Two bicycles of equal mass collide, as shown below. In the collision, the gears of the two bikes become intertwined so that the bikes are locked together after the collision and the two move as one. The upper bike has initial speed v = 2.3 m/s, while the lower bike has intial speed 1.7 m/s. a) What type of collision is this? How do you know? b) What is the speed of the two intertwined bikes after the collision? c) In what direction are they moving after the collision? (Give the angle). SO
Two bicycles of equal mass collide, as shown below. In the collision, the gears of the two bikes become intertwined so that the bikes are locked together after the collision and the two move as one. The upper bike has initial speed v = 2.3 m/s, while the lower bike has intial speed 1.7 m/s. a) What type of collision is this? How do you know? b) What is the speed of the two intertwined bikes after the collision? c) In what direction are they moving after the collision? (Give the angle). SO
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter6: Momentum And Collisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 36P: A car of mass m moving at a speed v1 collides and couples with the back of a truck of mass 2m moving...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Two bicycles of equal mass collide, as shown below. In the collision, the gears of the two bikes become intertwined so that the bikes are locked together after the collision and the two move as
one. The upper bike has initial speed v1 = 2.3 m/s, while the lower bike has intial speed 1.7 m/s.
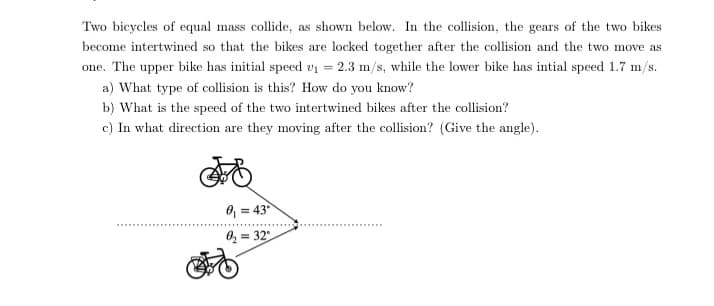
Transcribed Image Text:Two bicycles of equal mass collide, as shown below. In the collision, the gears of the two bikes
become intertwined so that the bikes are locked together after the collision and the two move as
one. The upper bike has initial speed vi = 2.3 m/s, while the lower bike has intial speed 1.7 m/s.
a) What type of collision is this? How do you know?
b) What is the speed of the two intertwined bikes after the collision?
c) In what direction are they moving after the collision? (Give the angle).
8, = 43
0, = 32
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning