The screw of the clamp exerts a compressive force of 500 N on the wooden blocks. The cross section at a-a is rectangular and has dimensions 3 cm x 1 cm. G 12 cm Icm 0.5cm Icm 3 cm 3cm a. Draw a FBD that includes the cross-section a-a. Include all necessary dimensions. b. Write down the force and moment equations to find the internal loadings at the cross- section. c. Find the state of stress at point B (there is an enlarged version of cross-section a-a to show the location of point B). Point B is located 0.5cm from the bottom. CLEARLY set up your equations (symbol form, then numbers) and explain your work. d. Sketch your final answer on the stress element shown. Write down the values for ax, ay, and Txy. Include the correct signs using our sign convention from class. 0x = dy = Txy = e. Find the orientation of the stress element that has the maximum in-plane shear stress. Also find the value of the maximum in-plane shear stress. Clearly set up your equations (symbol form, then numbers). f. Draw the orientation and stresses of the stress element you find, i.e. add the rotated element to the figure provided. Clearly indicate the angle of rotation.
The screw of the clamp exerts a compressive force of 500 N on the wooden blocks. The cross section at a-a is rectangular and has dimensions 3 cm x 1 cm. G 12 cm Icm 0.5cm Icm 3 cm 3cm a. Draw a FBD that includes the cross-section a-a. Include all necessary dimensions. b. Write down the force and moment equations to find the internal loadings at the cross- section. c. Find the state of stress at point B (there is an enlarged version of cross-section a-a to show the location of point B). Point B is located 0.5cm from the bottom. CLEARLY set up your equations (symbol form, then numbers) and explain your work. d. Sketch your final answer on the stress element shown. Write down the values for ax, ay, and Txy. Include the correct signs using our sign convention from class. 0x = dy = Txy = e. Find the orientation of the stress element that has the maximum in-plane shear stress. Also find the value of the maximum in-plane shear stress. Clearly set up your equations (symbol form, then numbers). f. Draw the orientation and stresses of the stress element you find, i.e. add the rotated element to the figure provided. Clearly indicate the angle of rotation.
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter11: Columns
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.5.15P: A frame ABCD is constructed of steel wide-flange members (W8 x 21; E = 30 x ID6 psi) and subjected...
Related questions
Question
Engineering of Materials review Need Help firnding the orientation
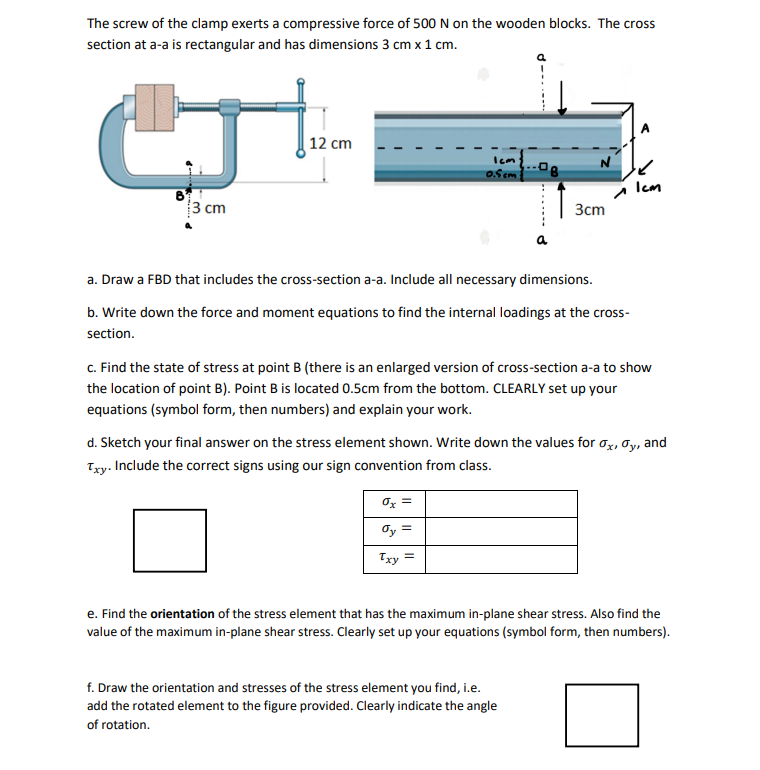
Transcribed Image Text:The screw of the clamp exerts a compressive force of 500 N on the wooden blocks. The cross
section at a-a is rectangular and has dimensions 3 cm x 1 cm.
GJ
12 cm
Icm
0.5cm
Icm
3 cm
3cm
a
a. Draw a FBD that includes the cross-section a-a. Include all necessary dimensions.
b. Write down the force and moment equations to find the internal loadings at the cross-
section.
c. Find the state of stress at point B (there is an enlarged version of cross-section a-a to show
the location of point B). Point B is located 0.5cm from the bottom. CLEARLY set up your
equations (symbol form, then numbers) and explain your work.
d. Sketch your final answer on the stress element shown. Write down the values for ox, y, and
Txy. Include the correct signs using our sign convention from class.
0x =
dy =
Txy
e. Find the orientation of the stress element that has the maximum in-plane shear stress. Also find the
value of the maximum in-plane shear stress. Clearly set up your equations (symbol form, then numbers).
f.Draw the orientation and stresses of the stress element you find, i.e.
add the rotated element to the figure provided. Clearly indicate the angle
of rotation.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning