The overall reaction of hydroxide radical with hydrogen gas occurs as follows: Part A OH'(G) + H2(g) - H,0(9) + H'(g) Determine the activation energy for the reaction of OH with H, reaction This reaction plays a significant role in the chemistry of the earth's atmosphere by eventually converting OH to HO, through the subsequent reaction of H with 02. HO, is involved in the destruction of stratospheric ozone (J. Phys Chem. A. 2006, 110, 6978). O 0 201 kJ mor O 165 kJ mol 1 O -0.167 kJ mol The rate constants for the reaction of OH with H2 were found to be 9.11x106 L molrls at 62. °C and 237 10 Lmot'st at-0. °C. O -0.201 kJ mol O -16.5 kJ mor Submit Request Answer
The overall reaction of hydroxide radical with hydrogen gas occurs as follows: Part A OH'(G) + H2(g) - H,0(9) + H'(g) Determine the activation energy for the reaction of OH with H, reaction This reaction plays a significant role in the chemistry of the earth's atmosphere by eventually converting OH to HO, through the subsequent reaction of H with 02. HO, is involved in the destruction of stratospheric ozone (J. Phys Chem. A. 2006, 110, 6978). O 0 201 kJ mor O 165 kJ mol 1 O -0.167 kJ mol The rate constants for the reaction of OH with H2 were found to be 9.11x106 L molrls at 62. °C and 237 10 Lmot'st at-0. °C. O -0.201 kJ mol O -16.5 kJ mor Submit Request Answer
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter11: Chemical Kinetics: Rates Of Reactions
Section11.5: Temperature And Reaction Rate: The Arrhenius Equation
Problem 11.9E: The frequency factor A is 6.31 108 L mol1 s1 and the activation energy is 10. kJ/mol for the...
Related questions
Question
Practice Pack
3.
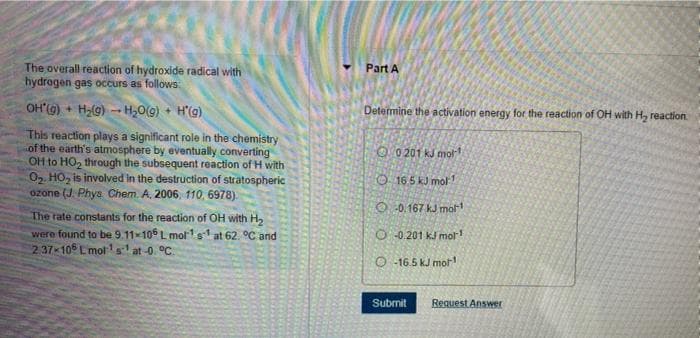
Transcribed Image Text:The overall reaction of hydroxide radical with
hydrogen gas occurs as follows:
Part A
OH'(G) + H2(g) - H20(9) + H'(g)
Determine the activation energy for the reaction of OH with H, reaction
This reaction plays a significant role in the chemistry
of the earth's atmosphere by eventually converting
OH to HO, through the subsequent reaction of H with
02. HO, is involved in the destruction of stratospheric
ozone (J. Phys Chem. A. 2006, 110, 6978).
O 0 201 kJ mot 1
O 165 kJ mol 1
O 0.167 kJ mol
The rate constants for the reaction of OH with H2
were found to be 9.11x106 L molr1s at 62. °C and
237 10 L mot'st at-0. °C.
O -0.201 kJ mol
O -16.5 kJ mor
Submit
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Includes step-by-step video
Learn your way
Includes step-by-step video
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning