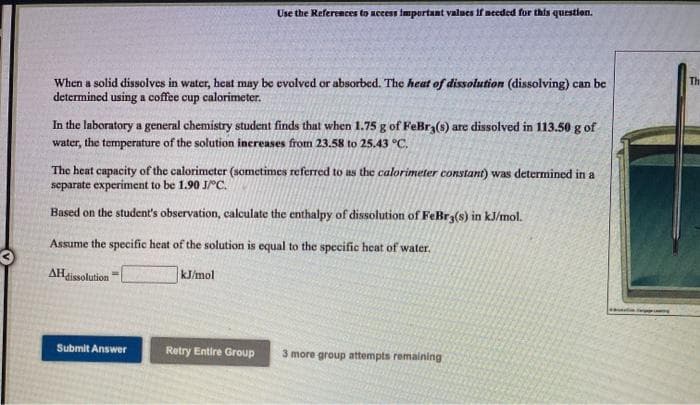
When a solid dissolves in water, heat may be evolved or absorbed. The heat of dissolution (dissolving) can be determined using a coffee cup calorimeter. In the Inboratory a general chemistry student finds that when 1.75 g of FeBr (s) are dissolved in 113.50 g of water, the temperature of the solution increases from 23.58 to 25.43 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (sometimes referred to as the calorimeter constant) was determined in a separate experiment to be 1.90 Jrc. Based on the student's observation, calculate the enthalpy of dissolution of FeBry(s) in kJ/mol. Assume the specific heat of the solution is equal to the specific heat of water. AHaissolution kJ/mol
When a solid dissolves in water, heat may be evolved or absorbed. The heat of dissolution (dissolving) can be determined using a coffee cup calorimeter. In the Inboratory a general chemistry student finds that when 1.75 g of FeBr (s) are dissolved in 113.50 g of water, the temperature of the solution increases from 23.58 to 25.43 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (sometimes referred to as the calorimeter constant) was determined in a separate experiment to be 1.90 Jrc. Based on the student's observation, calculate the enthalpy of dissolution of FeBry(s) in kJ/mol. Assume the specific heat of the solution is equal to the specific heat of water. AHaissolution kJ/mol
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
1st Edition
ISBN:9781559539418
Author:Angelica Stacy
Publisher:Angelica Stacy
ChapterU5: Fire: Energy , Thermodynamics, And Oxidation-reduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem SI4RE
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Use the References to accest important values if needed for this question.
When a solid dissolves in water, heat may be evolved or absorbed. The heat of dissolution (dissolving) can be
determined using a coffee cup calorimeter.
Th
In the laboratory a general chemistry student finds that when 1.75 g of FeBr3(s) are dissolved in 113.50 g of
water, the temperature of the solution increases from 23.58 to 25.43 °C.
The heat capacity of the calorimeter (sometimes referred to as the calorimeter constant) was determined in a
separate experiment to be 1.90 JrC.
Based on the student's observation, calculate the enthalpy of dissolution of FeBr3(s) in kJ/mol.
Assume the specific heat of the solution is equal to the specific heat of water.
AHissolution
kJ/mol
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group
3 more group attempts remaining
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781559539418
Author:
Angelica Stacy
Publisher:
MAC HIGHER

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781559539418
Author:
Angelica Stacy
Publisher:
MAC HIGHER

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
