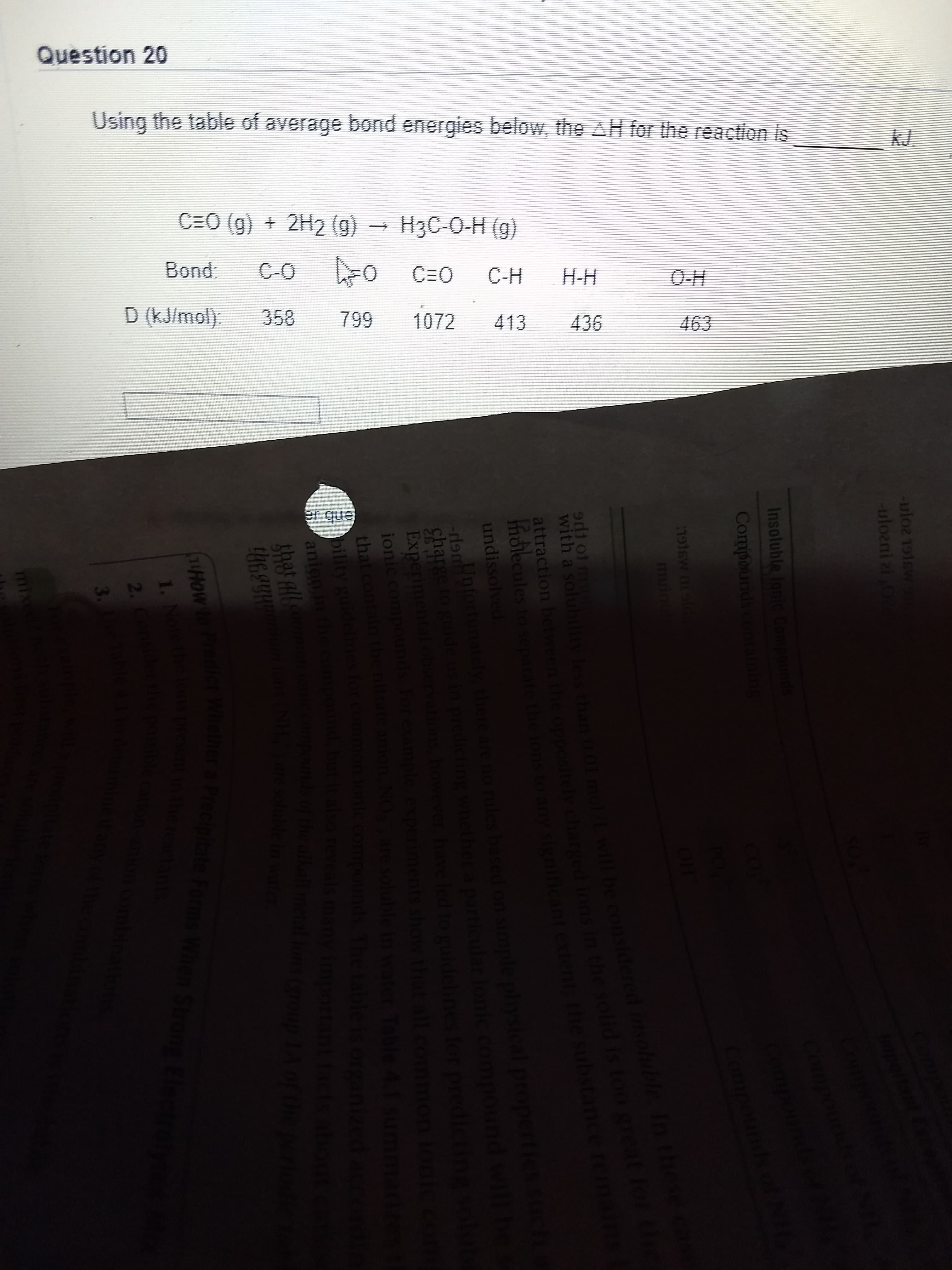
Using the table of average bond energies below, the AH for the reaction is kJ. C=O (g) + 2H2 (g) - НзC-0-Н (9) Bond: C-O C=O C-H H-H 0-Н D (kJ/mol). 358 799 1072 413 436 463
Q: ind ΔH for the reaction C3H8 (l) + 5O2(g) --> 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) ΔHrxn = ? Given:…
A: for the reaction C3H8 (l) + 5O2(g) --> 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) ΔHrxn = ? Given: [CO2(g)] =…
Q: Using the bond enthalpies and the equation shown below, calculate the ΔH for the combustion of…
A:
Q: 2. Calculate A H for 4FE0(s) + 02(g) → 2Fe203 (s) based on the reactions: 6FEO (s) + O2 (g) →2FE3O4…
A: Calculate enthalpy of the reaction, 4FeO + O2 -----> 2Fe2O3 ∆Hrxn = ?
Q: 3. Predict the target reaction which can be obtained by adding step 1 and 2 shown below. Also…
A:
Q: 7. Given that the standard enthalpies of formation in kJ mol" of CO(g). CO: (g) and H;0(g) are…
A: CO + H2O --> CO2 + H2 Standard enthalpy = enthalpy of products - change…
Q: CH,(g) + 2 0,(g) AH = -809.0 kJ/mol %3D rxn co,(9) + 2 H,O(g) AH 'cond-81.3 kJ 2 H,0U) Given the…
A: We have given that CH4(g) + 2O2(g) -------> CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ∆H = -809.0KJ/mole 2H2O(g)…
Q: Sodium fluoroacetate (Nao:C:H:F) is a common poison used in New Zealand to control invasive species,…
A: Given : NaO2C2H2Cl is undergoing substitution reaction to produce NaO2C2H2F by breaking C-Cl bond…
Q: Which reaction has Hrxn equal to Hf? Explain. How much energy would be released by the combustion…
A: Enthalpy of Reaction (∆Hrxn):- It is the energy change which occurs during a reaction. Enthalpy of…
Q: Using the given data in the table below, calculate the AH°xn for the reaction; PС3 (g) + 3 HСІ (g) —…
A:
Q: 5. Determine the bond enthalpy of the O-0 for the reaction below if AH -2800 kJ/mol %3D H H 2…
A: "Since you have asked multiple questions, we will solve the first question for you. If you want any…
Q: How do I solve this
A:
Q: Given the following data: Pals) + 6 Clzig) → 4PC|3(9) AH = -1225.6 kJ Pa(s) + 5 Oz(g) → P4O10/s) AH…
A: enthalpy is an extensive property which will depend on the number of particle.
Q: 1. Find the enthalpy of reaction ΔrHo for the following reaction : 2 S(s) + 3 O2(g) → 2 SO3(g).…
A: The enthalpy change is a state function and the Hess law states that the change of enthalpy in a…
Q: H2 (8) 2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(1) AH° = -571.6 kJ From the following enthalpy changes, calculate the…
A:
Q: Methane, CH4, reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat. CH4(g) + 2O2(g) .…
A: From the above reaction we can see that when 1 mole of CH4 reacts, ΔH = -890.3 KJ Hence the ΔH of…
Q: -778 KJ Use the following information to determine the enthalpy for the reaction shown below. CH4(g)…
A: To determine the enthalpy change for the given reaction, identify the reactants and products. In the…
Q: Find the AH for the reaction below, given the following reactions and subsequent AH values: C3H8(g)…
A:
Q: CWhat is the new value of A, H for Reaction 1, as now written? Original: New: 4 B(s) + 3 O₂(g) → 2…
A:
Q: In a coffee cup calorimeter, 50.0 ml of 0.300 M NaOH solution was added to neutralize 50.0 mL of…
A: Moles is obtained from molarity and volume - Moles of NaOH = Molarity ×Volume =0.30 M×50 mL=0.30…
Q: 2NOC(g)N2g) + O2(g) + Cl2(g) given the following set of reactions: 1/2 N2(g) + 1/2 O2(g)NO(g) NO(g)…
A: Using Hess's law, From the intermediate reactions we can the final reaction. 1/2N2 + 1/2 O2 --->…
Q: Photosynthesis in plants converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose (C,H1206) and oxygen…
A: Dear student, Since you have posted multiple questions, the answer for first question is given…
Q: 17. The enthalpy of formation for H20(g), CO2(g), and C2H5OH(1), in kJ/mol, are given as follows…
A:
Q: Predict the standard enthalpy of the reaction CH4 (g) + Cl2 CH2C12 + H2 Given : mean bond…
A: Welcome to bartleby ! We have to calculate enthalpy of reaction .
Q: Calculate the theoretical enthalpy of reaction where NH4NO3 (s) → NH41+ (aq) + NO31- (aq).…
A: The given reaction is: ∆Hf of the reaction is given by: where Σ∆Hf(products) is the summation of…
Q: Calculate the AH for the reaction of the compound below with HBr. Show all work. Is the reaction…
A: Given an unsaturated alkene. We have to calculate the heat of the reaction, (∆H) when this given…
Q: I. AHxn for the reaction below was determined using bond dissociation energies (BDES) to be -57 kJ.…
A:
Q: Drawing Enthalpy Diagrams and Determining the sign of AH FOLLOW-UP PROBLEM 6.2 this problem When 0.8…
A: Exothermicity depends on the evolution of heat whereas endothermicity depends on the absorption of…
Q: 2. Given: AH = -1220.6 kJ/mol C;H>(g) + 5/2 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + H2O (g) C (s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) H2(g)…
A: Using Hess law , for the following reaction that is, ∆H=∆H1+∆H2+∆H3 ∆H=1220.6-1007.0-103.8…
Q: unlv.instructure.com Question 3 Using Hess' law, determine AH for the following reaction: CS2(1) + 3…
A: In accordance with Hess law, enthalpy change for any specific reaction following multiple steps is…
Q: Given the following bond energies (in kJ/mol): BE(H–H) = 436; BE(C–C) = 345; BE(C=C) = 611; BE(N=N)…
A:
Q: Use the heats of formation, AH°, in the table to determine AH for the reaction: 2 C2H2 (g) + 5 02(g)…
A: The standard enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change of reaction in standard conditions when…
Q: Given the heat of formation of the following compounds from their elemer AH°F = -393.5 kJ/mol CO:(g)…
A: The question is based on concept of chemical thermodynamics. We have to calculate enthalpy change…
Q: I. AHxn for the reaction below was determined using bond dissociation energies (BDES) to be -57 kJ.…
A:
Q: Find the enthalpy change for the reaction CS2(l) +3 O2(g) -> CO2(g) + 2 SO2(g) when: C(s) + O2(g)…
A:
Q: What is the ΔH for the reaction below? C2H2(g) + 3 H2O(l) → CH4(g) + O2(g) + CH3OH(l)…
A:
Q: What is the AH for the reaction below? C2H2(g) +3 H20() → CH4(g) + 02(9) + CH3OH() Use the following…
A:
Q: Find the AH for the reaction below, given the following reactions and subsequent AH values: Zn(s) +…
A: Given values: Hess's law states that total enthalpy of given reaction remains same irrespective of…
Q: Using Hess's law, what is AH°rxn for the following reaction? AB3(9) + 6Cg) → As) + 3BC2(g) A(s) +…
A: Ans A. 235kj/mol
Q: SnCl2 (k) → Sn (k) + Cl2 (g) 2 SnCl2 (k) + 2 Cl2 (g) → 2 SnCl4 (s) +325.1 kJ -372.4 kJ Using the…
A: The enthalpy of a reaction provides us with the amount of energy that is used up (absorbed) or given…
Q: Calculate the AH°rxn for the combustion of methane using the given AH°r. CH4 (g) + 202 (g) 2H2O (1)…
A:
Q: An important step in the synthesis of nitric acid is the conversion of ammonia to nitric oxide, NO.…
A: Answer to the following question can be written as:
Q: 18. Calculate the AH of reaction for CIF(g)F2(g)> CIF3(g) given the following data: 1) 2CIF(g)O2(g)…
A:
Q: Find ΔG°rxn for the reaction: N2O(g) + NO2(g)¡ 3 NO(g) Use the following reactions with known ΔG°rxn…
A: N2O(g)+NO2(g) → 3NO(g) : ΔG = ? ------(1) 2NO(g)+O2(g) → 2NO2(g) : ΔG1 = −71.2kJ -----(2)…
Q: Calculate AH°rxn for the reaction below, using the bond enthalpies provided (you may not need to use…
A: Whenever reactant to form product than during this process, old bonds of reactant breaks while new…
Q: When 3 moles of Fe2O3(s) react with H2(g) to form Fe3O4(s) and H2O(g) according to the following…
A: The energy difference of the products and reactants is known as the energy change of a reaction.
Q: 4. Use the following reactions and AH° values given below to determine the heat of reaction for CH.…
A:
Q: Given the data below, H°, for the reaction rxn 3C12 (g) + PH3 (g) → PCI3 (g) + 3HCI (g) is kJ. AH°…
A:
Q: 4. Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction below, given the following: CHOH 1) + 202 () → 2CO2 ®+…
A: Enthalpy of reaction is sum pf enthalpies of formation of product - sum of enthalpies of formation…
Q: For which of the following reaction(s) is the enthalpy change for the reaction not equal to AH' of…
A: Enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is formed from elements in…
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

- Isomers are molecules with the same elemental composition but a different atomic arrangement. Three isomers with the formula C4H8 are shown in the models below. The enthalpy of combustion (cH) of each isomer, determined using a calorimeter, is as follows: (a) Draw an energy level diagram relating the energy content of the three isomers to the energy content of the combustion products, CO2(g) and H2O(). (b) Use the cH data in part (a), along with the enthalpies of formation of CO2(g) and H2O() from Appendix L, to calculate the enthalpy of formation for each of the isomers. (c) Draw an energy level diagram that relates the enthalpies of formation of the three isomers to the energy of the elements in their standard states. (d) What is the enthalpy change for the conversion of cis-2-butene to trans-2-butene?Find the heat of reaction and explain what happen to it. Calculate the ∆H of reaction for: C3H8 (g) + 5O2 (g) => 3CO2 (g) + 4H2O (l) The values of ∆H of reaction are as follows:C3H8 (g) = -103.95 kJ/molCO2 (g) = -393.5 kJ/molH2O (g) = -285.8 kJ/mol Topic: Enthalpy of Reaction0 Calculate AH for the following reaction, after it is properly balanced with smallest whole-number coefficients: rxn C,H%(g) + Ozg) → COz(g) + H,O(g) AH [C₂H6(g)] = -84.667 kJ/mol AH [CO₂(g)] = -393.5 kJ/mol AH [CO₂(aq)] = −412.9 kJ/mol AH [H₂O(g)]=-241.826 kJ/mol AH [H₂O()] = -285.840 kJ/mol f kJ [unbalanced]
- Find ΔG°rxn for the reaction: N2O(g) + NO2(g)¡ 3 NO(g) Use the following reactions with known ΔG°rxn values:2 NO(g) + O2(g)¡2 NO2(g) ΔG°rxn = -71.2 kJN2(g) + O2(g)¡2 NO(g) ΔG°rxn = +175.2 kJ2 N2O(g)¡2 N2(g) + O2(g) ΔG°rxn = -207.4 kJDiethyl ether, C4H10O(l), a flammable compound that wasonce used as a surgical anesthetic, has the structure H3C-CH2- O- CH2-0 CH3 The complete combustion of 1 mol of C4H10O1l2 to CO21g2and H2O(l) yields ΔH° = -2723.7 kJ. (a) Write a balancedequation for the combustion of 1 mol of C4H10O(l). (b) Byusing the information in this problem and data in Table 5.3,calculate ΔHf° for diethyl ether.Estimate the enthalpy change for the combustion of one mole of acetylene, C2H2, to form carbon dioxide and water vapor. 2C2H2(g) + 5O2(g) ⟶⟶ 4CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) BE(C–H) = 456 kJ/molBE(C≡C) = 962 kJ/molBE(O=O) = 499 kJ/molBE(C=O) = 802 kJ/molBE(O–H) = 462 kJ/mol Group of answer choices A.) +653 kJ/mol B.) –1010 kJ/mol C.) –1759 kJ/mol D.) –155 kJ/mol E.) +1010 kJ/mol
- When a neutralization reaction was carried out using 100.0 mL of 0.7890M NH3 water and 100.0 mL of 0.7940M acetic acid, ΔT was found to be 4.76 °C. The specific heat of the reaction mixture was 4.104 J g-l K-1 and its density was 1.03 g mL-1. The calorimeter constant was 3.36 JK-1 a) Calculate ΔH neutralization for the reaction of NH3 and acetic acid. b) At the end of the experiment, it was discovered that the thermometer had not been calibrated. When it was calibrated, it was found that the thermometer read 0.50 °C low. What effect would this thermometer reading have on the reported DH neutralization calculated above? c) When the temperature-time data graph was reviewed, it was found that an error had been made in determining ΔT. Instead of 4.76 °C, ΔT was actually 4.70 °C. Based on this change only, calculate the correct ΔH neutralization for the reaction of NH3, and acetic acid. d) Calculate the percent error for the correct ΔH neutralization if aΔ DT of 4.76 °C had been used.…When a neutralization reaction was carried out using 100.0 mL of 0.7890M NH3 water and 100.0 mL of 0.7940M acetic acid, ΔT was found to be 4.76 °C. The specific heat of the reaction mixture was 4.104 J g-l K-1 and its density was 1.03 g mL-1. The calorimeter constant was 3.36 JK-1 a) Calculate ΔH neutralization for the reaction of NH3 and acetic acid. b) At the end of the experiment, it was discovered that the thermometer had not been calibrated. When it was calibrated, it was found that the thermometer read 0.50 °C low. What effect would this thermometer reading have on the reported DH neutralization calculated above? c) When the temperature-time data graph was reviewed, it was found that an error had been made in determining ΔT. Instead of 4.76 °C, ΔT was actually 4.70 °C. Based on this change only, calculate the correct ΔH neutralization for the reaction of NH3, and acetic acid. d) Calculate the percent error for the correct ΔH neutralization if aΔ DT of 4.76 °C had been used.…An important step in the synthesis of nitric acid is the conversion of ammonia to nitric oxide, NO. Calculate ΔH∞rxn for the reaction below using the following information; ΔH∞f [NH3(g)] = -45.9 kJ/mol; ΔH∞f [NO(g)] = 90.3 kJ/mol; ΔH∞f [H2O(g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol. 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) → 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g)
- Use standard enthalpies of formation to calculate ΔH∘rxn for the following reaction: 4HCl(g) + O2(g) ---> 2Cl2(g) + 2 H2O(g) Please answer fast i give upvote .Liquid carbon disulfide burns in the presence of oxygen to produce two gaseous combustion products, carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide. Species DHf° (kJ/mol) DGf° (kJ/mol) CS2 (g) 117.4 65.3 CS2 (l) 89.7 65.3 O2 (g) 0.00 0.00 CO2 (g) - 393.5 - 394.4 SO2 (g) - 296.9 - 300.4 Write a balanced equation for this reaction. 2. Calculate the values of ΔH°rxn and ΔG°rxn for this reaction 3. Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? Liquid carbon disulfide is vapourised to gaseous carbon disulfide. Calculate the value of ΔS°vap for of liquid carbon disulfide at 25°Some bacteria can obtain energy for growth by oxidizing ethanol, first to acetaldehyde and then acetic acid. Calculate ΔH° for the reaction:(a) C2H5OH(l) + ½O2(g) ---> CH3CHO(l) + H2O(l)Use the following enthalpies of combustion: ΔcH°(C2H5OH, l) = -1362.8 kJ mol-1, ΔcH°(CH3CHO, l) = -886.8 kJ mol-1



