (c)
are compressible
(d) possess all the above properties
(e)
possess none of the above properties.
2) In a static fluid
(b) fluid pressure is zero (c) linear deformation is small
(a) resistance to shear stress is small
(e) viscosity is nil.
(d) only normal stresses can exist
3) When the flow parameters at any given instant remain same at every point, then flow is said to be
(d) uniform (e) Static. (a) Turbulent (b) Steady state (c) laminar
4) The increase of temperature results in
(a) increase in viscosity of gas
(d) decrease in viscosity of liquid
(b) increase in viscosity of liquid (c)decrease in viscosity of gas
(e) (a) and (d) above.
5) Consider the flow in pipe in figure. If P₁<P2 this conclude that:
1
a) The flo direction is from 1 to 2 if AZ > -AP/y.
b) The ow direction is from 2 to 1 if AZ <-AP/y.
c) T flow is zero if AZ = -AP/y.
d) The flow is zero if AZ = AP/y.
6) Air flow though the device shown in figure.
Select which set of the following conditions is
TRUE assuming incompressible non-viscous steady
flow
-1
2
(a) p4<p3; v1 > v3 (b) p3>pl; vl>v3
(c) p2>p3; v2> v3 (d) p4<pl; v4> vl
(e) p4>pl; v4 <vl
7) Bernoulli equation deals with the law of conservation of
(a) mass (b) momentum (c) energy (d) work (e) force.
8) A 5.9866 cm-diameter water jet with V₁-45 m/s, strikes a moving blade with
Vb-15 m/s. The power generated is -----.
(a) 76 kW
(b) 760 kW
(c) 760 W (d) None of these.
9) A 2 mm-diameter spherical water droplet with surface tension coefficient of 0.074 N/m². The pressure
inside the droplet is ------
(a) 37 kPa
(b) 80 kPa
(c) 74 Pa
(d) None of these
10) For Newtonian fluids, the relation between the shear stress and the rate of deformation (du/dy) is-------
(a) Non linear
(b) linear
(c) none of the above
11) I ne figure shown, the-------
(a) Adhesion > Cohesion (b) Cohesion > Adhesion
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning