The demand curves for cases of Coke and Pepsi are given respectively by Qc(Pc. Pe) = 200 - 10pc + 5pe. Q-(Pc. Pe) = 200 – 10p, + 5pc- Each firm has a marginal cost of $10 per case and must simultaneously choose their prices. Are the following statements true or false? 6. If Pepsi charges less than Coke, then all customers will buy from Pepsi. 7. Because Coke and Pepsi are substitutes, the best model for understanding this market is the Cournot Competition Model. For the next question, note that Coke's revenue, as a function of price, is Re(Pc. Pp) = Pc(200 - 10pc + 5pp). 8. Solving the equation (Pc. Pr) = 10 apc for pc will yield Coke's best-response function. 9. The best-response functions are p(Pp) = 15 + 0.25 Pp and pi(Pc) = 15 + 0.25 Pc-
The demand curves for cases of Coke and Pepsi are given respectively by Qc(Pc. Pe) = 200 - 10pc + 5pe. Q-(Pc. Pe) = 200 – 10p, + 5pc- Each firm has a marginal cost of $10 per case and must simultaneously choose their prices. Are the following statements true or false? 6. If Pepsi charges less than Coke, then all customers will buy from Pepsi. 7. Because Coke and Pepsi are substitutes, the best model for understanding this market is the Cournot Competition Model. For the next question, note that Coke's revenue, as a function of price, is Re(Pc. Pp) = Pc(200 - 10pc + 5pp). 8. Solving the equation (Pc. Pr) = 10 apc for pc will yield Coke's best-response function. 9. The best-response functions are p(Pp) = 15 + 0.25 Pp and pi(Pc) = 15 + 0.25 Pc-
Chapter10: Monopolistic Competition And Oligoply
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14SQ
Related questions
Question
part 7 8 9

Transcribed Image Text:The demand curves for cases of Coke and Pepsi are given respectively by
Qe(Pc. Pe) = 200 - 10pc + 5pp.
Qr (Pc. Pr) = 200 – 10pp + 5pc-
Each firm has a marginal cost of $10 per case and must simultaneously choose their prices.
Are the following statements true or false?
6. If Pepsi charges less than Coke, then all customers will buy from Pepsi.
7. Because Coke and Pepsi are substitutes, the best model for understanding this market is the
Cournot Competition Model.
For the next question, note that Coke's revenue, as a function of price, is
Re(Pc. Pp) = Pc(200 - 10pc + 5pp).
8. Solving the equation
(Pc. Pp) = 10
ape
for pe will yield Coke's best-response function.
9. The best-response functions are p(Pp) = 15 + 0.25 p, and pp(Pc) = 15 + 0.25 pc-
10. Both firms charging $20 is an equilibrium.
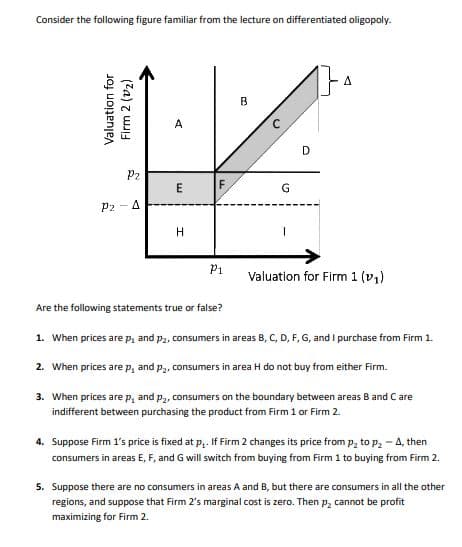
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following figure familiar from the lecture on differentiated oligopoly.
A
D
P2
F
P2 -4
H
P1
Valuation for Firm 1 (v1)
Are the following statements true or false?
1. When prices are p, and p2, consumers in areas B, C, D, F, G, and I purchase from Firm 1.
2. When prices are p, and p,, consumers in area H do not buy from either Firm.
3. When prices are p, and p2, consumers on the boundary between areas B and Care
indifferent between purchasing the product from Firm 1 or Firm 2.
4. Suppose Firm 1's price is fixed at p,. If Firm 2 changes its price from p, to p2 - 4, then
consumers in areas E, F, and G will switch from buying from Firm 1 to buying from Firm 2.
5. Suppose there are no consumers in areas A and B, but there are consumers in all the other
regions, and suppose that Firm 2's marginal cost is zero. Then p, cannot be profit
maximizing for Firm 2.
Valuation for
(Za) z w
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you







Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning