Suppose a random sample of 100 observations from a binomial population gives a value of p=0.48 and you wish to test the null hypothesis that the population parameter p is equal to 0.40 against the alternative hypothesis that p is greater than 0.40. Complete parts a through c Noting that p=0.48, what does your intuition tell you? Does the value of pappear to contradict the null hypothesis? OA. Yes, because p is very close to 0.40. OB. Yes, because p satisfies H₂: p>0.40 and is very close to 0.40. OC. No, because p is very close to 0.40. OD. Yes, because p satisfies H₂: p>0.40 and is not very close to 0.40. . Use the large-sample z-test to test H₂: p=0.40 against the alternative hypothesis, H₂: p>0.40. Use a=0.01. fa=0.01, find the rejection region for the test. Choose the correct answer below. OA. z<-2.575 OC. z<-2.575 or z>2.575 OB. z<-2.33 or z>2.33 OD. z<-2.33 OF. z>2.33 OE. z>2.575 Calculate the value of the test statistic (Round to two decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion of the test? OA. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is not in the rejection region. OB. Reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is not in the rejection region. OC. Reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is in the rejection region. OD. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is in the rejection region. Find and interpret the observed significance level of the test conducted in part b The p-value of the test is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What does this p-value mean? OA. Assuming p=0.40, the p-value is the probability that p is greater than 0.48 for a random sample of 100 observations. OB. Assuming p=0.48, the p-value is the probability that p is greater than 0.48 for a random sample of 100 observations OC. Assuming p=0.40, the p-value is the probability that is greater than 0.40 for a random sample of 100 observations. OD. Assuming p=0.48, the p-value is the probability that is greater than 0.40 for a random sample of 100 observations.
Suppose a random sample of 100 observations from a binomial population gives a value of p=0.48 and you wish to test the null hypothesis that the population parameter p is equal to 0.40 against the alternative hypothesis that p is greater than 0.40. Complete parts a through c Noting that p=0.48, what does your intuition tell you? Does the value of pappear to contradict the null hypothesis? OA. Yes, because p is very close to 0.40. OB. Yes, because p satisfies H₂: p>0.40 and is very close to 0.40. OC. No, because p is very close to 0.40. OD. Yes, because p satisfies H₂: p>0.40 and is not very close to 0.40. . Use the large-sample z-test to test H₂: p=0.40 against the alternative hypothesis, H₂: p>0.40. Use a=0.01. fa=0.01, find the rejection region for the test. Choose the correct answer below. OA. z<-2.575 OC. z<-2.575 or z>2.575 OB. z<-2.33 or z>2.33 OD. z<-2.33 OF. z>2.33 OE. z>2.575 Calculate the value of the test statistic (Round to two decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion of the test? OA. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is not in the rejection region. OB. Reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is not in the rejection region. OC. Reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is in the rejection region. OD. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is in the rejection region. Find and interpret the observed significance level of the test conducted in part b The p-value of the test is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What does this p-value mean? OA. Assuming p=0.40, the p-value is the probability that p is greater than 0.48 for a random sample of 100 observations. OB. Assuming p=0.48, the p-value is the probability that p is greater than 0.48 for a random sample of 100 observations OC. Assuming p=0.40, the p-value is the probability that is greater than 0.40 for a random sample of 100 observations. OD. Assuming p=0.48, the p-value is the probability that is greater than 0.40 for a random sample of 100 observations.
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter9: Counting And Probability
Section9.3: Binomial Probability
Problem 2E: If a binomial experiment has probability p success, then the probability of failure is...
Related questions
Question
Q5 solve all parts plzz
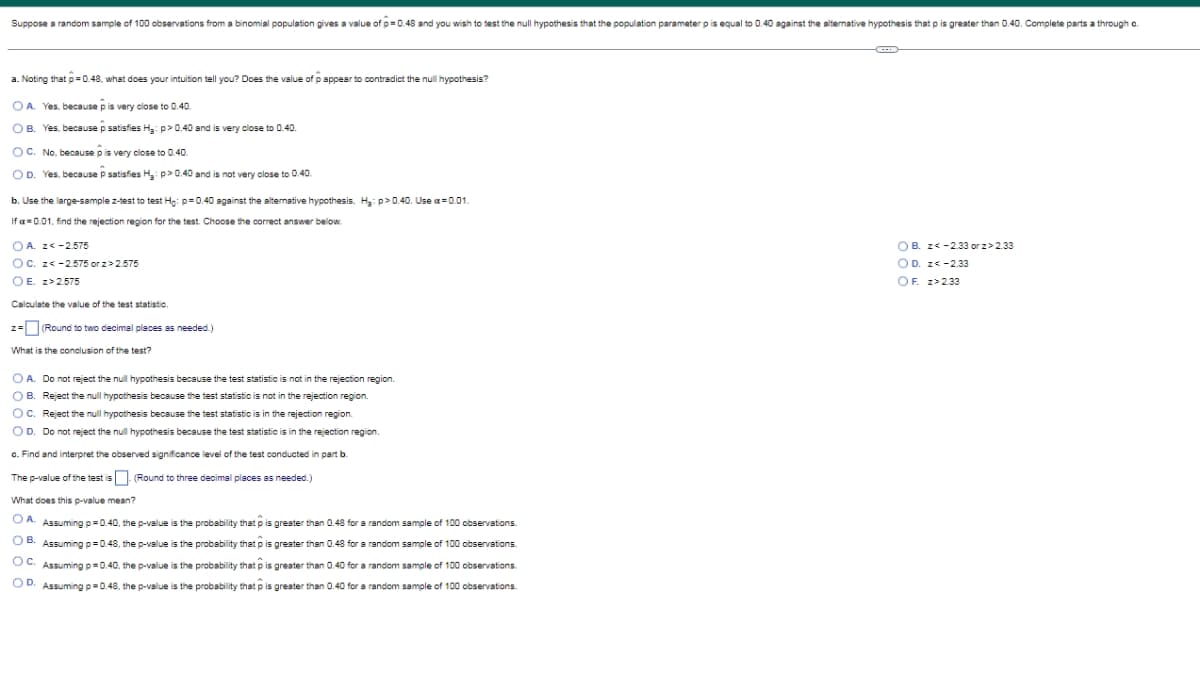
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose a random sample of 100 observations from a binomial population gives a value of p=0.48 and you wish to test the null hypothesis that the population parameter p is equal to 0.40 against the alternative hypothesis that p is greater than 0.40. Complete parts a through c.
a. Noting that p=0.48, what does your intuition tell you? Does the value of pappear to contradict the null hypothesis?
OA. Yes, because p is very close to 0.40.
OB. Yes, because p satisfies H₂: p>0.40 and is very close to 0.40.
OC. No, because p is very close to 0.40.
OD. Yes, because P satisfies H₂: p>0.40 and is not very close to 0.40.
b. Use the large-sample z-test to test Ho: p=0.40 against the alternative hypothesis, H₂: p>0.40. Use a=0.01.
If = 0.01, find the rejection region for the test. Choose the correct answer below.
OA. z<-2.575
OC. z<-2.575 or z>2.575
OB. z< -2.33 or z>2.33
OD. z<-2.33
OF. z>2.33
OE. z>2.575
Calculate the value of the test statistic.
z = (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
What is the conclusion of the test?
O A. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is not in the rejection region.
OB. Reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is not in the rejection region.
OC. Reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is in the rejection region.
OD. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the test statistic is in the rejection region.
c. Find and interpret the observed significance level of the test conducted in part b.
The p-value of the test is
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
What does this p-value mean?
OA. Assuming p=0.40, the p-value is the probability that is greater than 0.48 for a random sample of 100 observations.
is greater than 0.48 for a random sample of 100 observations.
OB. Assuming p=0.48, the p-value is the probability that
OC. Assuming p=0.40, the p-value is the probability that
OD. Assuming p=0.48, the p-value is the probability that is greater than 0.40 for a random sample of 100 observations.
is greater than 0.40 for a random sample of 100 observations.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning