Webmasters.com has developed a powerful new server that would be used for corporations' Internet activities. It would cost $10 million at Year 0 to buy the equipment necessary to manufacture the server. The project would require net working capital at the beginning of each year in an amount equal to 10% of the year's projected sales; for example, NWC = 10% (Sales). The servers would sell for $24,000 per unit, and Webmasters believes that variable costs would amount to $17,500 per unit. After Year 1, the sales price and variable costs will increase at the inflation rate of 3%. The company's nonvariable costs would be $1 million at Year 1 and would increase with inflation. The server project would have a life of 4 years. If the project is undertaken, it must be continued for the entire 4 years. Also, the project's returns are expected to be highly correlated with returns on the firm's other assets. The firm believes it could sell 1,000 units per year. The equipment would be depreciated over a 5-year period, using MACRS rates. The estimated market value of the equipment at the end of the project's 4-year life is $500,000. Webmasters' federal-plus-state tax rate is 40%. Its cost of capital is 10% for average-risk projects, defined as projects with a coefficient of variation of NPV between 0.8 and 1.2. Low-risk projects are evaluated with a WACC of 8%, and high-risk projects at 13%. a. Develop a spreadsheet model, and use it to find the project's NPV, IRR, and payback. Input Data (in thousands of dollars) Equipment cost Net operating working capital/Sales $10,000 10% First year sales (in units) 1,000 Sales price per unit $24.00 Variable cost per unit (excl. depr.) $17.50 Nonvariable costs (excl. depr.) $1,000 Market value of equipment at Year 4 Tax rate $500 40% WACC 10% Inflation in prices and costs 3.0% Estimated salvage value at year 4 $500 Key Results: NPV = IRR = Payback =
Webmasters.com has developed a powerful new server that would be used for corporations' Internet activities. It would cost $10 million at Year 0 to buy the equipment necessary to manufacture the server. The project would require net working capital at the beginning of each year in an amount equal to 10% of the year's projected sales; for example, NWC = 10% (Sales). The servers would sell for $24,000 per unit, and Webmasters believes that variable costs would amount to $17,500 per unit. After Year 1, the sales price and variable costs will increase at the inflation rate of 3%. The company's nonvariable costs would be $1 million at Year 1 and would increase with inflation. The server project would have a life of 4 years. If the project is undertaken, it must be continued for the entire 4 years. Also, the project's returns are expected to be highly correlated with returns on the firm's other assets. The firm believes it could sell 1,000 units per year. The equipment would be depreciated over a 5-year period, using MACRS rates. The estimated market value of the equipment at the end of the project's 4-year life is $500,000. Webmasters' federal-plus-state tax rate is 40%. Its cost of capital is 10% for average-risk projects, defined as projects with a coefficient of variation of NPV between 0.8 and 1.2. Low-risk projects are evaluated with a WACC of 8%, and high-risk projects at 13%. a. Develop a spreadsheet model, and use it to find the project's NPV, IRR, and payback. Input Data (in thousands of dollars) Equipment cost Net operating working capital/Sales $10,000 10% First year sales (in units) 1,000 Sales price per unit $24.00 Variable cost per unit (excl. depr.) $17.50 Nonvariable costs (excl. depr.) $1,000 Market value of equipment at Year 4 Tax rate $500 40% WACC 10% Inflation in prices and costs 3.0% Estimated salvage value at year 4 $500 Key Results: NPV = IRR = Payback =
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course List)
13th Edition
ISBN:9781337395083
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Chapter13: Capital Budgeting: Estimating Cash Flows And Analyzing Risk
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1MC
Related questions
Question
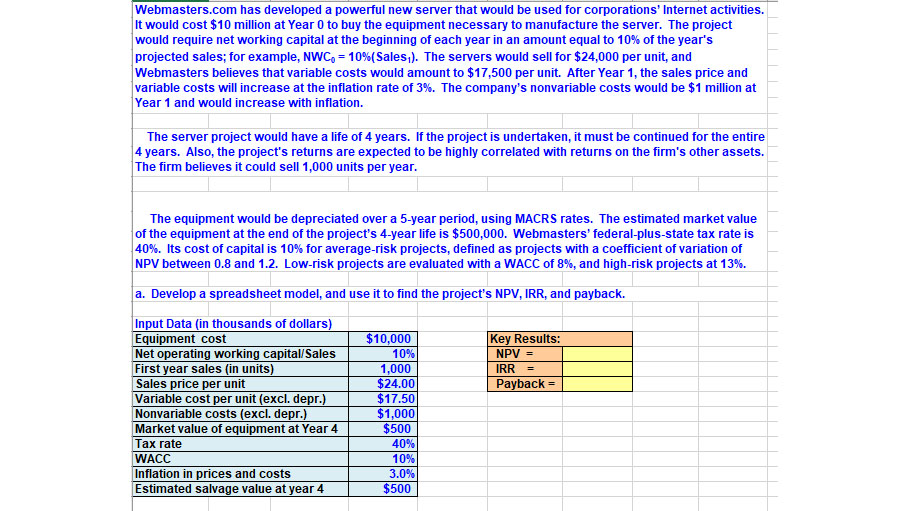
Transcribed Image Text:Webmasters.com has developed a powerful new server that would be used for corporations' Internet activities.
It would cost $10 million at Year 0 to buy the equipment necessary to manufacture the server. The project
would require net working capital at the beginning of each year in an amount equal to 10% of the year's
projected sales; for example, NWC = 10% (Sales). The servers would sell for $24,000 per unit, and
Webmasters believes that variable costs would amount to $17,500 per unit. After Year 1, the sales price and
variable costs will increase at the inflation rate of 3%. The company's nonvariable costs would be $1 million at
Year 1 and would increase with inflation.
The server project would have a life of 4 years. If the project is undertaken, it must be continued for the entire
4 years. Also, the project's returns are expected to be highly correlated with returns on the firm's other assets.
The firm believes it could sell 1,000 units per year.
The equipment would be depreciated over a 5-year period, using MACRS rates. The estimated market value
of the equipment at the end of the project's 4-year life is $500,000. Webmasters' federal-plus-state tax rate is
40%. Its cost of capital is 10% for average-risk projects, defined as projects with a coefficient of variation of
NPV between 0.8 and 1.2. Low-risk projects are evaluated with a WACC of 8%, and high-risk projects at 13%.
a. Develop a spreadsheet model, and use it to find the project's NPV, IRR, and payback.
Input Data (in thousands of dollars)
Equipment cost
Net operating working capital/Sales
$10,000
10%
First year sales (in units)
1,000
Sales price per unit
$24.00
Variable cost per unit (excl. depr.)
$17.50
Nonvariable costs (excl. depr.)
$1,000
Market value of equipment at Year 4
Tax rate
$500
40%
WACC
10%
Inflation in prices and costs
3.0%
Estimated salvage value at year 4
$500
Key Results:
NPV =
IRR =
Payback =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College