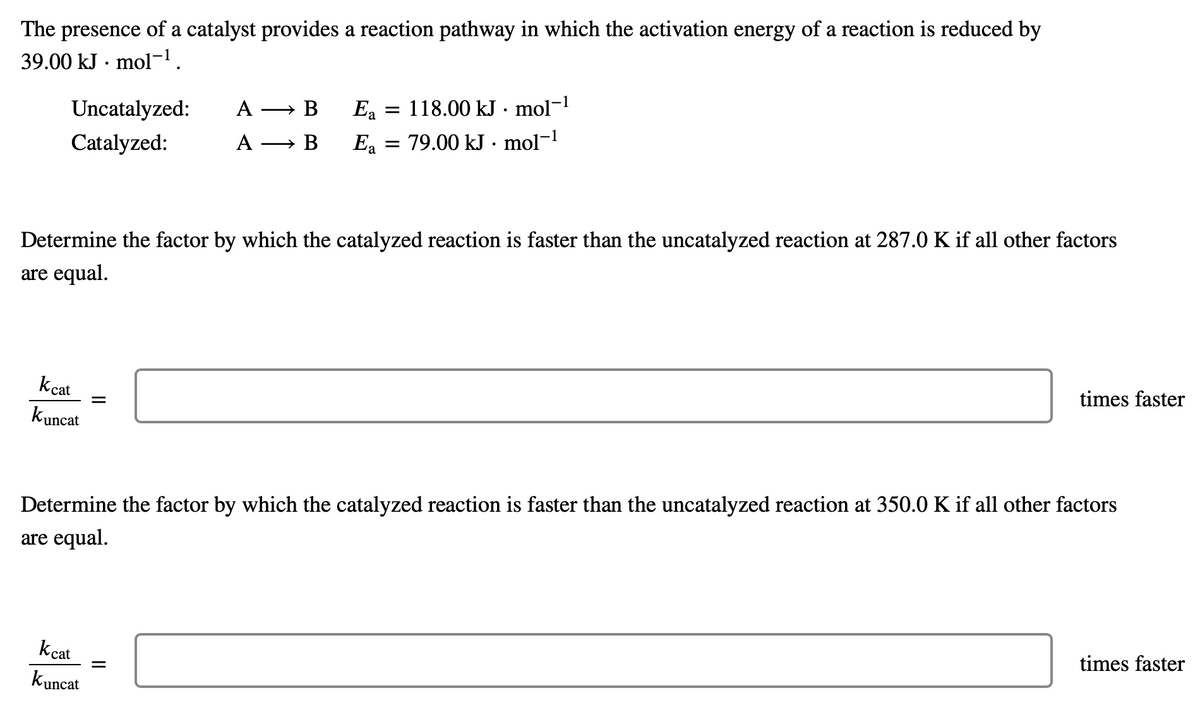
The presence of a catalyst provides a reaction pathway in which the activation energy of a reaction is reduced by 39.00 kJ. mol-¹. Uncatalyzed: Catalyzed: kcat kuncat Determine the factor by which the catalyzed reaction is faster than the uncatalyzed reaction at 287.0 K if all other factors are equal. A → B A → B = kcat kuncat Ea = 118.00 kJ. mol-1 Ea = 79.00 kJ. mol-¹ times faster Determine the factor by which the catalyzed reaction is faster than the uncatalyzed reaction at 350.0 K if all other factors are equal. times faster
The presence of a catalyst provides a reaction pathway in which the activation energy of a reaction is reduced by 39.00 kJ. mol-¹. Uncatalyzed: Catalyzed: kcat kuncat Determine the factor by which the catalyzed reaction is faster than the uncatalyzed reaction at 287.0 K if all other factors are equal. A → B A → B = kcat kuncat Ea = 118.00 kJ. mol-1 Ea = 79.00 kJ. mol-¹ times faster Determine the factor by which the catalyzed reaction is faster than the uncatalyzed reaction at 350.0 K if all other factors are equal. times faster
Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Chapter11: Chemical Kinetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 75E: One mechanism for the destruction of ozone in the upper atmosphere is a. Which species is a...
Related questions
Question
100%
Transcribed Image Text:The presence of a catalyst provides a reaction pathway in which the activation energy of a reaction is reduced by
39.00 kJ mol-¹.
Uncatalyzed:
Catalyzed:
kcat
kuncat
A → B
A → B
kcat
kuncat
Ea
Ea
=
=
Determine the factor by which the catalyzed reaction is faster than the uncatalyzed reaction at 287.0 K if all other factors
are equal.
=
118.00 kJ mol-1
79.00 kJ mol-¹
Determine the factor by which the catalyzed reaction is faster than the uncatalyzed reaction at 350.0 K if all other factors
are equal.
times faster
times faster
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning