The vector product of two vectors A and B is a vector and so has both a magnitude and direction: 1. Magnitude: The magnitude of the vector product Ax Bis: ||A × B|| = |A|| ||B|| sin e = AB₁ = A₁B where is the angle between the vectors. Here B₁ = B sin 6 is the component of B perpendicular to A while A₁ = A sine is the component of A perpendicular to B. Special Cases: Give answers to questions below in terms of the magnitudes A and B. What is Ax B if A and Bare parallel? If A and Bare perpendicular? 2. Direction: The direction of the vector product Ax B is perpendicular to the plane determined by the vectors A and B, and follows a "right hand rule". This "right hand rule" is different from the one we used to determine angular velocity. The steps to determining the direction of the vector product are a. Determine the two possible directions: First determine the only two possible directions that are perpendicular to both A and B. The vector product must be in one of these two directions. What are the two possible directions for Ax B for the vectors shown above? ar b. Apply right hand rule: We now use the right-hand rule to determine which of the choices is correct. • Point the fingers of your right hand in the direction the first vector (in this case A) points. • 100 With your fingers still pointing in that direction, twist your hands so that your palm faces the general direction the 2 vector points (in this case B). B What is the direction of the vector product B x A for the two vectors shown above? Note the direction of the vector product depends on which vector comes first with (Ã×B): • Stick out your thumb. This is the direction of the cross product. Make sure it is one of the two possible directions. If it is not you did something wrong. • Optional: Curl your fingers to determine the direction the torque will cause the object to spin. c. What is the direction of the vector product Ax B for the two vectors shown above? d. Let A be into the page and B point as shown. Follow the steps above and draw an arrow indicating the direction of (A x B) or write out, in or zero if the cross product is into or out of the page or zero. A (into page) B Ā Direction=
The vector product of two vectors A and B is a vector and so has both a magnitude and direction: 1. Magnitude: The magnitude of the vector product Ax Bis: ||A × B|| = |A|| ||B|| sin e = AB₁ = A₁B where is the angle between the vectors. Here B₁ = B sin 6 is the component of B perpendicular to A while A₁ = A sine is the component of A perpendicular to B. Special Cases: Give answers to questions below in terms of the magnitudes A and B. What is Ax B if A and Bare parallel? If A and Bare perpendicular? 2. Direction: The direction of the vector product Ax B is perpendicular to the plane determined by the vectors A and B, and follows a "right hand rule". This "right hand rule" is different from the one we used to determine angular velocity. The steps to determining the direction of the vector product are a. Determine the two possible directions: First determine the only two possible directions that are perpendicular to both A and B. The vector product must be in one of these two directions. What are the two possible directions for Ax B for the vectors shown above? ar b. Apply right hand rule: We now use the right-hand rule to determine which of the choices is correct. • Point the fingers of your right hand in the direction the first vector (in this case A) points. • 100 With your fingers still pointing in that direction, twist your hands so that your palm faces the general direction the 2 vector points (in this case B). B What is the direction of the vector product B x A for the two vectors shown above? Note the direction of the vector product depends on which vector comes first with (Ã×B): • Stick out your thumb. This is the direction of the cross product. Make sure it is one of the two possible directions. If it is not you did something wrong. • Optional: Curl your fingers to determine the direction the torque will cause the object to spin. c. What is the direction of the vector product Ax B for the two vectors shown above? d. Let A be into the page and B point as shown. Follow the steps above and draw an arrow indicating the direction of (A x B) or write out, in or zero if the cross product is into or out of the page or zero. A (into page) B Ā Direction=
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter14: Static Equilibrium, Elasticity, And Fracture
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8PQ
Related questions
Concept explainers
Rotational Equilibrium And Rotational Dynamics
In physics, the state of balance between the forces and the dynamics of motion is called the equilibrium state. The balance between various forces acting on a system in a rotational motion is called rotational equilibrium or rotational dynamics.
Equilibrium of Forces
The tension created on one body during push or pull is known as force.
Question
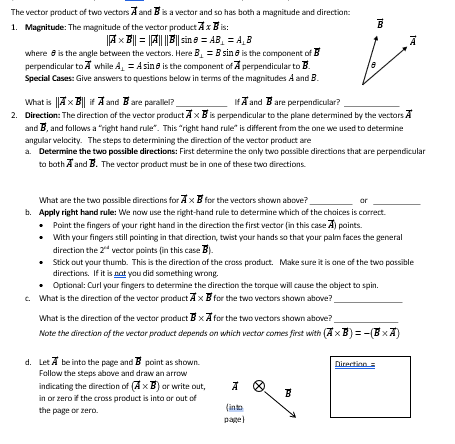
Transcribed Image Text:The vector product of two vectors A and B is a vector and so has both a magnitude and direction:
1. Magnitude: The magnitude of the vector product Ax Bis:
||A × B|| = |A|| ||B|| sin e = AB₁ = A₁B
where is the angle between the vectors. Here B₁ = B sin 6 is the component of B
perpendicular to A while A₁ = A sine is the component of A perpendicular to B.
Special Cases: Give answers to questions below in terms of the magnitudes A and B.
What is Ax B if A and Bare parallel?
If A and Bare perpendicular?
2. Direction: The direction of the vector product Ax B is perpendicular to the plane determined by the vectors A
and B, and follows a "right hand rule". This "right hand rule" is different from the one we used to determine
angular velocity. The steps to determining the direction of the vector product are
a. Determine the two possible directions: First determine the only two possible directions that are perpendicular
to both A and B. The vector product must be in one of these two directions.
What are the two possible directions for Ax B for the vectors shown above?
ar
b. Apply right hand rule: We now use the right-hand rule to determine which of the choices is correct.
• Point the fingers of your right hand in the direction the first vector (in this case A) points.
•
100
With your fingers still pointing in that direction, twist your hands so that your palm faces the general
direction the 2 vector points (in this case B).
B
What is the direction of the vector product B x A for the two vectors shown above?
Note the direction of the vector product depends on which vector comes first with (Ã×B):
•
Stick out your thumb. This is the direction of the cross product. Make sure it is one of the two possible
directions. If it is not you did something wrong.
• Optional: Curl your fingers to determine the direction the torque will cause the object to spin.
c. What is the direction of the vector product Ax B for the two vectors shown above?
d. Let A be into the page and B point as shown.
Follow the steps above and draw an arrow
indicating the direction of (A x B) or write out,
in or zero if the cross product is into or out of
the page or zero.
A
(into
page)
B
Ā
Direction=
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning