Suppose that Ruby's employer offers a retirement plan. Ruby decides to invest $350 per month into the account. The interest is compounded monthly. Historically, the account has earned 7% APR How much will be in his account if she retires in 25 years? $350 represents the .(payments or principal). In the TVM calculator, we put this amount in PMT (or payments). Remember that amounts you pay are negative, and amounts you receive are positive. Since you are putting in $350, you are (paying or receiving) money, so the number you put into PMT is The APR of the account is percentage and not a decimal. In the TVM calculator, we put the APR in as a
Suppose that Ruby's employer offers a retirement plan. Ruby decides to invest $350 per month into the account. The interest is compounded monthly. Historically, the account has earned 7% APR How much will be in his account if she retires in 25 years? $350 represents the .(payments or principal). In the TVM calculator, we put this amount in PMT (or payments). Remember that amounts you pay are negative, and amounts you receive are positive. Since you are putting in $350, you are (paying or receiving) money, so the number you put into PMT is The APR of the account is percentage and not a decimal. In the TVM calculator, we put the APR in as a
Chapter1: Making Economics Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1QTC
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:udiasirois1122/Xv7zYW5RnILBBINV2A9egx/unit-4-project-tvm-calculator-pdf?pg=7
-Sign-
At
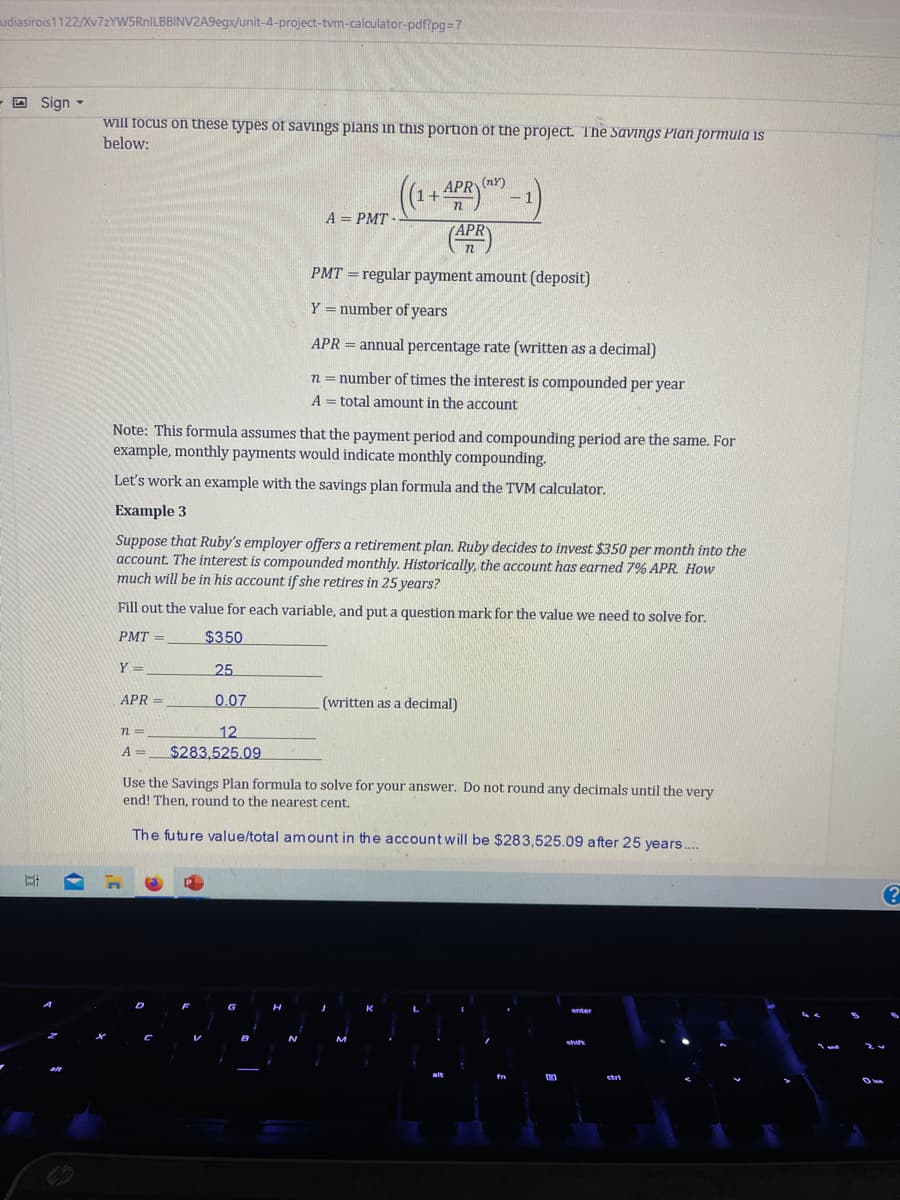
will focus on these types of savings plans in this portion of the project. The Savings Plan formula is
below:
Y =_
APR=
A = PMT-
n =
A =
Note: This formula assumes that the payment period and compounding period are the same. For
example, monthly payments would indicate monthly compounding.
Let's work an example with the savings plan formula and the TVM calculator.
Example 3
Suppose that Ruby's employer offers a retirement plan. Ruby decides to invest $350 per month into the
account. The interest is compounded monthly. Historically, the account has earned 7% APR. How
much will be in his account if she retires in 25 years?
Fill out the value for each variable, and put a question mark for the value we need to solve for.
PMT=
$350
25
0.07
12
$283,525.09
((1+ APR-1)
(APR)
PMT= regular payment amount (deposit)
Y = number of years
APR = annual percentage rate (written as a decimal)
n = number of times the interest is compounded per year
A total amount in the account
=
(written as a decimal)
Use the Savings Plan formula to solve for your answer. Do not round any decimals until the very
end! Then, round to the nearest cent.
The future value/total amount in the account will be $283,525.09 after 25 years....
M
enter
shift
ctri
?
Transcribed Image Text:Sign -
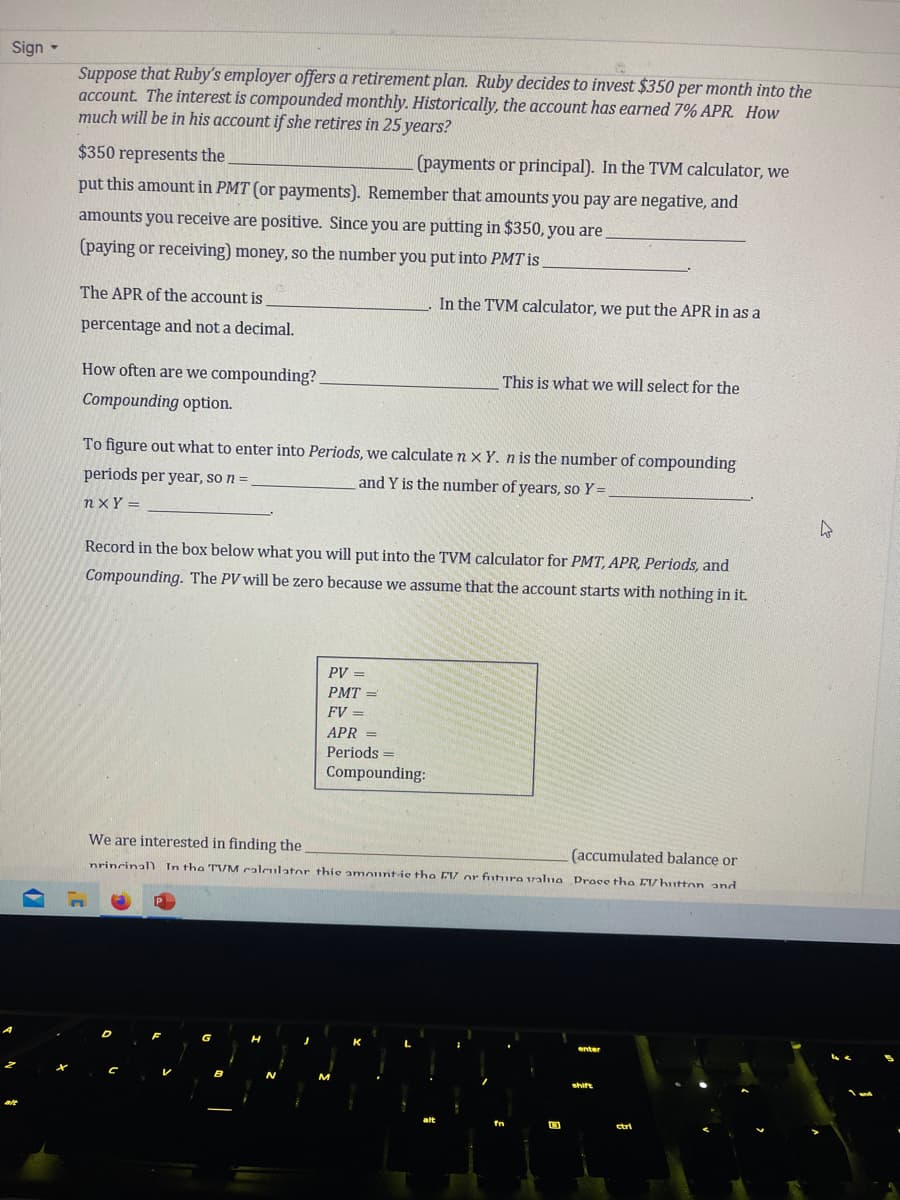
Suppose that Ruby's employer offers a retirement plan. Ruby decides to invest $350 per month into the
account. The interest is compounded monthly. Historically, the account has earned 7% APR. How
much will be in his account if she retires in 25 years?
$350 represents the
(payments or principal). In the TVM calculator, we
put this amount in PMT (or payments). Remember that amounts you pay are negative, and
amounts you receive are positive. Since you are putting in $350, you are
(paying or receiving) money, so the number you put into PMT is
The APR of the account is
percentage and not a decimal.
How often are we compounding?
Compounding option.
In the TVM calculator, we put the APR in as a
This is what we will select for the
To figure out what to enter into Periods, we calculate nx Y. n is the number of compounding
periods per year, so n =
and Y is the number of years, so Y =
nxy=
PV =
PMT=
FV =
APR =
Periods =
Compounding:
Record in the box below what you will put into the TVM calculator for PMT, APR, Periods, and
Compounding. The PV will be zero because we assume that the account starts with nothing in it.
We are interested in finding the
(accumulated balance or
nrincinal) In the TVM calculator this amount ie the EV or futura valna Prace tha EVhutton and
shift
ctri
4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-…
Economics
ISBN:
9781259290619
Author:
Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education