To find the arclength of y 3x2 +4 from r 0 to z 4, which is the correct integral? OL = V1+6z dx OL = | VI+ 36xdx OL = %3D OL V1 + 36x dr 6x to re-write the integral in terms of u. Now that you have the correct integral, use the substitution u = Which is the correct result? 24 1 OL | V1+ 3u'du %3D 24 1 OL V1+ u'du 24 OL= VIF budu %3D 24 OL - L VI+ udu %3D What is the value of the integral? Hint: Use a table or technology. You may enter a decimal approximation for your solution.
To find the arclength of y 3x2 +4 from r 0 to z 4, which is the correct integral? OL = V1+6z dx OL = | VI+ 36xdx OL = %3D OL V1 + 36x dr 6x to re-write the integral in terms of u. Now that you have the correct integral, use the substitution u = Which is the correct result? 24 1 OL | V1+ 3u'du %3D 24 1 OL V1+ u'du 24 OL= VIF budu %3D 24 OL - L VI+ udu %3D What is the value of the integral? Hint: Use a table or technology. You may enter a decimal approximation for your solution.
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
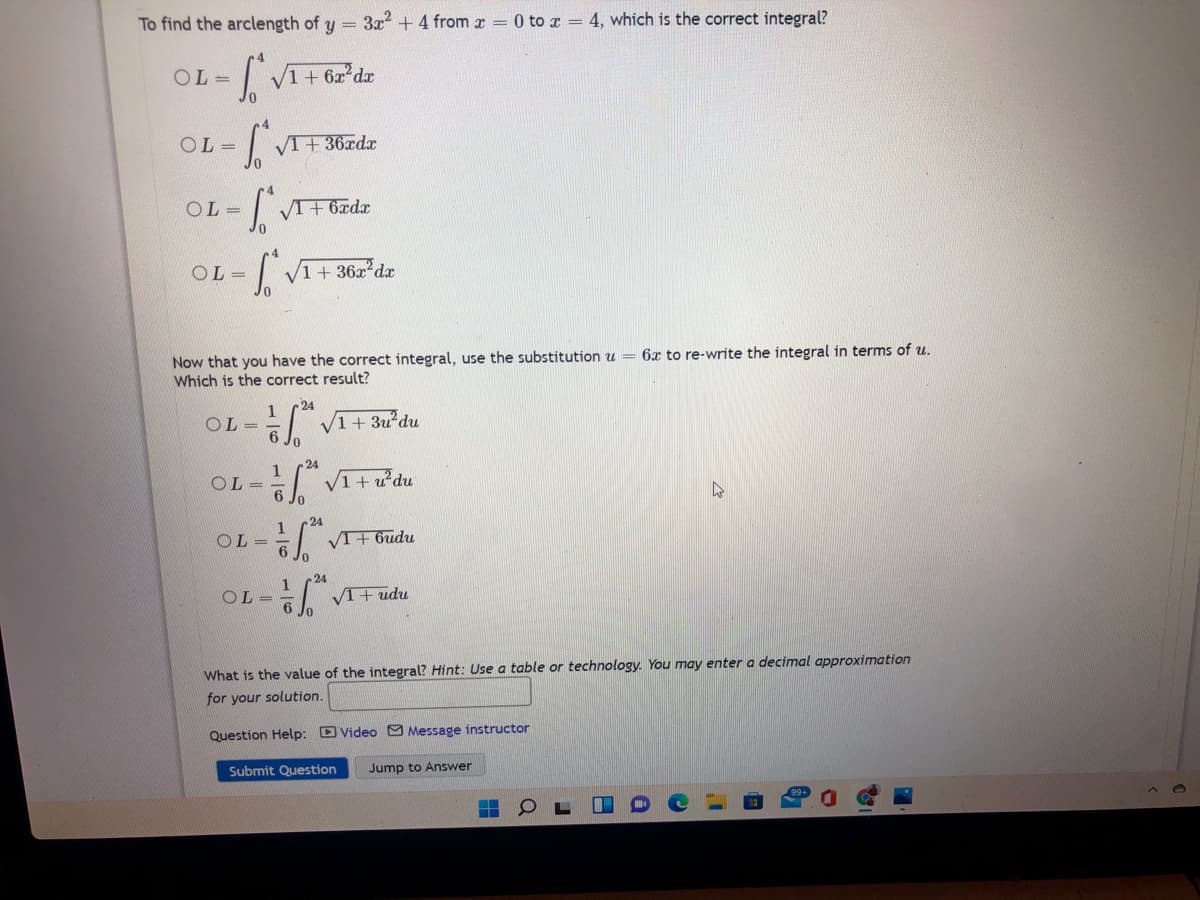
Transcribed Image Text:To find the arclength of y =
3x? + 4 from x = 0 to x = 4, which is the correct integral?
OL =
V1 + 6x dx
OL =
VI+ 36xdx
4
= 10
OL =
V1 + 36x dx
6x to re-write the integral in terms of u.
Now that you have the correct integral, use the substitution u
Which is the correct result?
24
OL =
1+ 3u du
24
1
OL =
24
OL =
VI+ 6udu
24
1
OL =
VI+ udu
What is the value of the integral? Hint: Use a table or technology. You may enter a decimal approximation
for your solution.
Question Help: D Video Message instructor
Submit Question
Jump to Answer
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning