Some reasoning would lead to the conclusion that C must be located to the left of A so that the repulsion interaction with B is balanced by the attractive interaction with A. Thus, the distance from A to C can be called x and the distance from B to C can be called 0.6 + x (where x is the absolute value of the coordinate position (in meters). Expressions for FAC and FBC can be written FAC = k• QA • Qc/ (dac)² FBC = k• QB • Qc/ (dec)² and set equal to each other since objects at equilibrium have balanced forces. Thus k• QA • Qc/ (dac)² = k • QB • Qc/ (dec)? The equation can be simplified by canceling k and Qc. Thus, QA/ (dac)? = QB/ (dgc)² Substitute x and 0.6 + x into this equation: QA/x² = QB / (0.6+x)² Then solve for x by taking the square root of each side and substituting the Q values into the equation.
Some reasoning would lead to the conclusion that C must be located to the left of A so that the repulsion interaction with B is balanced by the attractive interaction with A. Thus, the distance from A to C can be called x and the distance from B to C can be called 0.6 + x (where x is the absolute value of the coordinate position (in meters). Expressions for FAC and FBC can be written FAC = k• QA • Qc/ (dac)² FBC = k• QB • Qc/ (dec)² and set equal to each other since objects at equilibrium have balanced forces. Thus k• QA • Qc/ (dac)² = k • QB • Qc/ (dec)? The equation can be simplified by canceling k and Qc. Thus, QA/ (dac)? = QB/ (dgc)² Substitute x and 0.6 + x into this equation: QA/x² = QB / (0.6+x)² Then solve for x by taking the square root of each side and substituting the Q values into the equation.
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter6: Applications Of Newton's Laws
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 74P: In the simple Bohr model of the ground state of the hydrogen atom, the electron travels in a...
Related questions
Question
How do I solve for x in the last step? (steps and given provided in picture)

Transcribed Image Text:Answer:x = -267 cm
Some reasoning would lead to the conclusion that C must be located to the left of A so that the repulsion interaction with B is balanced by
the attractive interaction with A. Thus, the distance from A to C can be called x and the distance from B to C can be called 0.6 + x (where x is
the absolute value of the coordinate position (in meters).
Expressions for FAc and FBC can be written
FAC = k• QA • Qc/(dac)²
FBC = k• QB • Qc/ (dec)?
and set equal to each other since objects at equilibrium have balanced forces. Thus
k• QA • Qc/ (dAC)? = k• QB • Qc/ (dgc)2
The equation can be simplified by canceling k and Qc. Thus,
QA/ (dac)2 = QB/ (dgc)?
Substitute x and 0.6 + x into this equation:
QA/x2 = QB/ (0.6 + x )²
Then solve for x by taking the square root of each side and substituting the Q values into the equation.
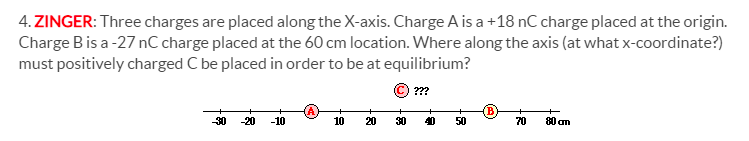
Transcribed Image Text:4. ZINGER: Three charges are placed along the X-axis. Charge A is a +18 nC charge placed at the origin.
Charge Bis a -27 nC charge placed at the 60 cm location. Where along the axis (at what x-coordinate?)
must positively charged C be placed in order to be at equilibrium?
(C) ???
-30
-20
-10
10
20
30
40
50
70
80 am
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University


University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University


University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax