Standard Reduction (Electrode) Potentials at 25 Half-Cell Reaction * (volts) F2(8) + 2 e2F (aq) 287 Ce* (aq) +e Ce (aq) 1.61 Mn0, (aq) + BH'(aq) +5e Mn"( "(aq) + 4 H20(1) 1.51 Cla(g) +2e -2 C (aq) 1.36 Cr20, (aq) + 14 H'(aq) - 6e2 Cr*"(aq) + 7 H20() 1.33 Oz() + 4 H'(aq) + 4e2 H20(1) 1.229 Br20) + 2 e2 Br (aq) 1.08 NO3 (aq) + 4 H'(aq) + 3eNO(g) + 2 H20() Hg"(aq) 0.96 2 Hg (aq) + 2e 0.920 Hg"(aq) + 2 e- Hg(1) 0.855 Ag (aq) +e Ag(s) 0.799 Hg2" (aq) - 2e-2 Hg(1) 0.789 Fe" (aq) +e Fe"(ag) 0.771 12(s) + 2e 21 (aq) 0.535 Fe(CN)"(aq) + e Fe(CN), (aq) 0.48 Cu (aq) + 2eCu(s) 0.337 Cu"(aq) +e- Cu (aq) 0.153 S(s) + 2 H'(aq) + 2 e H2S(aq) 0.14 2H'(aq) + 2e-H2(8) 0.0000 Pb (aq) + 2e- Ph(s) -0126 Sn (aq) + 2 e Sn(s) -014 Ni (aq) + 2 e- Ni(s) -0.25 Co (aq) + 2 e Co(s) -0.28 "(aq) + 2e Cd(s) -0.403 Cr"(aq) +e "(aq) -041 Fe"(aq) + 2 e Fe(s) -044 Cr"(aq) +3e-Cr(s) -0.74 Zn"(aq) +2 e- Zn(s) -0.763 2 H20() +2e Hz(z) + 2 OH (aq) -0.83 Mn"(aq) + 2e - Mn(s) -1.18 A" (aq) + 3e- Al(s) -1.66 Mg (aq) + 2 e- Mg(s) -237 Na (aq) +e Na(s) -2714 K' (aq) +e K(3) -2925 Li'(aq) +e- LI(s) -3.045 References Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Enter electrons as e. Use smallest possible integer coefficients. If a box is not needed, leave it blank. A voltaic cell is constructed from a standard Co*|Co half cell (E°red = -0.280V) and a standard Zn²“|Zn half cell (E°red = -0.763V). The anode reaction is: The cathode reaction is: The spontaneous cell reaction is: The cell voltage is V. Submit Answer
Standard Reduction (Electrode) Potentials at 25 Half-Cell Reaction * (volts) F2(8) + 2 e2F (aq) 287 Ce* (aq) +e Ce (aq) 1.61 Mn0, (aq) + BH'(aq) +5e Mn"( "(aq) + 4 H20(1) 1.51 Cla(g) +2e -2 C (aq) 1.36 Cr20, (aq) + 14 H'(aq) - 6e2 Cr*"(aq) + 7 H20() 1.33 Oz() + 4 H'(aq) + 4e2 H20(1) 1.229 Br20) + 2 e2 Br (aq) 1.08 NO3 (aq) + 4 H'(aq) + 3eNO(g) + 2 H20() Hg"(aq) 0.96 2 Hg (aq) + 2e 0.920 Hg"(aq) + 2 e- Hg(1) 0.855 Ag (aq) +e Ag(s) 0.799 Hg2" (aq) - 2e-2 Hg(1) 0.789 Fe" (aq) +e Fe"(ag) 0.771 12(s) + 2e 21 (aq) 0.535 Fe(CN)"(aq) + e Fe(CN), (aq) 0.48 Cu (aq) + 2eCu(s) 0.337 Cu"(aq) +e- Cu (aq) 0.153 S(s) + 2 H'(aq) + 2 e H2S(aq) 0.14 2H'(aq) + 2e-H2(8) 0.0000 Pb (aq) + 2e- Ph(s) -0126 Sn (aq) + 2 e Sn(s) -014 Ni (aq) + 2 e- Ni(s) -0.25 Co (aq) + 2 e Co(s) -0.28 "(aq) + 2e Cd(s) -0.403 Cr"(aq) +e "(aq) -041 Fe"(aq) + 2 e Fe(s) -044 Cr"(aq) +3e-Cr(s) -0.74 Zn"(aq) +2 e- Zn(s) -0.763 2 H20() +2e Hz(z) + 2 OH (aq) -0.83 Mn"(aq) + 2e - Mn(s) -1.18 A" (aq) + 3e- Al(s) -1.66 Mg (aq) + 2 e- Mg(s) -237 Na (aq) +e Na(s) -2714 K' (aq) +e K(3) -2925 Li'(aq) +e- LI(s) -3.045 References Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Enter electrons as e. Use smallest possible integer coefficients. If a box is not needed, leave it blank. A voltaic cell is constructed from a standard Co*|Co half cell (E°red = -0.280V) and a standard Zn²“|Zn half cell (E°red = -0.763V). The anode reaction is: The cathode reaction is: The spontaneous cell reaction is: The cell voltage is V. Submit Answer
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter17: Electrochemistry And Its Applications
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 38QRT
Related questions
Question
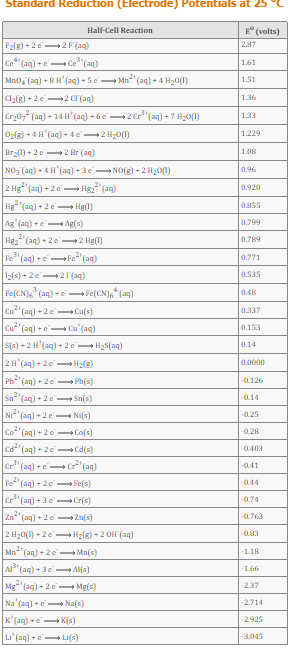
Transcribed Image Text:Standard Reduction (Electrode) Potentials at 25
Half-Cell Reaction
* (volts)
F2(8) + 2 e2F (aq)
287
Ce* (aq) +e Ce (aq)
1.61
Mn0, (aq) + BH'(aq) +5e Mn"(
"(aq) + 4 H20(1)
1.51
Cla(g) +2e -2 C (aq)
1.36
Cr20, (aq) + 14 H'(aq) - 6e2 Cr*"(aq) + 7 H20()
1.33
Oz() + 4 H'(aq) + 4e2 H20(1)
1.229
Br20) + 2 e2 Br (aq)
1.08
NO3 (aq) + 4 H'(aq) + 3eNO(g) + 2 H20()
Hg"(aq)
0.96
2 Hg (aq) + 2e
0.920
Hg"(aq) + 2 e- Hg(1)
0.855
Ag (aq) +e Ag(s)
0.799
Hg2" (aq) - 2e-2 Hg(1)
0.789
Fe" (aq) +e Fe"(ag)
0.771
12(s) + 2e 21 (aq)
0.535
Fe(CN)"(aq) + e Fe(CN), (aq)
0.48
Cu
(aq) + 2eCu(s)
0.337
Cu"(aq) +e- Cu (aq)
0.153
S(s) + 2 H'(aq) + 2 e H2S(aq)
0.14
2H'(aq) + 2e-H2(8)
0.0000
Pb (aq) + 2e- Ph(s)
-0126
Sn
(aq) + 2 e Sn(s)
-014
Ni (aq) + 2 e- Ni(s)
-0.25
Co (aq) + 2 e Co(s)
-0.28
"(aq) + 2e Cd(s)
-0.403
Cr"(aq) +e "(aq)
-041
Fe"(aq) + 2 e Fe(s)
-044
Cr"(aq) +3e-Cr(s)
-0.74
Zn"(aq) +2 e- Zn(s)
-0.763
2 H20() +2e Hz(z) + 2 OH (aq)
-0.83
Mn"(aq) + 2e - Mn(s)
-1.18
A" (aq) + 3e- Al(s)
-1.66
Mg (aq) + 2 e- Mg(s)
-237
Na (aq) +e Na(s)
-2714
K' (aq) +e K(3)
-2925
Li'(aq) +e- LI(s)
-3.045
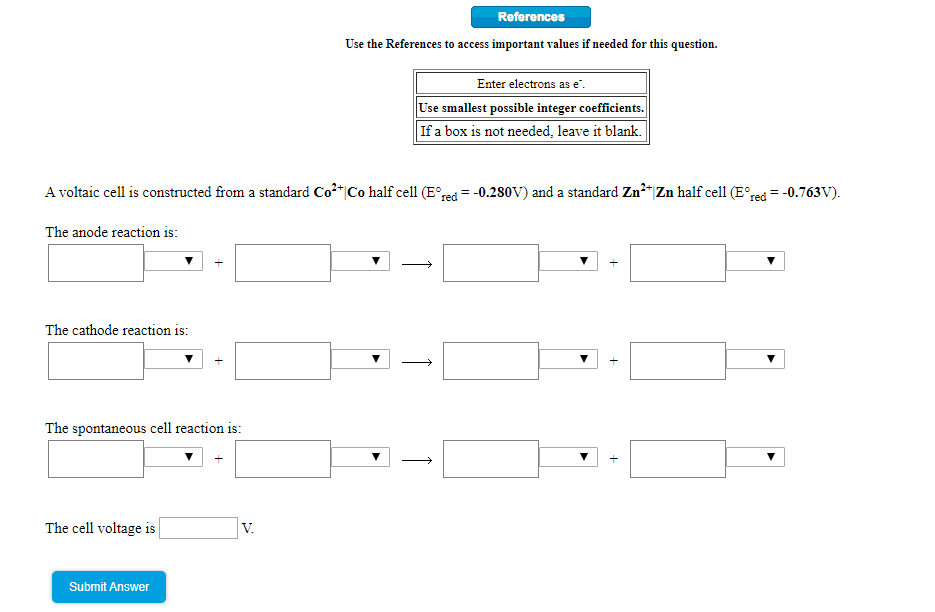
Transcribed Image Text:References
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
Enter electrons as e.
Use smallest possible integer coefficients.
If a box is not needed, leave it blank.
A voltaic cell is constructed from a standard Co*|Co half cell (E°red = -0.280V) and a standard Zn²“|Zn half cell (E°red = -0.763V).
The anode reaction is:
The cathode reaction is:
The spontaneous cell reaction is:
The cell voltage is
V.
Submit Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning