Which subatomic particle-proton, neutron, or electron-is equivalent to a B ray? B rays are deflected to a greater extent than a rays because (a) they are lighter, or (b) they are more highly charged. Negatively charged B rays bend toward the positively charged plate. |(+) y rays, which carry no charge, are Lead block unaffected by the charged plates. Positively charged a rays bend toward the negatively charged plate. (-) Photographic plate Electrically charged plates Radioactive substance Figure 2.7 Behavior of alpha (æ), beta (B), and gamma (y) rays in an electric field.
Which subatomic particle-proton, neutron, or electron-is equivalent to a B ray? B rays are deflected to a greater extent than a rays because (a) they are lighter, or (b) they are more highly charged. Negatively charged B rays bend toward the positively charged plate. |(+) y rays, which carry no charge, are Lead block unaffected by the charged plates. Positively charged a rays bend toward the negatively charged plate. (-) Photographic plate Electrically charged plates Radioactive substance Figure 2.7 Behavior of alpha (æ), beta (B), and gamma (y) rays in an electric field.
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter2: Atoms Molecules And Ions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 29PS
Related questions
Question
An unknown particle is caused to move between two electrically
charged plates, as illustrated in Figure 2.7. You hypothesize
that the particle is a proton. (a) If your hypothesis is
correct, would the particle be deflected in the same or opposite
direction as the β rays? (b) Would it be deflected by a
smaller or larger amount than the β rays?
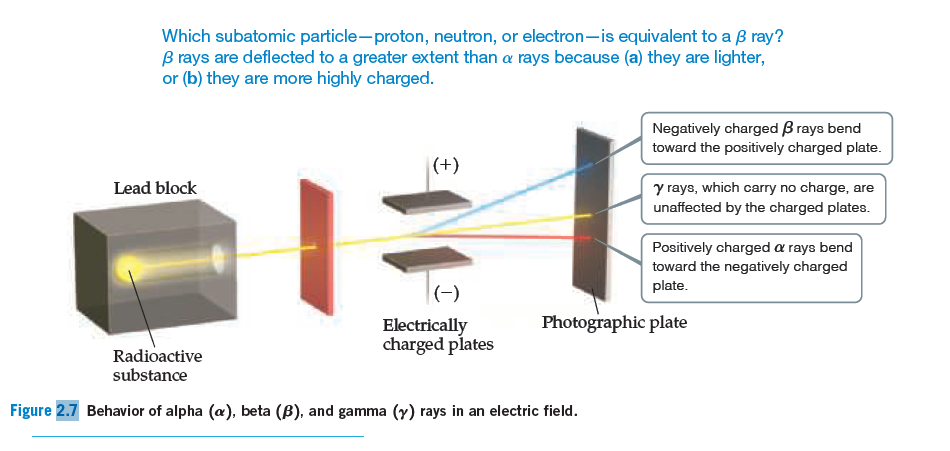
Transcribed Image Text:Which subatomic particle-proton, neutron, or electron-is equivalent to a B ray?
B rays are deflected to a greater extent than a rays because (a) they are lighter,
or (b) they are more highly charged.
Negatively charged B rays bend
toward the positively charged plate.
|(+)
y rays, which carry no charge, are
Lead block
unaffected by the charged plates.
Positively charged a rays bend
toward the negatively charged
plate.
(-)
Photographic plate
Electrically
charged plates
Radioactive
substance
Figure 2.7 Behavior of alpha (æ), beta (B), and gamma (y) rays in an electric field.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning