What kind of a control was used in the experiment? O Neutral control O Positive control O There was no control in the experiment • Negative contol
What kind of a control was used in the experiment? O Neutral control O Positive control O There was no control in the experiment • Negative contol
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Chapter1: Biochemistry: An Evolving Science
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
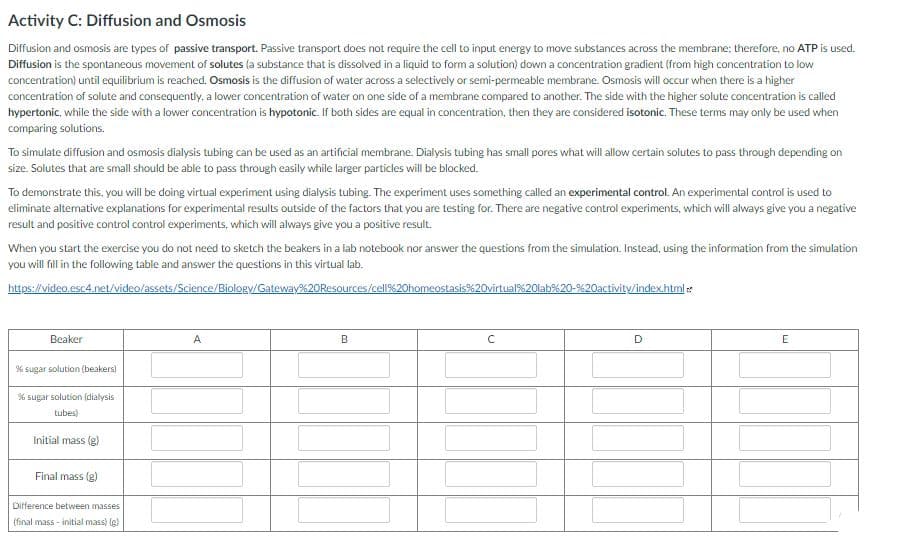
Transcribed Image Text:Activity C: Diffusion and Osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis are types of passive transport. Passive transport does not require the cell to input energy to move substances across the membrane: therefore, no ATP is used.
Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of solutes (a substance that is dissolved in a liquid to form a solution) down a concentration gradient (from high concentration to low
concentration) until equilibrium is reached. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively or semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis will occur when there is a higher
concentration of solute and consequently, a lower concentration of water on one side of a membrane compared to another. The side with the higher solute concentration is called
hypertonic, while the side with a lower concentration is hypotonic. If both sides are equal in concentration, then they are considered isotonic. These terms may only be used when
comparing solutions.
To simulate diffusion and osmosis dialysis tubing can be used as an artificial membrane. Dialysis tubing has small pores what will allow certain solutes to pass through depending on
size. Solutes that are small should be able to pass through easily while larger particles will be blocked.
To demonstrate this, you will be doing virtual experiment using dialysis tubing. The experiment uses something called an experimental control. An experimental control is used to
eliminate altemative explanations for experimental results outside of the factors that you are testing for. There are negative control experiments, which will always give you a negative
result and positive control control experiments, which will always give you a positive result.
When you start the exercise you do not need to sketch the beakers in a lab notebook nor answer the questions from the simulation. Instead, using the information from the simulation
you will fill in the following table and answer the questions in this virtual lab.
https://video.esc4.net/video/assets/Science/Biology/Gateway%20Resources/cell%20homeostasis%2
Jal%20lab%20-%20activity/index.html
Beaker
A
D.
E
% sugar solution (beakers)
% sugar solution (dialysis
tubes)
Initial mass (g)
Final mass (g)
Difference between masses
(final mass - initial mass) (g)
Transcribed Image Text:Question 10
What kind of a control was used in the experiment?
O Neutral control
O Positive control
There was no control in the experiment
• Negative contol
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological …
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9780134015187
Author:
John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:
PEARSON