Physical Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Chapter20: Kinetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20.80E
Related questions
Question
State. explain. and justify the steady-state approximation.
Expert Solution
Step 1
The steady state approximation is applied under those condition in which all steps that involve in the reaction have the approximately same speed or it is hard to predict the slowest step. Consider the hypothetical reaction, shown below where R is the reactant, R* is the radical, and P is the product.
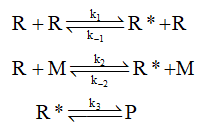
Step 2
In the above reaction mechanism, R* is intermediate in the reaction mechanism whose life spam is very short and according to steady state approximation, the intermediate is consumed as fast as it is produced. So, on applying steady state approximation to R*, the concentration of R* is calculated as shown below.
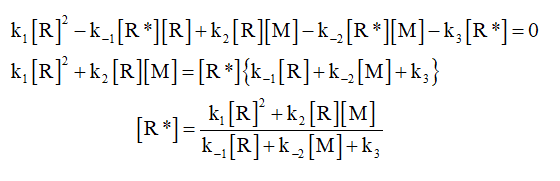
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning