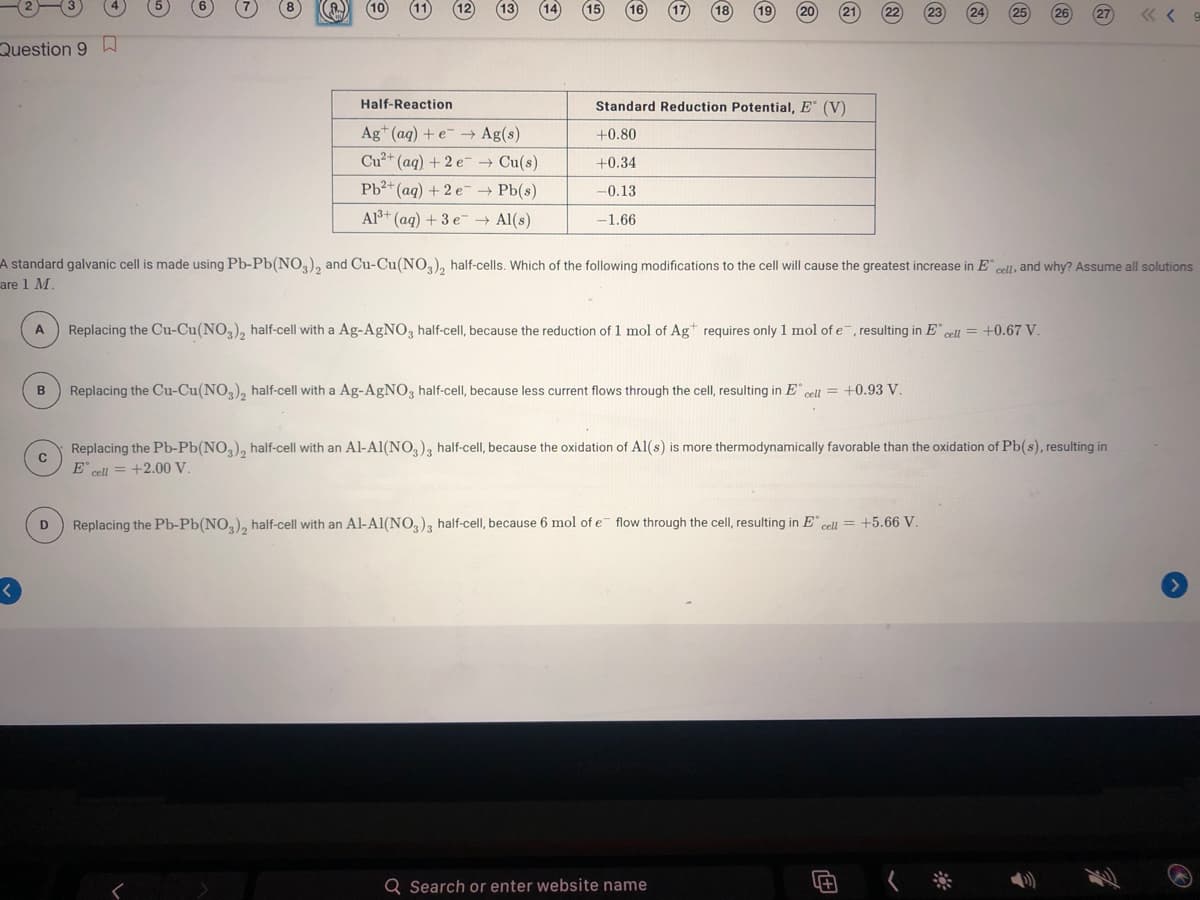
uestion 9 D Half-Reaction Standard Reduction Potential, E (V) Ag+ (aq) +e -→ Ag(s) +0.80 Cu2+ (aq) + 2 e Cu(s) +0.34 Pb2+ (aq) + 2 e- Pb(s) -0.13 Al+ (aq) + 3 e- Al(s) -1.66 standard galvanic cell is made using Pb-Pb(NO,), and Cu-Cu(NO,), half-cells. Which of the following modifications to the cell will cause the greatest increase in E cell, and why? Assume all solutio e1 M. Replacing the Cu-Cu(NO,), half-cell with a Ag-AgNO, half-cell, because the reduction of 1 mol of Ag requires only 1 mol of e, resulting in E cell = +0.67 V. Replacing the Cu-Cu(NO,), half-cell with a Ag-AGNO, half-cell, because less current flows through the cell, resulting in E cell = +0.93 V. Replacing the Pb-Pb(NO,), half-cell with an Al-Al(NO,), half-cell, because the oxidation of Al(s) is more thermodynamically favorable than the oxidation of Pb(s), resulting in E' cell = +2.00 V. Replacing the Pb-Pb(NO,), half-cell with an Al-Al(NO,), half-cell, because 6 mol of e flow through the cell, resulting in E" cell = +5.66 V D
uestion 9 D Half-Reaction Standard Reduction Potential, E (V) Ag+ (aq) +e -→ Ag(s) +0.80 Cu2+ (aq) + 2 e Cu(s) +0.34 Pb2+ (aq) + 2 e- Pb(s) -0.13 Al+ (aq) + 3 e- Al(s) -1.66 standard galvanic cell is made using Pb-Pb(NO,), and Cu-Cu(NO,), half-cells. Which of the following modifications to the cell will cause the greatest increase in E cell, and why? Assume all solutio e1 M. Replacing the Cu-Cu(NO,), half-cell with a Ag-AgNO, half-cell, because the reduction of 1 mol of Ag requires only 1 mol of e, resulting in E cell = +0.67 V. Replacing the Cu-Cu(NO,), half-cell with a Ag-AGNO, half-cell, because less current flows through the cell, resulting in E cell = +0.93 V. Replacing the Pb-Pb(NO,), half-cell with an Al-Al(NO,), half-cell, because the oxidation of Al(s) is more thermodynamically favorable than the oxidation of Pb(s), resulting in E' cell = +2.00 V. Replacing the Pb-Pb(NO,), half-cell with an Al-Al(NO,), half-cell, because 6 mol of e flow through the cell, resulting in E" cell = +5.66 V D
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Chapter24: Coulometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 24.4QAP: Halide ions can he deposited at a silver anode, the reaction being Ag(s) + X- AgX(s) +e- Suppose...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:(12
Question 9 h
Half-Reaction
Standard Reduction Potential, E (V)
Ag* (aq) + e- → Ag(s)
+0.80
Cu2+ (aq) + 2 e- → Cu(s)
+0.34
Pb2+ (ag) + 2 e- → Pb(s)
-0.13
Alš+ (aq) + 3 e → Al(s)
-1.66
A standard galvanic cell is made using Pb-Pb(NO3), and Cu-Cu(NO,), half-cells. Which of the following modifications to the cell will cause the greatest increase in E cell, and why? Assume all solutions
are 1 M.
A
Replacing the Cu-Cu(NO,), half-cell with a Ag-AgNO3 half-cell, because the reduction of 1 mol of Ag requires only 1 mol of e, resulting in E cell = +0.67 V.
B
Replacing the Cu-Cu(NO,), half-cell with a Ag-AgNO3 half-cell, because less current flows through the cell, resulting in E" cell = +0.93 V.
Replacing the Pb-Pb(NO,), half-cell with an Al-Al(NO,), half-cell, because the oxidation of Al(s) is more thermodynamically favorable than the oxidation of Pb(s), resulting in
E" cell = +2.00 V.
D
Replacing the Pb-Pb(NO,), half-cell with an Al-Al(NO,), half-cell, because 6 mol of e flow through the cell, resulting in E" cell = +5.66 V.
Q Search or enter website name
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning