State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test. Ho: ? v H1:? v Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. O left-tailed O right-tailed O two-tailed Should the standard normal (z) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test? O The Student's t distribution should be used O The standard normal (z) distribution should be used
State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test. Ho: ? v H1:? v Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. O left-tailed O right-tailed O two-tailed Should the standard normal (z) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test? O The Student's t distribution should be used O The standard normal (z) distribution should be used
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.6: Summarizing Categorical Data
Problem 30PPS
Related questions
Question
100%
#31). Both pictures are the same problem.
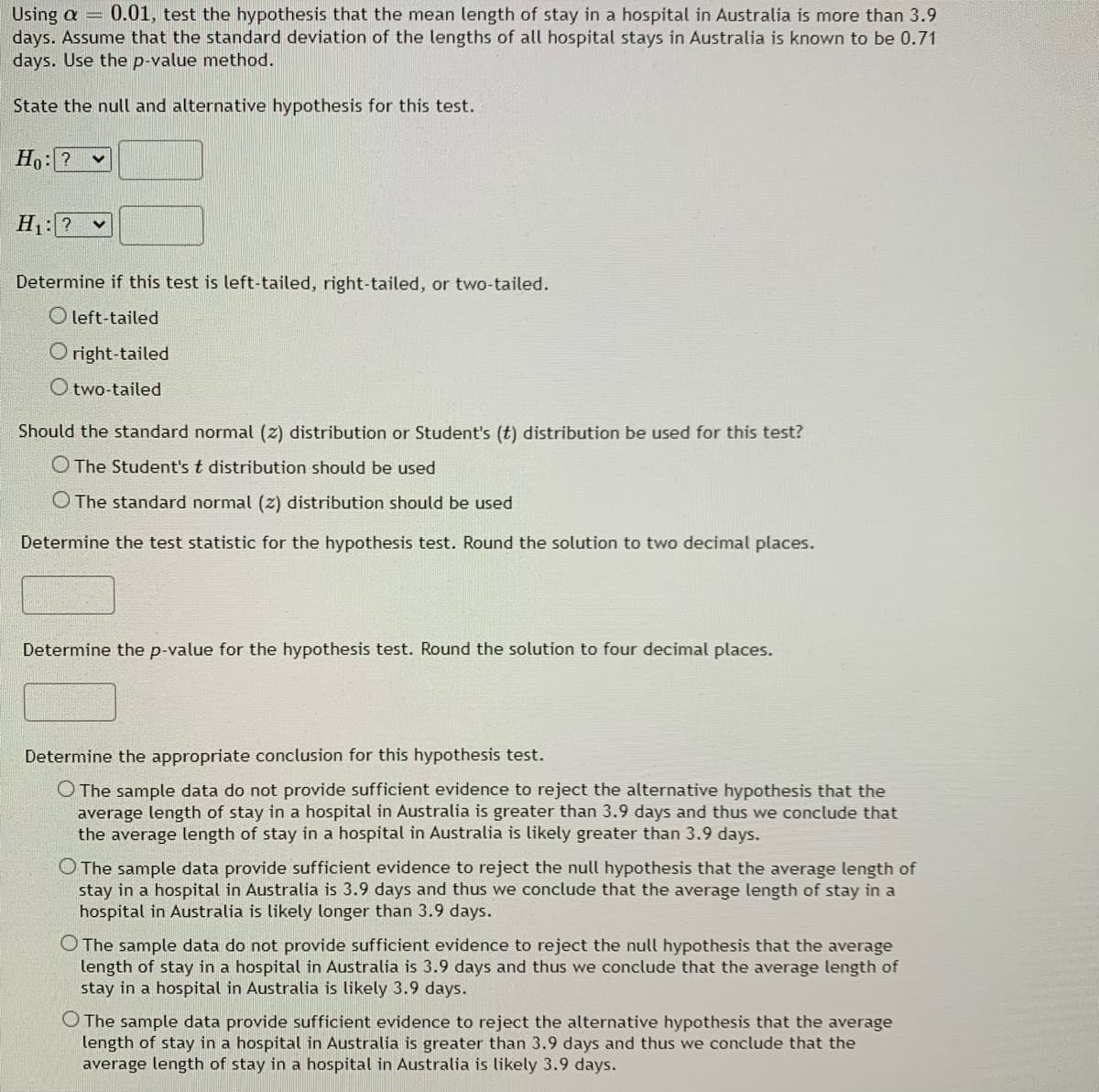
Transcribed Image Text:0.01, test the hypothesis that the mean length of stay in a hospital in Australia is more than 3.9
Using a =
days. Assume that the standard deviation of the lengths of all hospital stays in Australia is known to be 0.71
days. Use the p-value method.
State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.
Ho:?
H: ? v
Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed.
O left-tailed
right-tailed
O two-tailed
Should the standard normal (z) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test?
O The Student's t distribution should be used
O The standard normal (z) distribution should be used
Determine the test statistic for the hypothesis test. Round the solution to two decimal places.
Determine the p-value for the hypothesis test. Round the solution to four decimal places.
Determine the appropriate conclusion for this hypothesis test.
O The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the alternative hypothesis that the
average length of stay in a hospital in Australia is greater than 3.9 days and thus we conclude that
the average length of stay in a hospital in Australia is likely greater than 3.9 days.
O The sample data provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis that the average length of
stay in a hospital in Australia is 3.9 days and thus we conclude that the average length of stay in a
hospital in Australia is likely longer than 3.9 days.
O The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis that the average
length of stay in a hospital in Australia is 3.9 days and thus we conclude that the average length of
stay in a hospital in Australia is likely 3.9 days.
O The sample data provide sufficient evidence to reject the alternative hypothesis that the average
length of stay in a hospital in Australia is greater than 3.9 days and thus we conclude that the
average length of stay in a hospital in Australia is likely 3.9 days.
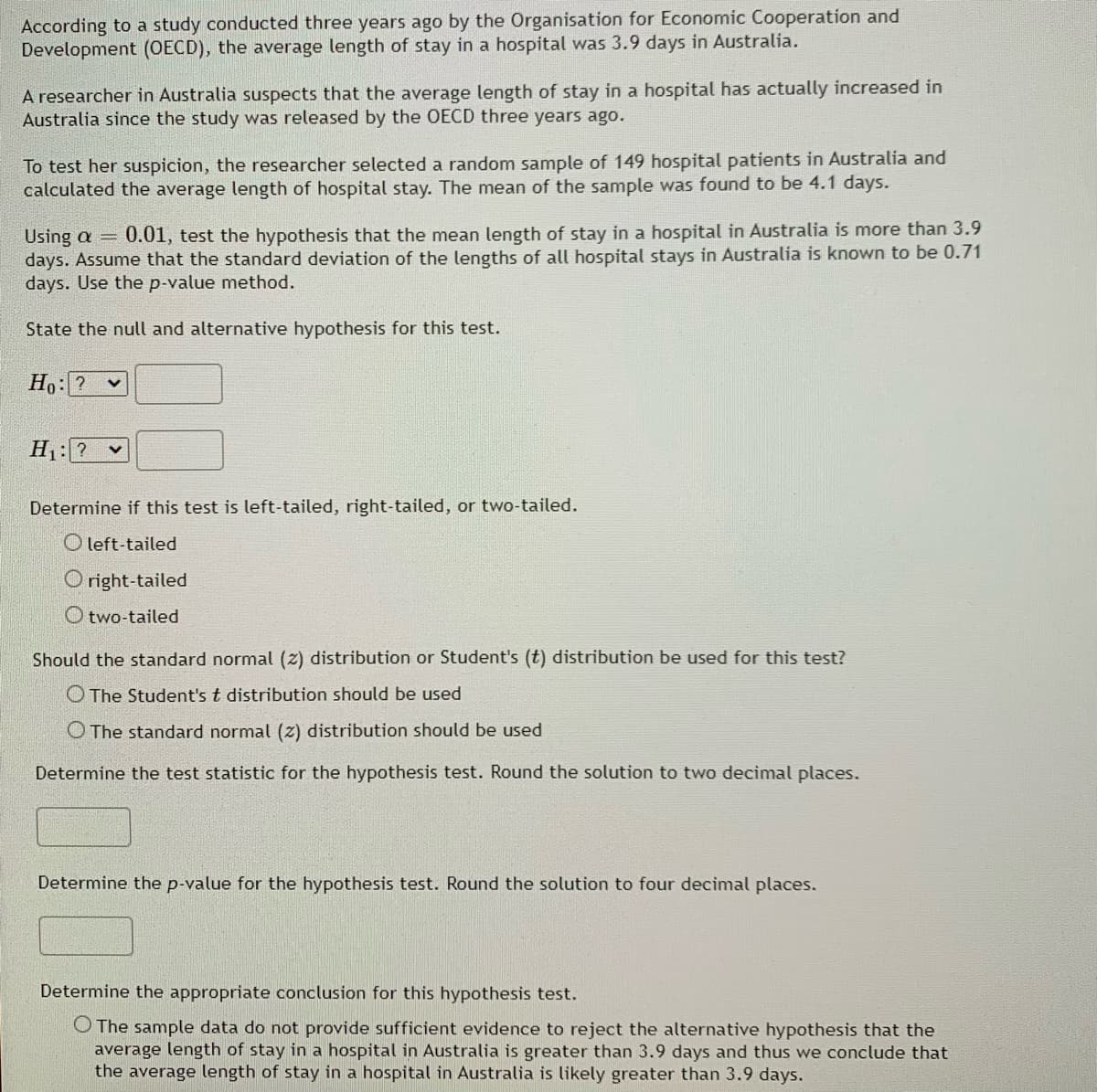
Transcribed Image Text:According to a study conducted three years ago by the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and
Development (OECD), the average length of stay in a hospital was 3.9 days in Australia.
A researcher in Australia suspects that the average length of stay in a hospital has actually increased in
Australia since the study was released by the OECD three years ago.
To test her suspicion, the researcher selected a random sample of 149 hospital patients in Australia and
calculated the average length of hospital stay. The mean of the sample was found to be 4.1 days.
0.01, test the hypothesis that the mean length of stay in a hospital in Australia is more than 3.9
Using a =
days. Assume that the standard deviation of the lengths of all hospital stays in Australia is known to be 0.71
days. Use the p-value method.
State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.
Ho: ?
H1:? v
Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed.
O left-tailed
Oright-tailed
O two-tailed
Should the standard normal (z) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test?
O The Student's t distribution should be used
O The standard normal (z) distribution should be used
Determine the test statistic for the hypothesis test. Round the solution to two decimal places.
Determine the p-value for the hypothesis test. Round the solution to four decimal places.
Determine the appropriate conclusion for this hypothesis test.
O The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the alternative hypothesis that the
average length of stay in a hospital in Australia is greater than 3.9 days and thus we conclude that
the average length of stay in a hospital in Australia is likely greater than 3.9 days.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning