Tanufacturing is a cost center and the two sales departments are profit centers. full cost of each roll of carpeting produced (including fully absorbed overhead) is transferred to the sales department ordering the carpet. The evaluation of the sales departments includes the fully absorbed cost of each roll as the transfer price. The current manufacturing plant is operating at capacity. A new plant is being built that will more than double capacity. Within two years, management believes that its businesses will grow such that most of the excess capacity will be eliminated. When the new plant comes online, the plan is for one plant to produce exclusively commercial carpeting and the other to produce exclusively residential carpeting. This change will simplify scheduling, ordering, and inventory control in each plant. It will also create some economies of scale by producing longer mill runs. Nevertheless, it will take a couple of years before these economies of scale can be realized. Each mill produces carpeting in four-meter-wide rolls of up to 100 meters in length. The output of each mill is measured in terms of meters of four-meter rolls produced. Overhead is assigned to carpet rolls using carpet meters produced in the mill. The cost structure of each plant is as follows: Old Plant New Plant Normal machine hours per year 6,000 5,000 Normal carpet meters per hour 1,000 1,400 Normal capacity 6,000,000 meters 7,000,000 meters Annual manufacturing overhead costs excluding accounting depreciation €15,000,000 €21,000,000 Accounting depreciation per year € 6,000,000 €21,000,000 Karsten's new mill will run at higher speed and therefore produce more meters of carpet per hour. Moreover, the new mill will use 15 percent less direct materials and direct labor because the new machines, being more automated, produce less scrap and 497
Tanufacturing is a cost center and the two sales departments are profit centers. full cost of each roll of carpeting produced (including fully absorbed overhead) is transferred to the sales department ordering the carpet. The evaluation of the sales departments includes the fully absorbed cost of each roll as the transfer price. The current manufacturing plant is operating at capacity. A new plant is being built that will more than double capacity. Within two years, management believes that its businesses will grow such that most of the excess capacity will be eliminated. When the new plant comes online, the plan is for one plant to produce exclusively commercial carpeting and the other to produce exclusively residential carpeting. This change will simplify scheduling, ordering, and inventory control in each plant. It will also create some economies of scale by producing longer mill runs. Nevertheless, it will take a couple of years before these economies of scale can be realized. Each mill produces carpeting in four-meter-wide rolls of up to 100 meters in length. The output of each mill is measured in terms of meters of four-meter rolls produced. Overhead is assigned to carpet rolls using carpet meters produced in the mill. The cost structure of each plant is as follows: Old Plant New Plant Normal machine hours per year 6,000 5,000 Normal carpet meters per hour 1,000 1,400 Normal capacity 6,000,000 meters 7,000,000 meters Annual manufacturing overhead costs excluding accounting depreciation €15,000,000 €21,000,000 Accounting depreciation per year € 6,000,000 €21,000,000 Karsten's new mill will run at higher speed and therefore produce more meters of carpet per hour. Moreover, the new mill will use 15 percent less direct materials and direct labor because the new machines, being more automated, produce less scrap and 497
Accounting (Text Only)
26th Edition
ISBN:9781285743615
Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Chapter21: Cost Behavior And Cost-volume-profit Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21.4CP: Variable costs and activity bases in decision making The owner of Warwick Printing, a printing...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:AIP 10.7 Overhead Costs from a New Factory
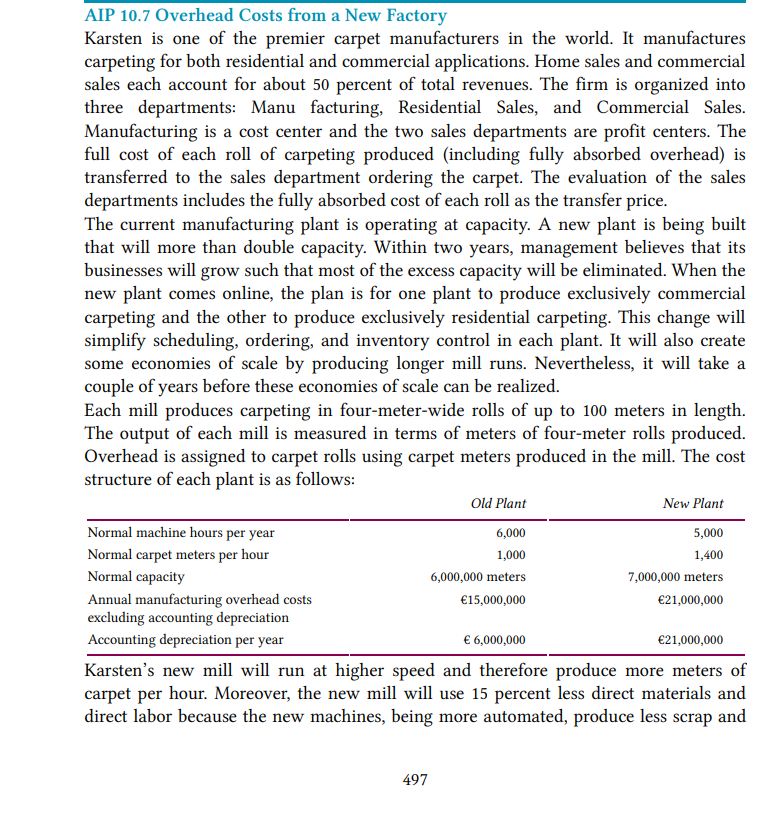
Karsten is one of the premier carpet manufacturers in the world. It manufactures
carpeting for both residential and commercial applications. Home sales and commercial
sales each account for about 50 percent of total revenues. The firm is organized into
three departments: Manu facturing, Residential Sales, and Commercial Sales.
Manufacturing is a cost center and the two sales departments are profit centers. The
full cost of each roll of carpeting produced (including fully absorbed overhead) is
transferred to the sales department ordering the carpet. The evaluation of the sales
departments includes the fully absorbed cost of each roll as the transfer price.
The current manufacturing plant is operating at capacity. A new plant is being built
that will more than double capacity. Within two years, management believes that its
businesses will grow such that most of the excess capacity will be eliminated. When the
new plant comes online, the plan is for one plant to produce exclusively commercial
carpeting and the other to produce exclusively residential carpeting. This change will
simplify scheduling, ordering, and inventory control in each plant. It will also create
some economies of scale by producing longer mill runs. Nevertheless, it will take a
couple of years before these economies of scale can be realized.
Each mill produces carpeting in four-meter-wide rolls of up to 100 meters in length.
The output of each mill is measured in terms of meters of four-meter rolls produced.
Overhead is assigned to carpet rolls using carpet meters produced in the mill. The cost
structure of each plant is as follows:
Old Plant
New Plant
Normal machine hours per year
6,000
5,000
Normal carpet meters per hour
Normal capacity
1,000
1,400
6,000,000 meters
7,000,000 meters
Annual manufacturing overhead costs
excluding accounting depreciation
€15,000,000
€21,000,000
Accounting depreciation per year
€ 6,000,000
€21,000,000
Karsten's new mill will run at higher speed and therefore produce more meters of
carpet per hour. Moreover, the new mill will use 15 percent less direct materials and
direct labor because the new machines, being more automated, produce less scrap and
497

Transcribed Image Text:require less direct labor per meter. A job sheet run at the old mill is as follows:
Carpet A6106: (100-meter roll)
Direct materials
€ 800
Direct labor
600
Direct costs
€1,400
Although the new mill has lower direct costs of carpet production than the old mill
does, the new facility's higher overhead costs per meter have the sales department
managers worried. They already are lobbying senior management to have the old mill
assigned to produce their products. The Commercial Sales department manager argues,
“More of my customers are located closer to the old plant than are the Residential Sales
department's customers. Therefore, to economize on transportation costs, my products
should be produced in the old plant." The Residential Sales department manager
counters with the argument, "Transportation costs are less than 1 percent of total
revenues. The new plant should produce commercial products because we expect new
commercial products to use more synthetic materials and the latest technology at the
new mill is better able to adapt to the new synthetics." Senior management is worried
about how to deal with the two sales department managers' reluctance to have their
products produced at the new plant. One suggestion put forth is for each plant to
produce about half of Commercial Sales products and about half of Residential Sales
products. However, this proposal would eliminate most of the economies of scale that
would result from specializing production in each plant to one market segment.
a. Calculate the overhead rates for the new plant and the old plant, where overhead
is assigned to carpet based on normal meters per year.
b. Calculate the expected total cost of carpet A6106, if run at the old mill and if run
at the new mill.
c. Put forth two new potential solutions that overcome the desire of the Residential
and Commercial Sales department managers to have their products produced in
the old plant. Discuss the pros and cons of your two solutions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Accounting (Text Only)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781285743615
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial & Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781285866307
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Accounting (Text Only)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781285743615
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial & Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781285866307
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial & Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337119207
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning