Suppose an economy is in long-run equilibrium. The central bank raises the money supply by 5 percent. Use your diagram to show what happens to output and the price level as the economy moves from the initial to the new short-run equilibrium. Price Level LRAS AS₁ Quantity of Output AS2 Aggregate Demand Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply
Suppose an economy is in long-run equilibrium. The central bank raises the money supply by 5 percent. Use your diagram to show what happens to output and the price level as the economy moves from the initial to the new short-run equilibrium. Price Level LRAS AS₁ Quantity of Output AS2 Aggregate Demand Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply
Economics (MindTap Course List)
13th Edition
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Roger A. Arnold
Chapter9: Classical Macroeconomics And The Self Regulating Economy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14QP
Related questions
Question
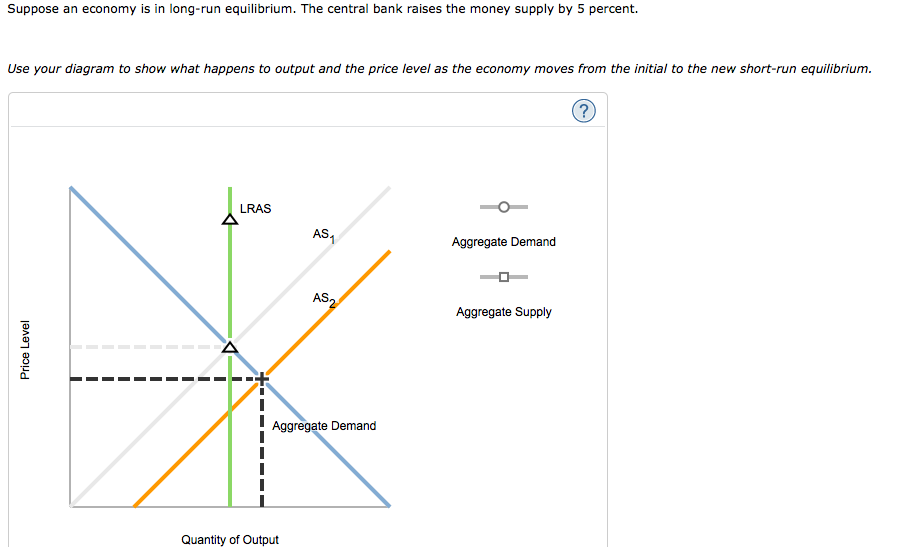
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose an economy is in long-run equilibrium. The central bank raises the money supply by 5 percent.
Use your diagram to show what happens to output and the price level as the economy moves from the initial to the new short-run equilibrium.
Price Level
LRAS
-------
AS1
Quantity of Output
AS2
Aggregate Demand
Aggregate Demand
Aggregate Supply
(?)

Transcribed Image Text:Now adjust the graph to show the new long-run equilibrium.
What causes the economy to move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium?
The government must increase spending to increase aggregate demand.
Nominal wages, prices, and perceptions will adjust upward to this new price level.
The government must increase taxes to curb aggregate demand.
Nominal wages, prices, and perceptions will adjust downward to this new price level.
According to the sticky-wage theory of aggregate supply, nominal wages at the initial equilibrium are greater than nominal wages at the
short-run equilibrium, and equal to
nominal wages at the long-run equilibrium. Real wages at the initial equilibrium
are greater than nominal wages at the short-run equilibrium, and greater than nominal wages at the long-run equilibrium. Judging by the
impact of the money supply on nominal and real wages, this analysis is not consistent with the proposition that money has real effects in the
short run but is neutral in the long run.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 8 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

