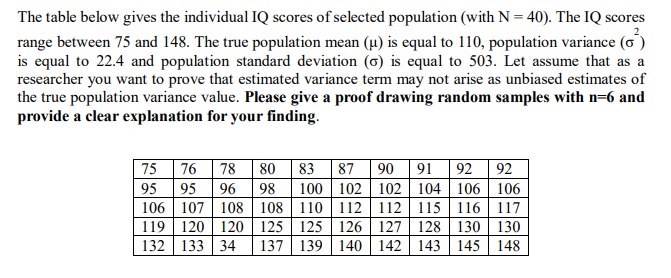
The table below gives the individual IQ scores of selected population (with N = 40). The IQ scores 2 range between 75 and 148. The true population mean (µ) is equal to 110, population variance (o) is equal to 22.4 and population standard deviation (6) is equal to 503. Let assume that as a researcher you want to prove that estimated variance term may not arise as unbiased estimates of the true population variance value. Please give a proof drawing random samples with n=6 and provide a clear explanation for your finding. 75 76 78 80 83 87 90 91 92 92 05 05 06 08 100 102 102 104 106 106
Inverse Normal Distribution
The method used for finding the corresponding z-critical value in a normal distribution using the known probability is said to be an inverse normal distribution. The inverse normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution with a family of two parameters.
Mean, Median, Mode
It is a descriptive summary of a data set. It can be defined by using some of the measures. The central tendencies do not provide information regarding individual data from the dataset. However, they give a summary of the data set. The central tendency or measure of central tendency is a central or typical value for a probability distribution.
Z-Scores
A z-score is a unit of measurement used in statistics to describe the position of a raw score in terms of its distance from the mean, measured with reference to standard deviation from the mean. Z-scores are useful in statistics because they allow comparison between two scores that belong to different normal distributions.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









