Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter3: Equation, The Mole, And Chemical Formulas
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3.49QE:
One of the ways to remove nitrogen monoxide gas, a serious source of air pollution, from smokestack...
Related questions
Question
What is the amount of excess reactant left over at the end of the reaction. Use the first image as an example.
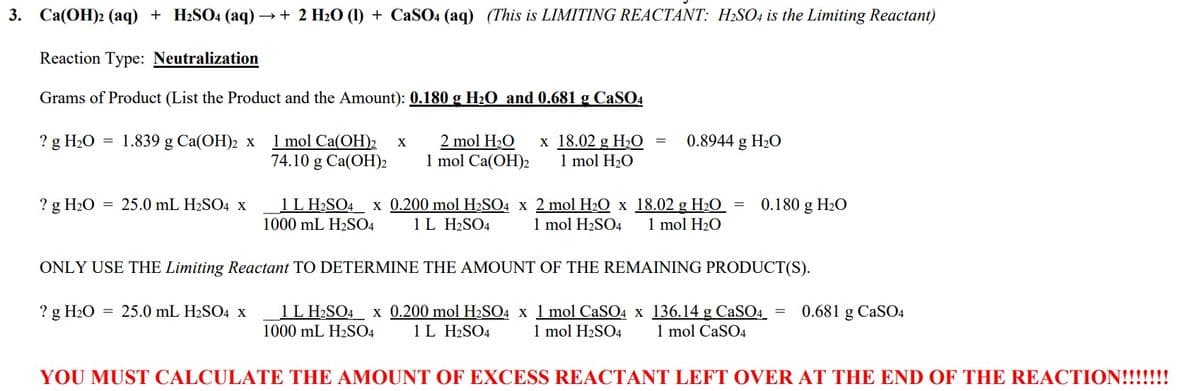
Transcribed Image Text:3. Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H₂SO4 (aq) → + 2 H₂O (1) + CaSO4 (aq) (This is LIMITING REACTANT: H₂SO4 is the Limiting Reactant)
Reaction Type: Neutralization
Grams of Product (List the Product and the Amount): 0.180 g H₂O and 0.681 g CaSO4
? g H₂O
=
1.839 g Ca(OH)2 x
? g H₂O = 25.0 mL H₂SO4 X
1 mol Ca(OH)2 X
74.10 g Ca(OH)2
2 mol H₂O x 18.02 g H₂O
1 mol Ca(OH)2 1 mol H₂O
= 0.8944 g H₂O
1 L H₂SO4 x 0.200 mol H₂SO4 x 2 mol H₂O x 18.02 g H₂O = 0.180 g H₂O
1000 mL H₂SO4 1 L H2SO4 1 mol H₂SO4 1 mol H₂O
ONLY USE THE Limiting Reactant TO DETERMINE THE AMOUNT OF THE REMAINING PRODUCT(S).
? g H₂O = 25.0 mL H₂SO4 x
1 L H₂SO4 x 0.200 mol H₂SO4 x 1 mol CaSO4 x 136.14 g CaSO4 = 0.681 g CaSO4
1000 mL H₂SO4 1 L H2SO4 1 mol H₂SO4 1 mol CaSO4
YOU MUST CALCULATE THE AMOUNT OF EXCESS REACTANT LEFT OVER AT THE END OF THE REACTION!!!!!!!
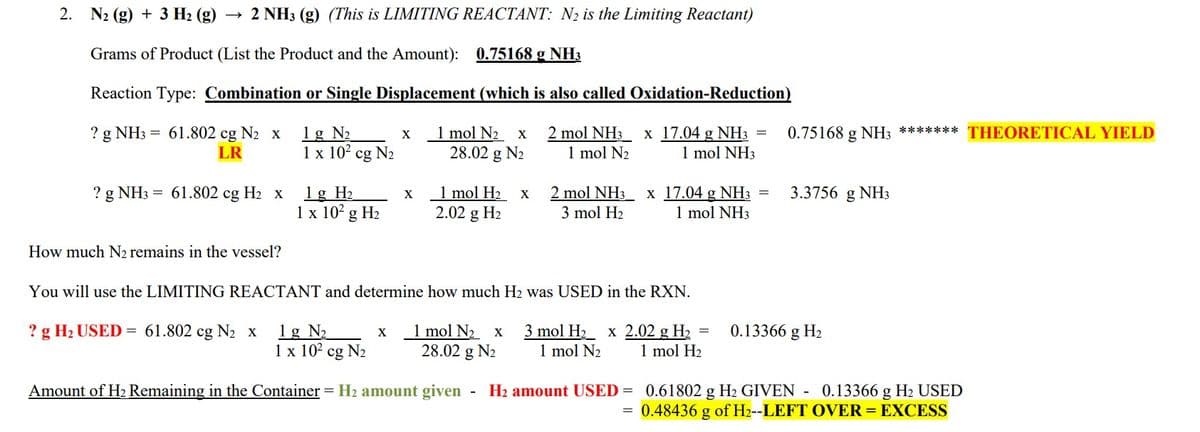
Transcribed Image Text:2.
N₂ (g) + 3 H₂(g) → 2 NH3 (g) (This is LIMITING REACTANT: N₂ is the Limiting Reactant)
Grams of Product (List the Product and the Amount): 0.75168 g NH3
Reaction Type: Combination or Single Displacement (which is also called Oxidation-Reduction)
? g NH3 = 61.802 cg N₂ x 1g №₂
2 mol NH3 x 17.04 g NH3
1 mol N₂
1 mol NH3
LR
? g NH3 = 61.802 cg H₂ x
How much N₂ remains in the vessel?
1 x 10² cg N₂
? g H₂ USED = 61.802 cg N₂ x
1 g H₂
1 x 10² g H₂
1g N₂
1 x 10² cg N₂
X
X
X
1 mol N₂ x
28.02 g N₂
You will use the LIMITING REACTANT and determine how much H2 was USED in the RXN.
1 mol N₂ x 3 mol H₂ x 2.02 g H₂ =
28.02 g N₂ 1 mol N₂ 1 mol H₂
1 mol H₂ x
2.02 g H₂
2 mol NH3 x 17.04 g NH3 =
3 mol H₂
1 mol NH3
Amount of H₂ Remaining in the Container = H₂ amount given H₂ amount USED =
=
0.75168 g NH3 ******* THEORETICAL YIELD
3.3756 g NH3
0.13366 g H₂
0.61802 g H₂ GIVEN - 0.13366 g H₂ USED
0.48436 g of H2--LEFT OVER = EXCESS
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning