The mean of a normally distributed population is 15. A random sample of 15 measurements from the said population were selected producing x-17.25 and s 13.15. Test the null hypothesis against the alternative hypothesis u> 15 using a- 0.05. Steps Solution 1. Population parameter of interest 2. Formulate the null and alternative hypotheses. 3. Identify the appropriate test statistic. 4. Set the level of significance. Determine if the test is one or two tailed. Determine the critical value. 5. Decision rule for rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis
The mean of a normally distributed population is 15. A random sample of 15 measurements from the said population were selected producing x-17.25 and s 13.15. Test the null hypothesis against the alternative hypothesis u> 15 using a- 0.05. Steps Solution 1. Population parameter of interest 2. Formulate the null and alternative hypotheses. 3. Identify the appropriate test statistic. 4. Set the level of significance. Determine if the test is one or two tailed. Determine the critical value. 5. Decision rule for rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
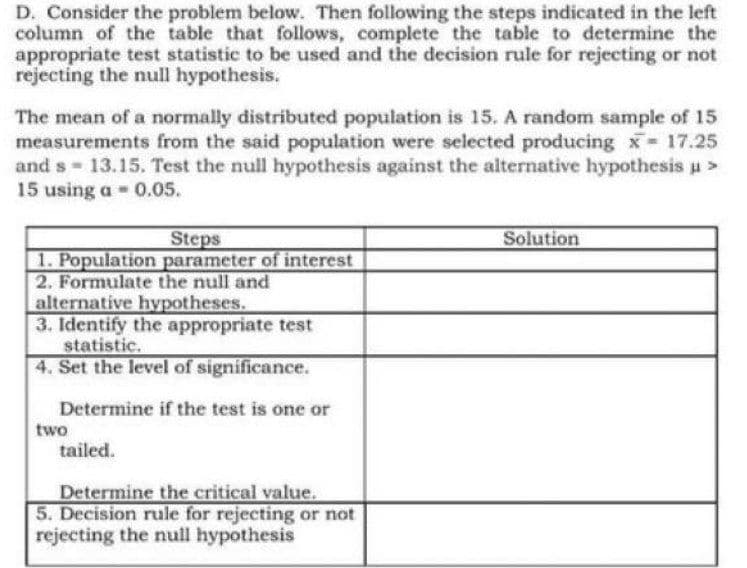
Transcribed Image Text:D. Consider the problem below. Then following the steps indicated in the left
column of the table that follows, complete the table to determine the
appropriate test statistic to be used and the decision rule for rejecting or not
rejecting the null hypothesis.
The mean of a normally distributed population is 15. A random sample of 15
measurements from the said population were selected producing x 17.25
and s 13.15. Test the null hypothesis against the alternative hypothesis u>
15 using a 0.05.
Steps
Solution
1. Population parameter of interest
2. Formulate the null and
alternative hypotheses.
3. Identify the appropriate test
statistic.
4. Set the level of significance.
Determine if the test is one or
two
tailed.
Determine the critical value.
5. Decision rule for rejecting or not
rejecting the null hypothesis
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman