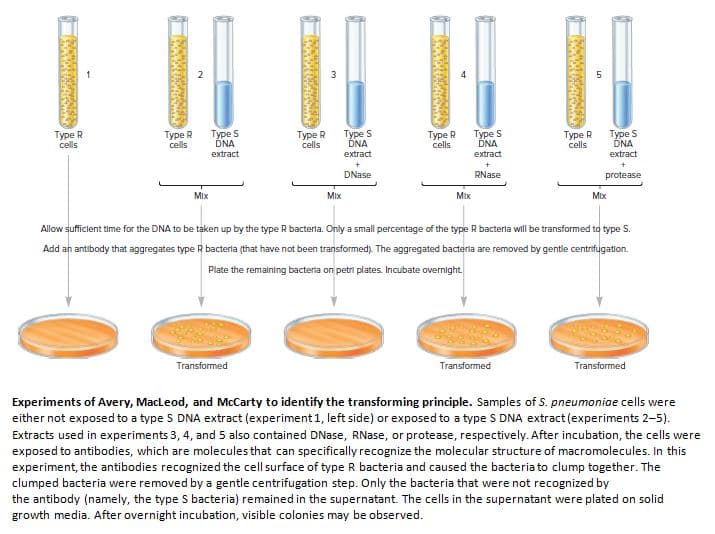
Type R cells Type R cells Type S DNA extract Type R cells Type S DNA Type R cells Type S DNA extract Type R cells Type S DNA extract extract DNase RNase protease Mix Mix Mix Mix Allow sufficlent time for the DNA to be taken up by the type R bacterla. Only a small percentage of the type R bacterla will be transformed to type S. Add an antibody that aggregates type R bacterla (that have not been transformed). The aggregated bacterla are removed by gentle centrifugation. Plate the remalning bacterla on petri plates. Incubate overnight. Transformed Transformed Transformed Experiments of Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty to identify the transforming principle. Samples of S. pneumoniae cells were either not exposed to a type S DNA extract (experiment 1, left side) or exposed to a type S DNA extract (experiments 2-5). Extracts used in experiments 3, 4, and 5 also contained DNase, RNase, or protease, respectively. After incubation, the cells were exposed to antibodies, which are molecules that can specifically recognize the molecular structure of macromolecules. In this experiment, the antibodies recognized the cell surface of type R bacteria and caused the bacteria to clump together. The clumped bacteria were removed by a gentle centrifugation step. Only the bacteria that were not recognized by the antibody (namely, the type S bacteria) remained in the supernatant. The cells in the supernatant were plated on solid growth media. After overnight incubation, visible colonies may be observed. র
Molecular Techniques
Molecular techniques are methods employed in molecular biology, genetics, biochemistry, and biophysics to manipulate and analyze nucleic acids (deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA)), protein, and lipids. Techniques in molecular biology are employed to investigate the molecular basis for biological activity. These techniques are used to analyze cellular properties, structures, and chemical reactions, with a focus on how certain molecules regulate cellular reactions and growth.
DNA Fingerprinting and Gel Electrophoresis
The genetic makeup of living organisms is shown by a technique known as DNA fingerprinting. The difference is the satellite region of DNA is shown by this process. Alex Jeffreys has invented the process of DNA fingerprinting in 1985. Any biological samples such as blood, hair, saliva, semen can be used for DNA fingerprinting. DNA fingerprinting is also known as DNA profiling or molecular fingerprinting.
Molecular Markers
A known DNA sequence or gene sequence is present on a chromosome, and it is associated with a specific trait or character. It is mainly used as a genetic marker of the molecular marker. The first genetic map was done in a fruit fly, using genes as the first marker. In two categories, molecular markers are classified, classical marker and a DNA marker. A molecular marker is also known as a genetic marker.
DNA Sequencing
The most important feature of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecules are nucleotide sequences and the identification of genes and their activities. This the reason why scientists have been working to determine the sequences of pieces of DNA covered under the genomic field. The primary objective of the Human Genome Project was to determine the nucleotide sequence of the entire human nuclear genome. DNA sequencing selectively eliminates the introns leading to only exome sequencing that allows proteins coding.
What was the purpose of adding RNase or protease to a DNA extract?
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps






